Configure workload management
Before you can configure workload management in Splunk Enterprise, you must set up Linux cgroups on your underlying Linux operating system. For instructions, see Set up Linux for workload management.
This topic discusses how to configure workload management on a single instance. For information on how to configure workload management on distributed deployments, see Configure workload management on distributed deployments.
Before you can enable workload management, you must create a default pool in the search category and a default pool in the ingest category. You can optionally create workload rules to control access to workload pools at any time. You can configure workload management using Splunk Web, CLI, or REST.
Follow these steps to configure workload management on a single instance:
- Run preflight checks.
- Configure workload categories.
- Create workload pools.
- Create workload rules.
- Enable workload management.
- Check workload management status.
Run preflight checks
When you open workload management in Splunk Web, a set of system checks runs automatically to determine if your underlying Linux operating system is set up properly for workload management.
If all preflight checks pass, this means your system is set up correctly and you can proceed to configure workload management. If any preflight checks fail, review the error messages to identify the Linux configuration issues you must fix before you can configure workload management.
You can optionally run preflight checks manually using the CLI or REST API.
Workload management preflight checks reflect the status of the local instance only.
Workload management runs the following preflight checks:
| Name | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Operating system must be Linux. Workload management is not currently supported on Windows OS. |
| Cgroup Version | Cgroup must be version 1. Workload management does not support pre-cgroup or cgroup version 2 Linux kernels. |
| CPU Splunk base directory present | CPU Splunk base directory Splunkd.service is missing.
The See Configure systemd distributions for workload management. For non-systemd, the base directory is The base directory name must match the |
| CPU Splunk base directory permissions | CPU Splunk base directory Splunkd.service requires read and write permissions.
For non-systemd, use |
| Memory Splunk base directory present | Memory Splunk base directory Splunkd.service is missing.
For non-systemd, the base directory is |
| Memory Splunk base directory permissions | Memory Splunk base directory Splunkd.service requires read and write permissions.
For non-systemd, use |
| Unit file present | The unit file Splunkd.service is missing.
|
| Delegate property set to true | The Delegate property in the unit file must be set to true.
|
Splunk launched under systemd |
splunkd is running as a systemd service. In the unit file, the Restart property must be set to always. The ExecStart property must include _internal_launch_under_systemd.
|
For more information on unit file properties, see systemd unit file properties.
For more information on how to set up Linux for workload management, see Set up Linux for workload management.
Run preflight checks in Splunk Web
- Click Setttings > Workload Management. The Linux preflight checks run automatically. If all preflight checks pass, the workload management UI opens, and you can proceed to configure workload management.
- If any preflight check fails, a page appears showing the check results. Review the error messages and fix the specified Linux configuration issues.
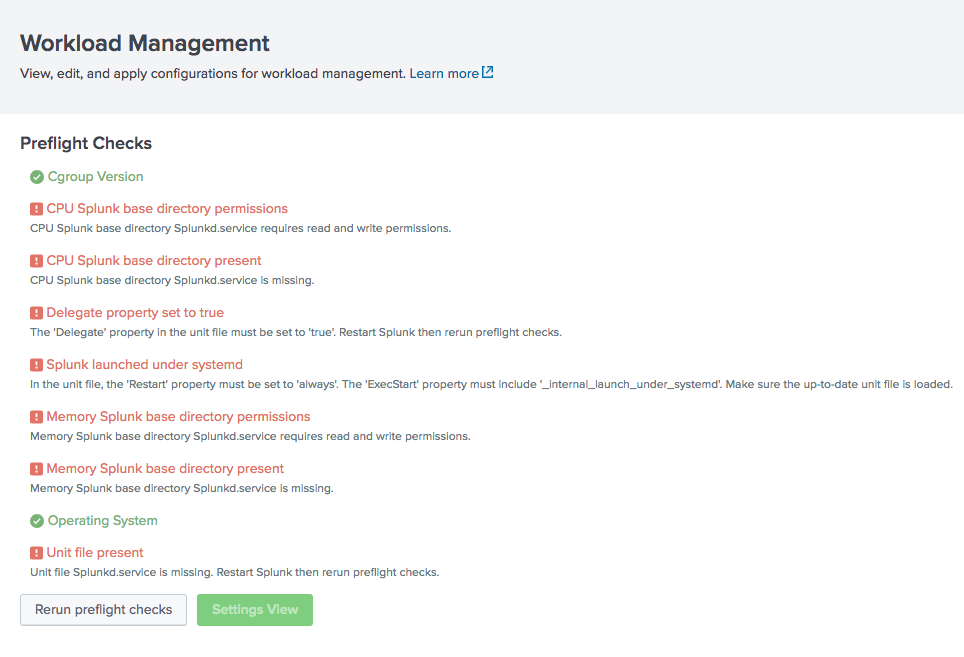
- Click Rerun preflight checks.
Run preflight checks using the CLI
To run preflight checks for workload management using the CLI:
- Log into your Linux machine.
- Run the following CLI command.
./splunk check workload-config
Here is an example of the output from this command:
Workload Management Preflight Checks failed. Fix the following issues: CPU Splunk base directory Splunkd.service requires read and write permissions. CPU Splunk base directory Splunkd.service is missing. The 'Delegate' property in the unit file must be set to 'true'. Restart Splunk then rerun preflight checks. In the unit file, the 'Restart' property must be set to 'always'. The 'ExecStart' property must include '_internal_launch_under_systemd'. Make sure the up-to-date unit file is loaded. Memory Splunk base directory Splunkd.service requires read and write permissions. Memory Splunk base directory Splunkd.service is missing. Unit file Splunkd.service is missing. Restart Splunk then rerun preflight checks.
Run preflight checks using REST
Send a GET request to:
workloads/config/preflight-checks
For endpoint details, see workloads/config/preflight-checks in the REST API Reference Manual.
Configure workload categories
Workload categories determine the total amount of system cpu and memory resources available for workload pools running specific process types in Splunk Enterprise. For example, the search category determines the total amount of resources available to all workload pools running search processes. When you create a workload pool you must assign it to a workload category.
Workload management provides the following three workload categories:
- search: Scheduled searches and ad hoc searches, accelerated reports and data models.
- ingest: Indexing and other
splunkdprocesses, including process runner, KV store, app server, and introspection. - misc: Scripted inputs and modular inputs only.
Each workload category has its own cpu and memory resource allocation. And each workload pool within a category is assigned a fraction of the total cpu and a percentage of the total memory allocated to that category. You can modify the resource allocation for a category to ensure that sufficient resources are available to workload pools running high-priority processes.
You can edit workload categories using Splunk Web, CLI, or REST.
Edit workload categories using Splunk Web
To edit the resource allocation for a workload category in Splunk Web:
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management.
The workload management UI opens.
- Click the All Categories tile.
- Click Edit under the specific category.
- Specify the resource allocation:
Field Action CPU Weight Specify the total CPU weight available for pools in this category.
Memory Limit % Specify the maximum percentage of Memory available for pools in this category. - Click Submit.
The percentage of CPU allocated to a category is a ratio of the total CPU weight across all categories. When you change the CPU weight for one category the CPU allocated to all other categories and all workload pools updates to reflect the change.
For more information, see Resource allocation in workload management.
Edit workload categories using the CLI
To edit a workload category, run the following CLI command:
./splunk edit workload-category <category> [-cpu_weight <number> -mem_weight <number>]
where <category> is search, ingest, or misc.
To list workload categories:
./splunk list workload-category
Edit workload categories using REST
Send a POST request to:
workloads/categories
For endpoint details, see workloads/categories in the REST API Reference Manual.
Create workload pools
A workload pool is a specified amount of CPU and memory resources that you can define and allocate to processes in Splunk Enterprise, including search, indexing, and other splunkd processes.
To configure workload management, you must create, at a minimum, these two workload pools:
- Default pool in the search category: Searches that are not explicitly mapped to a workload rule are assigned to this pool by default.
- Default pool in the ingest category: Indexing and other non-search processes are assigned to this pool by default.
You can optionally create a default pool in the misc category. Scripted and modular inputs run in this pool by default. If you do not create a default pool in the misc category, scripted and modular inputs run in the default pool in the ingest category.
You can only create one workload pool in the ingest and misc categories.
Create a workload pool in Splunk Web
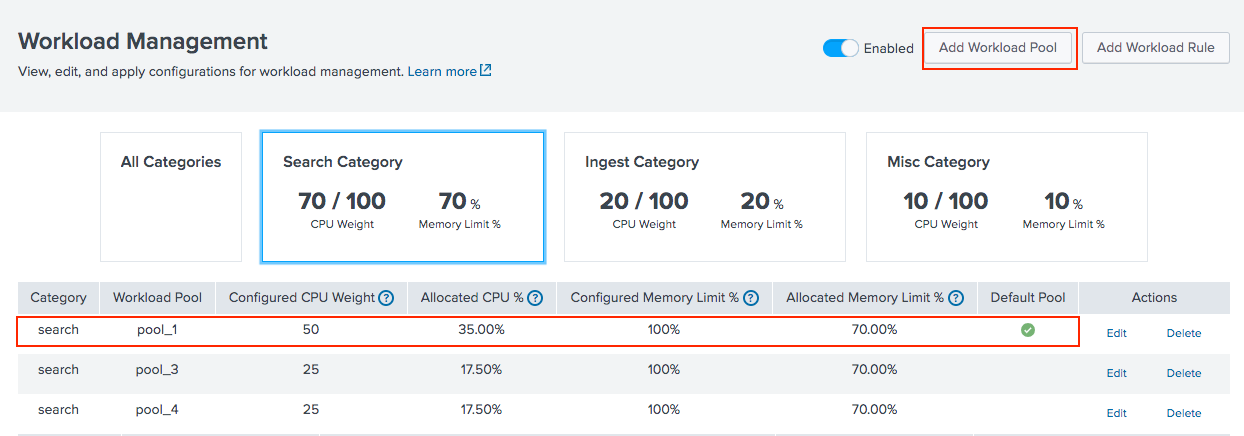
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management.
- Click Add Workload Pool.
-
Specify the following fields:
Field Action Pool Category Select a workload category based on the type of process the pool will run (search, ingest, or misc). See Configure workload categories. Name Specify the name of the workload pool. Valid characters are alphanumeric and underscore only.
CPU Weight The fraction of total available CPU for this pool. Memory Limit % The maximum percentage of total available memory for this pool. Default Pool Toggle the switch to make this pool the default pool for the selected category. -
Click Submit.
The workload pool appears in the Workload Management UI.
For more information, see Resource allocation in workload management.
Create a workload pool using the CLI
Run the following CLI command:
./splunk add workload-pool <pool_name> [-category <search/ingest/misc> -cpu_weight <number> -mem_weight <number> -default_category_pool <true|false>]
Create a workload pool using REST
Send a POST request to:
workloads/pools
For endpoint details, see workloads/pools in the REST API Reference Manual.
View workload_pools.conf
Do not place workload_pools.conf files in more than a single app context. Having identical workload_pools.conf stanzas in multiple app contexts can cause workload management enable/disable functions to fail and cause other issues.
When you create a workload pool, the configuration is stored in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/<app_name>/local/workload_pools.conf.
workload_pools.conf defines the cpu and memory resource allocation for workload categories (search, ingest, and misc) and the individual workload pools created under those categories. For example:
[general] default_pool = pool_1 ingest_pool = pool_3 enabled = 0 [workload_category:search] cpu_weight = 70 mem_weight = 70 [workload_category:ingest] cpu_weight = 20 mem_weight = 20 [workload_category:misc] cpu_weight = 10 mem_weight = 10 [workload_pool:pool_1] cpu_weight = 70 mem_weight = 70 category = search default_category_pool = 1 [workload_pool:pool_2] cpu_weight = 30 mem_weight = 30 category = search default_category_pool = 0 [workload_pool:pool_3] cpu_weight = 100 mem_weight = 100 category = ingest default_category_pool = 1 [workload_pool:pool_4] cpu_weight = 100 mem_weight = 100 category = misc default_category_pool = 1
For more information workload pool settings, see workload_pools.conf.
Delete workload pools
You can delete any workload pool under a category, except for the default category pool. If you try to delete the default category pool an error message appears. You can delete workload pools using Splunk Web, CLI, REST, or editing workload_pools.conf.
To delete a workload pool using the CLI:
./splunk remove workload-pool <pool_name>
You cannot delete a workload pool while a process is running in that pool. Any pool you delete that has an active process running in it will not be deleted until after workload_pools.conf reloads or splunkd restarts.
Create workload rules
Workload rules provide a policy-based method for assigning searches to workload pools. Each rule specifies a predicate condition that must match before you can assign searches to the designated pool. You can use workload rules to ensure that high-priority searches have access to adequate resources while low-priority searches are restricted.
Workload rules are evaluated in the order that you create them. If the predicate condition defined in a rule does not match, the next rule in order is evaluated. If there is no match with any rule, the search is assigned to the default search pool. In this way, workload rules let you prioritize the assignment of system resources based on conditions that you define.
Create a workload rule in Splunk Web
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management.
- Click Add Workload Rule.
- Configure your new workload rule by defining the following fields:
Field Action Name Specify the name of the workload rule. Predicate Specify a predicate condition to access the workload pool. The format is a logical expression where <type>=<value> with optional AND, OR, NOT, (). The valid <type> are "app", "role", "index", or "user". For example, "app=search AND role=power" maps all searches belonging to both the search app and the power role to the corresponding workload pool. For more information on predicates, see workload_rules.conf. Workload Pool Select the workload pool to which this rule applies. - Click Submit.
Create a workload rule using the CLI
Run the following CLI command:
./splunk add workload-rule <rule_name> -predicate <predicate> -workload_pool <pool_name>
where <predicate> is a logical expression in the format <type>=<value> with optional AND, NOT, OR, (). For example:
./splunk add workload-rule "my_role_rule" -predicate "app=search AND (NOT index=_internal)" -workload_pool "pool_a"
Create a workload rule using REST
Send a POST request to:
workloads/rules
For endpoint details, see workloads/rules in the REST API Reference Manual.
View workload_rules.conf
When you create a workload rule, the configuration is stored in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/<app_name>/local/workload_rules.conf.
workload_rules.conf defines both the mapping of rules to workload pools and the order in which rules are evaluated. For example:
[workload_rules_order] rules = new_rule_2,new_rule,SearchAppRule,DMC_rule [workload_rule:SearchAppRule] predicate = app=search workload_pool = app_search [workload_rule:DMC_rule] predicate = app=splunk_monitoring_console workload_pool = app_dmc [workload_rule:new_rule] predicate = app=search AND (NOT index=_internal) workload_pool = pool_1 [workload_rule:new_rule_2] predicate = NOT role=power OR user=admin workload_pool = pool_2
For more information on workload rules settings, see workload_rules.conf.
Enable or disable workload management
After you create your workload pools and rules, you must enable workload management. When you initiate a request to enable workload management, a series of health checks run in the background to validate both the workload management configuration and the underlying Linux system configuration. If these health checks fail, you cannot enable workload management and a failure message appears.
For more information on Linux configuration requirements, see Set up Linux for workload management.
Enable or disable workload management in Splunk Web
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management.
- Toggle the switch to Enabled.
This applies any pending configuration changes and enables workload management.To disable workload management, toggle the switch to '''Disabled'''.
Enable or disable workload management using the CLI
To enable or disable workload management, run the following CLI command:
./splunk <enable|disable> workload-management
Enable or disable workload management using REST
You can enable or disable workload management using REST. For endpoint details, see workloads/config/enable or workloads/config/disable in the REST API Reference Manual
Check workload management status
You can view the current active configuration of workload management using the CLI or REST. Output shows configuration details of all workload pools and rules, and whether workload management is supported and enabled on the instance.
Check workload management status using the CLI
Run the following CLI command:
./splunk show workload-management-status
Here is an example of the output from the command:
Workload Management Status: Enabled: 1 Supported: 1 Error: Workload Category: ingest CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/ingest Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/ingest CPU Weight: 25 Memory Weight: 25 Default Category Pool: pool_2 pool_2: CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/ingest/pool_2 Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/ingest/pool_2 CPU Weight: 100 Memory Weight: 100 Workload Category: search CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search CPU Weight: 75 Memory Weight: 75 Default Category Pool: pool_1 pool_1: CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search/pool_1 Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search/pool_1 CPU Weight: 20 Memory Weight: 20 pool_3: CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search/pool_3 Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/search/pool_3 CPU Weight: 20 Memory Weight: 20 Workload Category: misc CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/misc Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/misc CPU Weight: 12 Memory Weight: 12 Default Category Pool: misc_pool misc_pool: CPU Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/Splunkd.service/misc/misc_pool Memory Group: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/Splunkd.service/misc/misc_pool CPU Weight: 100 Memory Weight: 100 Workload Rules: rule_1: Order: 1 Predicate: app="search" Workload Pool: pool_1 rule_2: Order: 2 Predicate: app="search" AND (NOT index="_internal") Workload Pool: pool_3
Check workload management status using REST
To view workload management status information, send a GET request to:
workloads/status
For endpoint details, see workloads/status in the REST API Reference Manual.
Next Step
After you configure workload management, you can allocate resources to individual scheduled and ad-hoc search processes in Splunk Enterprise. For more information, see Assign searches to workload pools.
| Configure Linux systems not running systemd | Configure workload management on distributed deployments |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!