mvcombine
Description
Takes a group of events that are identical except for the specified field, which contains a single value, and combines those events into a single event. The specified field becomes a multivalue field that contains all of the single values from the combined events.
The mvcombine command does not apply to internal fields.
See Use default fields in the Knowledge Manager Manual.
Syntax
mvcombine [delim=<string>] <field>
Required arguments
- field
- Syntax: <field>
- Description: The name of a field to merge on, generating a multivalue field.
Optional arguments
- delim
- Syntax: delim=<string>
- Description: Defines the string to use as the delimiter for the values that get combined into the multivalue field. For example, if the values of your field are "1", "2", and "3", and
delimis a semi-colon ( ; ), then the combined multivalue field is"1";"2";"3". - Default: a single space, (" ")
To see the output of the
delimargument, you must use thenomvcommand immediately after themvcombinecommand. See Usage
Usage
The mvcombine command is a transforming command. See Command types.
You can use evaluation functions and statistical functions on multivalue fields or to return multivalue fields.
The mvcombine command accepts a set of input results and finds groups of results where all field values are identical, except the specified field. All of these results are merged into a single result, where the specified field is now a multivalue field.
Because raw events have many fields that vary, this command is most useful after you reduce the set of available fields by using the fields command. The command is also useful for manipulating the results of certain transforming commands, like stats or timechart.
Specifying delimiters
The mvcombine command creates a multivalue version of the field you specify, as well as a single value version of the field. The multivalue version is displayed by default.
The single value version of the field is a flat string that is separated by a space or by the delimiter that you specify with the delim argument.
By default the multivalue version of the field is displayed in the results. To display the single value version with the delimiters, add the | nomv command to the end of your search. For example ...| mvcombine delim= "," host | nomv host.
Some modes of search result investigation prefer this single value representation, such as exporting to CSV in the UI, or running a command line search with splunk search "..." -output csv. Some commands that are not multivalue aware might use this single value as well.
Most ways of accessing the search results prefer the multivalue representation, such as viewing the results in the UI, or exporting to JSON, requesting JSON from the command line search with splunk search "..." -output json or requesting JSON or XML from the REST API. For these forms of, the selected delim has no effect.
Other ways of turning multivalue fields into single-value fields
If your primary goal is to convert a multivalue field into a single-value field, mvcombine is probably not your best option. mvcombine is mainly meant for the creation of new multivalue fields. Instead, try either the nomv command or the mvjoin eval function.
| Conversion option | Description | For more information |
|---|---|---|
nomv command
|
Use for simple multivalue field to single-value field conversions. Provide the name of a multivalue field in your search results and nomv will convert each instance of the field into a single-value field.
|
nomv |
mvjoin eval function
|
Use when you want to perform multivalue field to single-value field conversion where the former multivalues are separated by a delimiter that you supply. For example, you start with a multivalue field that contains the values 1, 2, 3,4, 5. You can use mvjoin to transform your multivalue field into a single-valued field with OR as the delimiter. The new single value of the field is 1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4 OR 5.
|
Multivalue eval functions |
Examples
1. Creating a multivalue field
| This example uses the sample dataset from the Search Tutorial. To try this example yourself, download the data set from Get the tutorial data into Splunk and follow the instructions in the Search Tutorial to upload the data. |
To understand how mvcombine works, let's explore the data.
- Set the time range to All time.
- Run the following search.
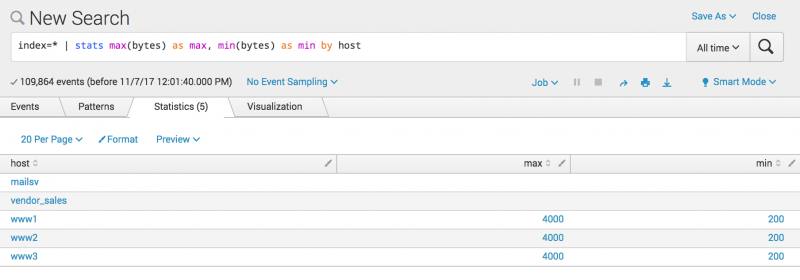
index=* | stats max(bytes) AS max, min(bytes) AS min BY hostThe results show that the max and min fields have duplicate entries for the hosts that start with
www. The other hosts show no results for the max and min fields. - To remove the other hosts from your results, modify the search to add
host=www*to the search criteria.index=* host=www* | stats max(bytes) AS max, min(bytes) AS min BY hostBecause the values in the
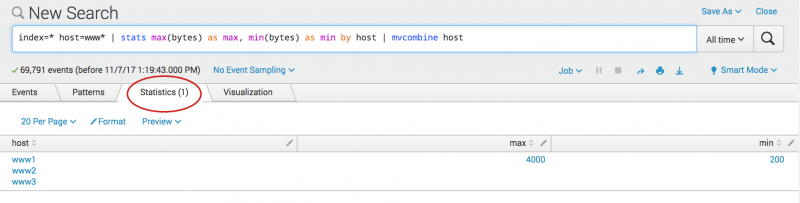
maxandmincolumns contain the exact same values, you can use themvcombineto combine the host values into a multivalue result. - Add
| mvcombine hostto your search and run the search again.index=* host=www* | stats max(bytes) AS max, min(bytes) AS min BY host | mvcombine hostInstead of three rows, one row is returned. The host field is now a multvalue field.
2. Returning the delimited values
As mentioned in the Usage section, by default the delimited version of the results are not returned in the output. To return the results with the delimiters, you must return the single value string version of the field.
Add the nomv command to your search. For example:
index=* host=www* | stats max(bytes) AS max, min(bytes) AS min BY host | mvcombine delim="," host | nomv host
The search results that are returned are shown in the following table.
| host | max | min |
|---|---|---|
| www1,www2,www3 | 4000 | 200 |
To return the results with a space after each comma, specify delim=", ".
Example 3:
In multivalue events:
sourcetype="WMI:WinEventLog:Security" | fields EventCode, Category,RecordNumber | mvcombine delim="," RecordNumber | nomv RecordNumber
Example 4:
Combine the values of "foo" with a colon delimiter.
... | mvcombine delim=":" foo
See also
Commands:
makemv
mvexpand
nomv
Functions:
Multivalue eval functions
Multivalue stats and chart functions
split
| multisearch | mvexpand |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.0.0, 7.0.1, 7.0.2, 7.0.3, 7.0.4, 7.0.5, 7.0.6, 7.0.7, 7.0.8, 7.0.9, 7.0.10, 7.0.11, 7.0.13, 7.1.0, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.1.5, 7.1.6, 7.1.7, 7.1.8, 7.1.9, 7.1.10, 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10, 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9, 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.2, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.1.5, 8.1.6, 8.1.7, 8.1.8, 8.1.9, 8.1.10, 8.1.11, 8.1.12, 8.1.13, 8.1.14, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.2.4, 8.2.5, 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.1.9, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.2.6, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.3.4, 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!