How to use these reference tables
Each topic in this section contains a use case for the data model, a breakdown of the required tags for the event objects or searches in that model, and a listing of all extracted and calculated fields included in the model.
How to read the tags tables
The tags tables communicate which tags you must apply to your events in order to make them CIM-compliant. These tags act as constraints to identify your events as relevant to this data model, so that this data is included in Pivot reports and dashboards based on this model.
There might be additional constraints outside the scope of these tables. Refer to the data model itself using its editor view in Splunk Web for required fields, field=value combinations, or base searches that the model depends on.
Ensure your data is populated in the correct dashboards and Pivot reports.
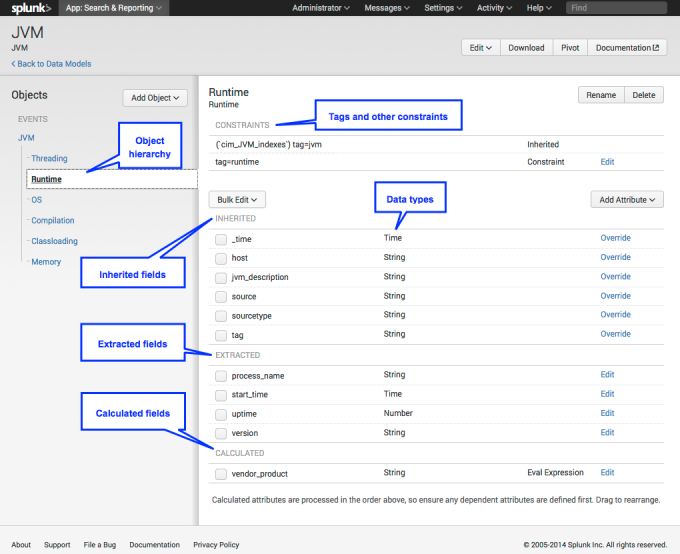
- Identify the CIM object relevant to your events.
- Observe which tags are required for that object.
- Observe which tags are required for any parent objects.
- Apply those tags to your events using event types.
- Repeat for any additional relevant CIM objects.
For a detailed walkthrough of these steps, see Use the CIM to normalize data at search time.
How to read the fields tables
The fields tables list the extracted and calculated fields for the event and search objects in the model and provide descriptions and expected values (if relevant) for these fields. The table presents the fields in alphabetical order, starting with the fields for the parent object in the model, then proceeding to any unique fields for child objects. The table does not repeat any fields that a child object inherits from a parent object, so refer to the parent object to see the description and expected values for that field.
Because the fields tables exclude inherited fields, many child objects have no fields listed in the table at all. Those child objects include only inherited fields from one or more of their parent objects, so there are no unique extracted or calculated fields to display. All data models inherit the fields _time, host, source, and sourcetype, so those fields are always available to you for use in developing Pivot reports and dashboards.
Use the tables to apply the Common Information Model to your data
The tables in this section of documentation are intended to be supplemental reference for the data models themselves. Use the documentation and the data model editor in Splunk Web together.
Prerequisite
You need Write access to a data model in order to browse it in its editor view. If you do not have this access, request it from your Splunk administrator.
Steps
- In Splunk Web, go to Settings > Data Models to open the Data Model Manager.
- Click a data model to view it in the Data Model Editor. There, you can see the full object hierarchy, a complete listing of constraints for each object, and full listing of all inherited, extracted, and calculated fields for each object.
- Compare this information with the reference tables in the documentation for descriptions and expected values of the fields in each object.
| Information available in documentation |
Information available in Data Model Editor in Splunk Web | |
|---|---|---|
| Required tags | YES | YES |
| Other constraints | NO | YES |
| Full object hierarchy | NO | YES |
| Inherited fields | NO | YES |
| Extracted fields | YES | YES |
| Calculated fields | YES | YES |
| Data types | YES | YES |
| Descriptions | YES | NO |
| Expected values | YES | NO |
| Support and resource links for the Splunk Common Information Model Add-on | Alerts |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Common Information Model Add-on: 4.3.0, 4.3.1, 4.4.0, 4.5.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!