About Splunk Phantom
Splunk Phantom is a world-class Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) system. The Splunk Phantom platform combines security infrastructure orchestration, playbook automation and case management capabilities to integrate your team, processes, and tools together.
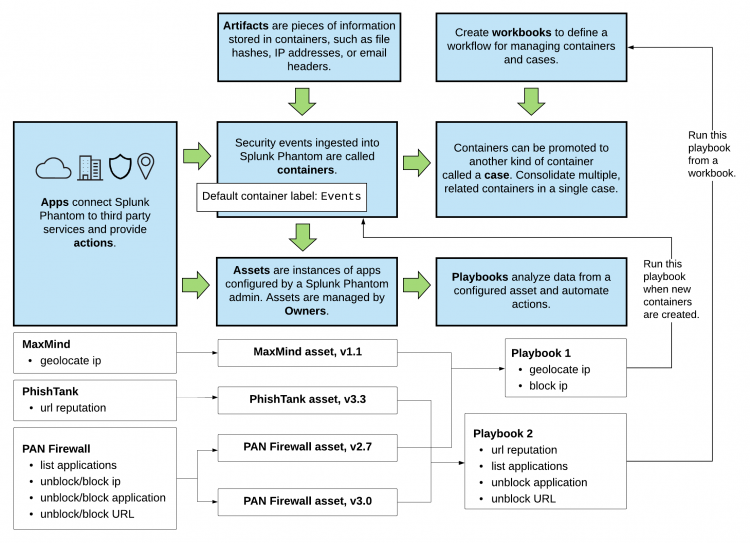
The diagram shows the end-to-end flow of security automation in Splunk Phantom.
The main components of Splunk Phantom each play a role in delivering end-to-end security automation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| App | An App extends the Splunk Phantom platform by adding connectivity to third party security technologies. The connections allow Splunk Phantom to access and run actions that are provided the third party technologies. Some apps may also provide a visual component such as widgets that can be used to render data produced by the app.
See Add and configure apps and assets to provide actions in Splunk Phantom in Administer Splunk Phantom. |
| Asset | An Asset is a specific instance of an app. Each asset represents a physical or virtual device within your organization such as a server, endpoint, router, or firewall. For example, you have a Palo Alto Network (PAN) firewall app that connects the firewall to Splunk Phantom. Then, you configure an asset with the specific connection details to a specific firewall. If your environment has multiple firewalls, you can configure one asset for each firewall.
This example shows one MaxMind asset, one PhishTank asset, and two PAN firewall assets. The PAN assets have different version numbers, which is the reason for having two assets. See Add and configure apps and assets to provide actions in Splunk Phantom in Administer Splunk Phantom. |
| Container | A container is a security event that is ingested into Splunk Phantom.
You can create custom labels in Splunk Phantom as needed. See Configure labels to apply to containers. |
| Case | A case is a special kind of container that can hold other containers. For example, if you have several closely related containers for a security incident, you can promote one of those containers to a case and then add the other related containers to the case. Doing this enables you to consolidate your investigation rather than having to investigate each container individually.
|
| Artifact | An artifact is a piece of information added to a container, such as a file hash, IP address, or email header. |
| Indicator, or Indicator of Compromise (IOC) | An indicator is a piece of data such as an IP address, host name, or file hash that populates the Common Event Format (CEF) fields in an artifact. Indicators are the smallest unit of data that can be acted upon in Splunk Phantom. |
| Playbook | A Playbook defines a series of automation tasks that act on new data entering Splunk Phantom. For example, you configure a playbook to run specific against all new containers with a specific label. Or, you can configure running a playbook as part of the workflow in a workbook.
See Create playbooks to automate analyst workflows in Splunk Phantom. |
| Workbook | A workbook is a template providing a list of standard tasks that analysts can follow when evaluating containers or cases.
|
| Action | An Action is a high level primitive used throughout the Splunk Phantom platform, such as get process dump, block ip, suspend vm, or terminate process. Actions are run in playbooks or manually from the Splunk Phantom web interface.
|
| Owner | An Owner is responsible managing assets in your organization. Owners receive approvals, which are requests to execute a particular action on a particular asset. Approvals are sent to the asset owners and contain a service level agreement (SLA) dictating the expected response time. Approvals are first sent to the primary asset owners. If the SLA is breached, then the approval is redirected to the secondary asset owner. SLAs can be set on events, phases, and tasks.
|
| Who should read this manual? |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Phantom (Legacy): 4.8
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!