Configure threat intelligence sources
A threat intelligence source represents a collection of knowledge about a specific type of security threat or activity. The knowledge is made available as a structured data file or stream, and can be loaded into the Enterprise Security app. By comparing the contents of multiple threat sources to events in Splunk Enterprise, the Enterprise Security app provides threat intelligence and context for security monitoring and investigation.
The Enterprise Security app supports multiple threat intelligence collection sources, and includes connections to a selection of threat sources.
Supported threat collection methods
Any content that is available as a structured text file can be presented to the Enterprise Security app as a threat source. The ES app includes support for:
- STIX documents and TAXII feeds
- OpenIOC documents
- Content collected via API or URL
- File-based content
- Database hosted content.
Supported threat intelligence groups
| Supported IOC data types | Threat Collection | Details |
|---|---|---|
| X509 Certificates | certificate_intel | Threat collections are defined in collections.conf, and stored in KVStore.
|
| email_intel | ||
| Files names/hashes | file_intel | |
| HTTP | http_intel | |
| IP/Domains | ip_intel | |
| Processes | process_intel | |
| Registry entries | registry_intel | |
| Services | service_intel | |
| Users | user_intel |
Review the provided threat sources
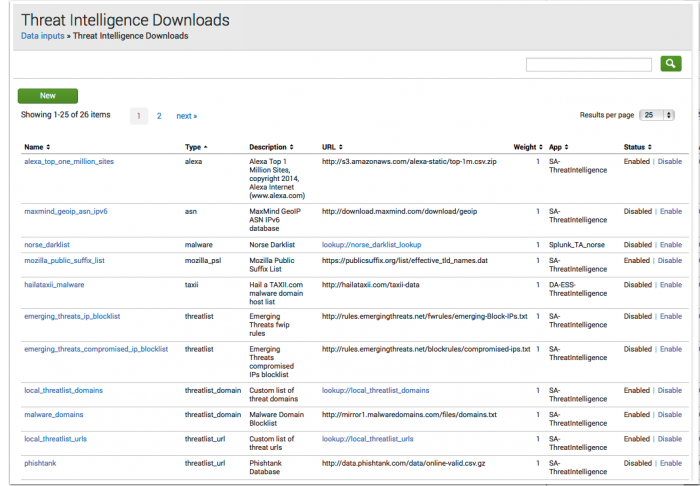
The Splunk App for Enterprise Security comes with pre-configured threat intelligence sources.
- Browse to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads, and review the Description field in all defined threat intelligence sources.
- Use the Threat Intelligence Download Settings page to configure settings such as proxy server details, authentication credentials, or change the Weight assigned to a source.
- Enable or disable the source that corresponds to the security domain, data sources, and defined use case for the ES installation.
- Use the Threat Intelligence Audit dashboard to review the status of all threat download sources.
- Use the Threat Artifacts dashboard to find or query on individual threat elements.
Threat sources included with ES
| Threat Source | Threat Provider | Source site |
|---|---|---|
| Appendix_D_FQDNs.xml | Mandiant APT1 Report: | https://stix.mitre.org |
| Appendix_F_SSLCertificates.xml | ||
| Appendix_G_IOCs_No_OpenIOC.xml | ||
| Mandiant_APT1_Report.xml | ||
| FireEye Poison Ivy Report | FireEye | https://stix.mitre.org |
| Alexa Top 1 Million Sites | Alexa Internet | http://s3.amazonaws.com/alexa-static/ |
| Emerging Threats compromised IPs blocklist | Emerging Threats | http://rules.emergingthreats.net/blockrules |
| Emerging Threats fwip rules | Emerging Threats | http://rules.emergingthreats.net/fwrules |
| Malware domain host list | Hail a TAXII.com | http://hailataxii.com |
| iblocklist Logmein | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Piratebay | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Proxy | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Rapidshare | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Spyware | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Tor | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| iblocklist Web attacker | I-Blocklist | http://list.iblocklist.com |
| ICAAN Top-level Domains List | IANA | http://data.iana.org |
| Malware Domain Blocklist | Malware Domains | http://mirror1.malwaredomains.com |
| MaxMind GeoIP ASN IPv4 Database | MaxMind | http://download.maxmind.com |
| MaxMind GeoIP ASN IPv6 Database | MaxMind | http://download.maxmind.com |
| Mozilla Public Suffix List | Mozilla | https://publicsuffix.org |
| abuse.ch Palevo C&C IP Blocklist | abuse.ch | https://palevotracker.abuse.ch |
| Phishtank Database | Phishtank | http://data.phishtank.com |
| SANS blocklist | SANS | http://isc.sans.edu |
| abuse.ch ZeuS blocklist (bad IPs only) | abuse.ch | https://zeustracker.abuse.ch |
| abuse.ch ZeuS blocklist (standard) | abuse.ch | https://zeustracker.abuse.ch |
Threat Intelligence Download Settings
As an analyst, you will use the Threat Intelligence Download page to implement, configure, and enable threat intelligence sources that require an API or URL connection, or are lookup based. Browse to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads.
Select the threat source name field to view the settings.
| Threat Intelligence Download Setting |
|
|---|---|
| Parsing Options |
|
| Download Options |
|
| Proxy Options: (Optional) |
|
Edit a threat source
Use the Threat Intelligence Download Settings editor to modify information about an existing threat source.
To edit a threat source:
1. Go to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads and select the name of the threat source you want to edit.
2. In the Threat Intelligence Download Settings editor, make changes to the fields as required.
3. Save the changes.
Note: To allow non-admin users to edit threat sources, see the topic on "Custom capabilities" in this manual.
Add a hosted threat download source
To add additional threat sources, determine the type and review the instructions.
Add a TAXII feed
1. Go to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads.
2. Click New to open the Threat Intelligence Download Settings editor.
3. Enter the information about the threat source where appropriate. In addition to filling out all required fields, a TAXII feed configuration requires additional customized field content:
| Field Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Must be set to taxii for TAXII feeds.
|
| POST Arguments | The POST arguments field accepts taxii specific parameters in line, space delimited.
|
| Fields | The setting is not used by taxii feeds, but as a required field it must be populated with text. Example: thereisnospoon
|
4. Save the changes when you are done.
5. Validate the TAXII feed is properly configured and downloading by reviewing the "Threat Intelligence Audit" dashboard.
Add a URL based source
1. Go to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads.
2. Click New to open the Threat Intelligence Download Settings editor.
3. Enter the information about the threat source where appropriate, filling in all required fields. Use the threat sources provided in Enterprise Security as configuration examples, as threat source formats vary by provider.
4. Save the changes when you are done.
5. Validate the source is properly configured and downloading by reviewing the "Threat Intelligence Audit" dashboard.
Add database hosted content
Example: A blog post discussing custom threat feed integration with Enterprise Security (http://blogs.splunk.com/2014/03/10/custom-threat-feed-integration-with-enterprise-security)
Add a file based threat source
The Enterprise Security app includes inputs configured to monitor specified folders and ingest threat intelligence files. Use the Threat Intelligence Manager page to review, add, or change inputs for file based threat sources.
Default settings
The modular input da_ess_threat_local is configured to monitor the $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/DA-ESS-ThreatIntelligence/local/data/threat_intel folder, ingest any .ioc and .xml files found, and delete the documents after processing.
To review or modify the da_ess_threat_local inputs settings:
- Navigate to Settings > Data Input > Threat Intelligence Manager
- Select the da_ess_threat_local modular input.
- Review or modify the settings as required.
Note: Do not modify the da_ess_threat_default, or sa_threat_local inputs, as they are used for other threat processing.
Create a new input monitor for threat intel documents
- Navigate to Settings > Data Input > Threat Intelligence Manager
- Select New
- Provide a descriptive name for the modular input.
- Provide a path to the file repository.
- Optionally, provide a maximum file size in bytes.
- Optionally, set the sinkhole option. The default is to retain all documents.
Add an STIX file
All file-based threat sources must be uploaded to the da_ess_threat_local monitored path, or made available on a mounted network share.
A STIX file must have a .xml extension to be read and parsed.
Add an OpenIOC file
All file-based threat sources must be uploaded to the da_ess_threat_local monitored path, or made available on a mounted network share.
An OpenIOC file must have a .ioc extension to be read and parsed.
Add a static threat source
All .csv based threat sources are configured and managed as lookup files. For details on adding lookup files, see "Add lookup based source" in this topic.
Add lookup based source
A lookup based threat source is limited to IP, URL, or domain data. To add a new lookup table and enable it as a threat source:
1. Create and upload a lookup table file.
- Browse to Settings > Lookups > Lookup table files.
- Choose Add New.
- Select the Destination App. Example: SA-ThreatIntelligence
- Select the lookup file to upload. The file must be a csv format.
- Provide the destination file name. Enter the name this lookup table file will have on the Splunk server. When uploading a plaintext csv file, the filename should end in
.csv. Example: threatening_stuff.csv - Save.
2. Set the permissions on the lookup table.
- In Lookup Table Files find the new lookup and select Permissions.
- Set Object should appear in to All apps.
- Set Read access for Everyone.
- Set Write access for
admin. Optionally, add other roles with lookup editor permissions. See "Custom capabilities" in this manual. - Save.
3. Add a lookup definition.
- Browse to Settings > Lookups > Lookup definitions.
- Choose Add New.
- Select the Destination App. Example: SA-ThreatIntelligence
- Provide a name for the lookup threat source. The name defined here is the name used in the Threatlist input stanza definition. Example: threatening_stuff_list
- Select the Type: of File based
- Select the Lookup File:
- Save.
4. Set the permissions on the lookup definition.
- In Lookup definitions find the new definition and select Permissions.
- Set Object should appear in to All apps.
- Set Read access for Everyone.
- Set Write access for
admin. Optionally, add other roles with lookup editor permissions. See "Custom capabilities" in this manual. - Save.
5. Add a threat source input stanza.
- Browse to Configure > Data Enrichment > Threat Intelligence Downloads.
- Determine which type of threat source input is the best match for the new content.
Supported lookup content Details Threat by ip address The fields ipanddescriptionare required fields. Theipfield supports hyphen-separated ranges. All other fields will not be referenced. Use the predefined input local_threatlist as an example, or for cloning.Threat by url The fields urlanddescriptionare required fields. All other fields will not be referenced. Use the predefined input local_threatlist_urls as an example, or for cloning.Threat by domain The fields domainanddescriptionare required fields. All other fields will not be referenced. Use the predefined input local_threatlist_domains as an example, or for cloning.
6. Create or clone an input.
- If one of the pre-configured inputs is a match for your threat intel source, select the Clone option under the Actions column.
- Fill out the required fields in the newly cloned threat source input.
- Name The new threat source name. Example: threatening stuff list
- Description A descriptive identifier.
- URL Add a reference to the lookup definition. Example: lookup://threatening_stuff_list
- Fields Verify and update the fields parameter to match the required fields in the threat source. Example: if the source includes 2 fields in csv
34.55.89.144,fibonacci_serverthen the Fields parameter must reflect that order:ip:$1,description:$2
- If one of the pre-configured inputs isn't a match for your threat intel source, select New.
- Fill out the required fields in the newly created threat source input.
7. Verify the new lookup based threat source was imported.
- Browse to Audit > Threat Intelligence Audit and verify the threat source is enabled. Use the panel Threat Intelligence Audit Events to find errors associated with the lookup name.
- Browse to Advanced Threat > Threat Artifacts and verify an object in the threat source can be found.
| Configure lists and lookups | Configure correlation searches |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security: 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.3.3
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!