Using gauges
Use a radial, filler, or marker gauge to map a value in relation to a range. A gauge visualization provides metric status and range information that you can interpret quickly. You can use a real-time search to generate a gauge tracking value fluctuations as they occur.
Data formatting
To generate a gauge, use a search that returns a single numerical value. For example, use a search that returns an event count for events with a specific field value in a time period or real-time window. If you are using a real-time search, the range marker moves to show the metric changing over time.
Gauge types
All gauge types visualize a single aggregated metric.
For example, this search aggregates error log events.
index=_internal source="*splunkd.log" log_level="error" | stats count as errors
The search can generate any of the available gauge types.
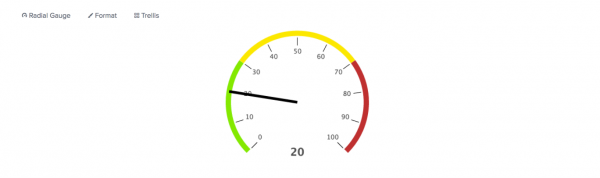
Radial gauge
A radial gauge includes a round value scale and a pointer to show the current value on the scale. The current value also appears at the bottom of the gauge. You can configure a radial gauge to use specific colors for each value range in the scale.
If the search generates a current value outside of the configured minimum or maximum range, the gauge pointer bounces at the lower or upper end of the value scale.
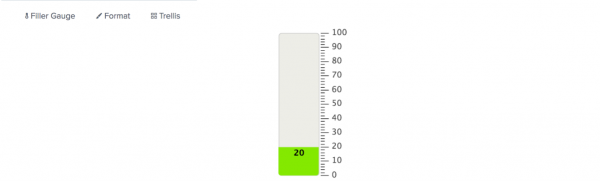
Filler gauge
A filler gauge includes a value scale container that fills and empties as the current value changes. The fill level shows where the current value is on the value scale.
The current value also appears inside the filled portion of the gauge. The container appears empty for a value lower than the minimum and full for a value higher than the maximum.
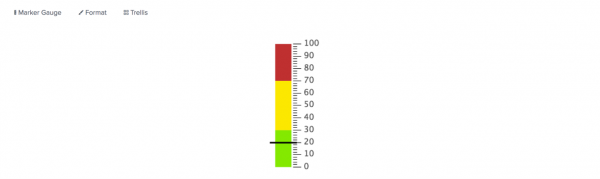
Marker gauge
A marker gauge shows value ranges and colors with a marker that moves to indicate the current value.
If the search generates a current value outside of the configured minimum or maximum range, the marker bounces at the lower or upper end of the value scale.
Configuration options
Use the Format menu to configure gauge style and color ranges.
Color ranges
Use the Format > Color Ranges panel to select manual or automatic color range configuration. By default the first three ranges are green, yellow, and red.
Set the Color Ranges handling to Automatic if the query includes the gauge command for range configuration.
If the query includes gauge, Format menu range configurations override the gauge command settings in the query.
Create a gauge visualization
Prerequisites
Review the following details about building column and bar charts.
Steps
- Write a search that generates a single aggregated value.
- Run the search.
- Select the Visualization tab and use the Visualization Picker to select a radial, filler, or marker gauge.
- (Optional) Use the Format menu to configure the visualization.
| Customize a single value | Mapping data |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.1.0, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.1.5, 7.1.6, 7.1.7, 7.1.8, 7.1.9, 7.1.10, 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10, 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9, 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.2, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.1.5, 8.1.6, 8.1.7, 8.1.8, 8.1.9, 8.1.10, 8.1.11, 8.1.12, 8.1.13, 8.1.14, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.2.4, 8.2.5, 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.4.0, 9.4.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!