Introduction to Getting Data In
Splunk Cloud Platform administrators can add data to their Splunk Cloud Platform deployment using a variety of methods. This topic provides an overview of those methods.
Fundamental Splunk and Splunk Cloud Platform concepts
Before attempting to get data into your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment, you should have a solid understanding of certain Splunk and Splunk Cloud Platform concepts. The table lists these concepts. You should also review the Splunk Cloud Platform information in the Getting Data In manual.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment server | A deployment server is a Splunk Enterprise instance that acts as a centralized configuration manager for any number of forwarders, called "deployment clients". The deployment server is hosted on your premises or your Cloud environment (such as AWS or Azure). For a more detailed description of the components of a deployment server, see Deployment Server Architecture. |
| indexes | The index is the repository for your data. When the Splunk platform indexes raw data, it transforms the data into searchable events. For more information about indexes, see Manage Splunk Cloud Platform Indexes. |
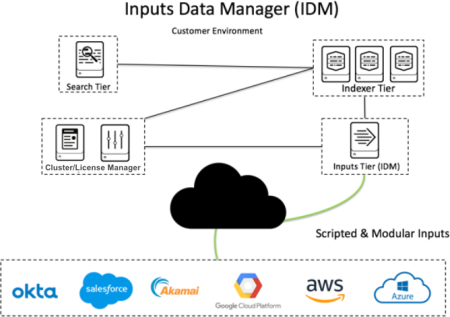
| Inputs Data Manager | The Inputs Data Manager (IDM) is a component of your Splunk Cloud Platform environment optimized for data ingestion. It is intended for use with cloud data sources or when using add-ons that require inputs on the search tier. Splunk Cloud Platform deployments on Victoria Experience do not require IDM. If your deployment is on Victoria Experience you can run add-ons that contain scripted and modular inputs directly on the search head. To determine if your deployment has the Classic or Victoria experience, see Determine your Splunk Cloud Platform Experience. |
| search head search head cluster |
For more information, see search head and search head cluster in the Splexicon. |
| source types | A source type is one of the critical default fields that Splunk software assigns to all incoming data. It tells Splunk software what kind of data you have, so that it can format the data intelligently during indexing. For more information, see Why source types matter. |
| Splunk applications and add-ons | A Splunk app is an application that runs on the Splunk platform and typically addresses several use cases. Add-ons support and extend the functionality of the Splunk platform and the apps that run on it, usually by providing inputs for a specific technology or vendor. For more information about add-ons, see About Splunk add-ons. |
| universal forwarder | To forward data to Splunk Cloud Platform, you typically use the Splunk universal forwarder. The universal forwarder is a dedicated, streamlined version of Splunk Enterprise that contains only the essential components needed to forward data. The universal forwarder does not support Python and does not expose a UI. In most situations, the universal forwarder is the best way to forward data to indexers. Its main limitation is that it forwards unparsed data, except in certain cases, such as structured data. For more information, see Work with forwarders. |
Types of data that Splunk Cloud Platform accepts
Splunk Cloud accepts a wide variety of data, and can also monitor relational databases and third-party infrastructures. For more information, see the following sections in the Getting Data In manual:
- What data can I index?
- Monitor files and directories
- Get data from TCP and UDP ports
- Monitor Windows data with the Splunk platform
- Share HEC Data
- Monitor First In, First Out (FIFO) queues
See also the Data Manager for Splunk Cloud Platform User Manual.
Tools to get data into Splunk Cloud Platform
This section is designed to help you make decisions about the best way to get data into your Splunk Cloud Platform instance. There are a few different ways to get data into Splunk Cloud Platform: forwarders, HTTP Event Collector (HEC), apps and add-ons, or the Inputs Data Manager (IDM). The best way to get data in depends on the source of the data and what you intend to do with it.
Work with forwarders
Usually, to get data from your customer site to Splunk Cloud Platform, you use a forwarder.
A forwarder is a version of Splunk Enterprise optimized to send data. A universal forwarder is a purpose-built data collection mechanism with very minimal resource requirements, whereas a heavy forwarder is full Splunk Enterprise deployment configured to act as a forwarder with indexing disabled.
Splunk forwarders send data from a datasource to your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment for indexing, which makes the data searchable. Forwarders are lightweight processes, so they can usually run on the machines where the data originates. For more information, see the following topics:
- Forward data from files and directories to Splunk Cloud Platform
- Upgrade your Forwarders
- Use forwarders to get data into Splunk Cloud Platform in the Getting Data In manual
- The Forwarding Data manual
Work with HTTP Event Collector
The HTTP Event Collector (HEC) uses a token-based authentication model so you can securely send data and application events to a Splunk deployment over the HTTP and Secure HTTP (HTTPS) protocols.
For more information, see the following sections in Set up and use HTTP Event Collector in Splunk Web in the Getting Data In manual:
- HEC and Splunk Cloud Platform
- Configure HTTP Event Collector on Splunk Cloud Platform
- For general and specific information on sending data: Send data to HTTP Event Collector and Send data to HTTP Event Collector on Splunk Cloud Platform
Work with Apps and Add-ons
Splunk apps and add-ons extend the capability and simplify the process of getting data into your Splunk platform deployment.
For more information, see Use apps and add-ons to get data in in the Getting Data In manual.
Splunk Cloud Platform considerations
Apps and add-ons that contain a data collection component should be installed on forwarders, IDMs, or your Splunk Cloud Platform instance search head for their data collection functions (modular or scripted inputs). For more information, see Work with forwarders and Work with Inputs Data Manager (IDM).
If your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment is on Classic Experience, you must install apps and add-ons that contain modular or scripted inputs on a separate IDM instance. If your deployment is on Victoria Experience, you can install apps or add-ons that contain modular or scripted inputs directly on your Splunk Cloud Platform instance search head. To determine if your deployment is on Classic Experience or Victoria Experience, see Determine your Splunk Cloud Platform Experience.
Regardless of your Splunk Cloud Platform Experience designation, you can deploy apps and add-ons that perform data collection functions, including those that contain modular or scripted inputs, to forwarders hosted locally in your environment.
Splunk Cloud Platform supports self-service installation of both public apps and add-ons from Splunkbase and private apps that you can create based on your unique requirements. For more information on public apps, see Install apps on your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment. For more information on private apps, see Manage private apps on your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment.
Work with Inputs Data Manager
The Inputs Data Manager (IDM) is a hosted solution for Splunk Cloud Platform that supports scripted and modular inputs and cloud-based inputs that you want to send directly to Splunk Cloud Platform. In most cases, an IDM eliminates the need for customer-managed infrastructure.
IDM is required to run modular and scripted inputs on Splunk Cloud Platform deployments on Classic Experience only. If your deployment is on Victoria Experience, you can run modular and scripted inputs directly on the search head. To determine if your deployment is on Classic Experience or Victoria Experience, see Determine your Splunk Cloud Platform Experience.
As a best practice, use an IDM in the following cases:
- You have scripted or modular inputs that you want to send to Splunk Cloud Platform. For example, you can poll a cloud-based database, web service, or API for specific data and process the results.
- You have cloud-based inputs such as Microsoft Azure or AWS that you want to send directly to Splunk Cloud Platform without the intermediary step of sending data to an on-premise forwarder. You can send these inputs directly to an IDM rather than routing them through a forwarder to get the data into Splunk Cloud Platform.
The following graphic shows the typical architecture of IDM. Note that the search tier and index tier are not hosted on the IDM. The IDM is not intended to store data or perform searches.
IDM is not supported on the Splunk Cloud Platform Free Trial.
Ports opened for IDM
The following port access applies to inbound and outbound IDM ports:
- Inbound access to ports 443 and 8089 are controlled by an access list. Contact Support if you need to modify the access list.
- Outbound access to port 443 is open by default. Contact Support if you need to open additional outbound ports.
When you contact Support, provide a list of public IP addresses and subnets with this request. For example, you might want to open port 8089, the port for the REST API. Note that opening a specific outbound port opens the same port for all tiers in your Splunk Cloud environment.
Apps supported on IDM
If the app contains modular inputs and is Splunk Cloud Platform certified, it is compatible with Splunk Cloud Platform IDM. Generally, apps that are cloud-based are well-suited to IDM. Many cloud-based apps are supported.
To verify if your app is supported on IDM, check Splunkbase.
Limitations when working with IDM
The IDM is intended to function specifically as a forwarder for modular and scripted inputs, or to obviate the need to route cloud-based inputs through an on-premise forwarder. The following functions are not intended to be performed on the IDM:
- Search capabilities are capped for users on IDM. The IDM is not intended to function as a search head.
- IDM does not currently support Self-Service App Installations. To get modular and scripted input onto the IDM, you need to create a private app and request that Support upload it.
- If an add-on is packaged with or related to an Enterprise Security search head, do not use IDM. Instead, run the add-on on the Enterprise Security search head.
- HEC inputs are not supported with IDM.
- IDM isn't a syslog sink, nor can it receive unencrypted TCP streams.
- IDM isn't a one-to-one replacement for a heavy forwarder. You must still use a heavy forwarder if you need to perform parsing or activities other than standard scripted and modular data inputs.
Use IDM with scripted and modular inputs
To use scripted or modular inputs, you must package them in a private app. To do this, complete the following high-level steps:
- Create your modular or scripted inputs. For instructions on creating these inputs, see Get data from APIs and other remote data interfaces through scripted inputs in the Getting Data In manual.
- Package the script or modular input in a private app. For instructions on building a private app for Splunk Cloud Platform, see Overview of developing a private Splunk Cloud Platform app.
- Submit the private app for Splunk Cloud Platform vetting.
- Request that Support upload the app to your IDM.
Use IDM with cloud-based add-ons
When you work with IDM and Cloud-based add-ons, complete the following high-level steps to get data in:
- Create a support request to install the Add-on.
- Configure an index on your Splunk Cloud Platform instance. This index is going to be associated with your cloud input.
- Perform any configurations needed on the cloud-based source that enables you to get data in.
- Configure the Splunk Add-on on your Inputs Data Manager (IDM).
- You will also need to configure inputs on the IDM. The IDM is responsible for data ingestion.
- Verify that data is flowing to your Splunk Cloud Platform environment.
As a best practice, install cloud-based add-ons on an IDM, and install on-premises-based add-ons on a universal forwarder or heavy forwarder.
See also
| For more information about | See |
|---|---|
| Getting AWS data in using IDM | Get Amazon Web Services (AWS) data into Splunk Cloud Platform |
| Getting Microsoft Azure data in using IDM | Get Microsoft Azure data into Splunk Cloud Platform |
| Change the UI theme of Splunk Cloud Platform | Get Amazon Web Services (AWS) data into Splunk Cloud Platform |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk Cloud Platform™: 8.2.2112, 8.2.2201, 8.2.2202, 8.2.2203, 9.0.2205, 9.0.2208, 9.0.2209, 9.0.2303, 9.0.2305, 9.1.2308, 9.1.2312, 9.2.2403, 9.2.2406, 9.3.2408, 9.3.2411 (latest FedRAMP release)
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!