Match TA event types with CIM data models to accelerate searches
Splunk Enterprise Security uses the Common Information Model (CIM) add-on to accelerate searches by associating event types generated by Technology Add-ons with the data models.
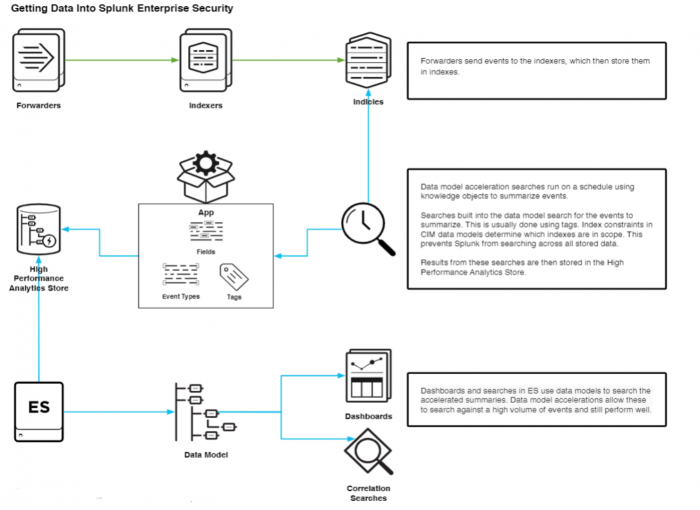
Forwarders send events to the Splunk indexers. These events are stored in indexes. To identify the type of event, tags are assigned to the events based on certain field conditions. Events can be classified based on event type and associated with specific data models defined in the CIM app.
The CIM data models are implementations of schemas that represent the different types of events. Data model acceleration searches run on a schedule using knowledge objects and summarize the events. Searches built into the CIM data models use tags to search for the summarized events that match the data model. Index constraints in CIM data models determine which indexes might be included in a search.
These index constraints prevent the Splunk Platform from searching across all stored data and focus only on the relevant indexes. Thus, searches can be accelerated because the data is normalized through the connection established between the field tags, event types, and the CIM data models, which reduces the scope of the search.
Event types are a categorization system that help to make sense of the data. Event types are defined for a subset of events. For more information on event types, see About event types.
Use the following figure for an overview of how data is ingested into Splunk Enterprise Security and normalized using CIM data models:
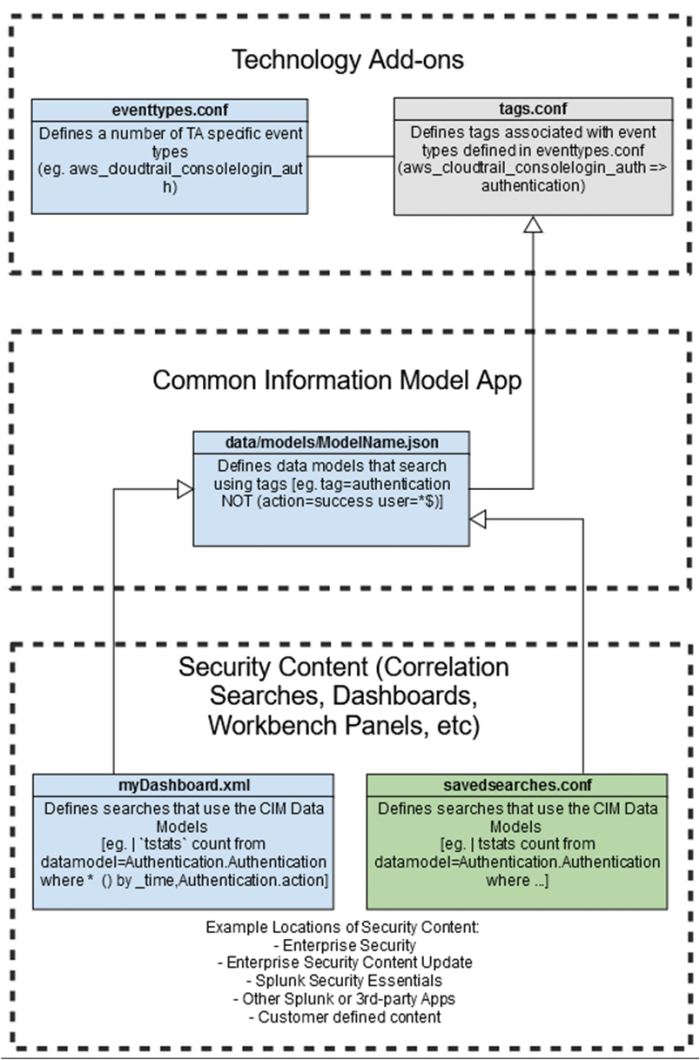
The following example illustrates how event types are matched using data models and are used in correlation searches to accelerate searches and generate alerts. In this example, aws_cloudtrail_consolelogin-auth is a type of event ingested from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that feeds into Technology Add-ons (TA).
- TAs identify events that match the event type defined in the
eventtypes.conffile. - The following search in the
eventtypes.conffile identifies the events that match the event type"aws_cloudtrail_consolelogin-auth" search = sourcetype="aws_cloudtrail" (eventname="ConsoleLogin" additions(EventData.LoginTo=*) - Tags that are applicable to the event are defined in the
tags.conffile. The tag defined for this event type intags.conffile is:authentication. Tags can help to assign names to specific field and value combinations that reflect different aspects of their identity and enable you to perform tag-based searches to help you narrow the search results. For more information on tags, see Tags - TA's assign the authentication tag to the event types. CIM's Authentication data model searches by the
authenticationtag. - Dashboards and searches in Splunk Enterprise Security uses the Authentication data model to search the accelerated summaries of event data that describe login activities from any data source. For more information on the Authentication data model, see Authentication.
- Results from the searches are stored in a High Performance Analytics Store. Data model accelerations allow searches against a high volume of events and maintain performance levels.
- Data models are also used in correlation searches to search on accelerated data and generate alerts.
The following figure provides an overview of how TA event types are associated with CIM data models to accelerate searches in Splunk Enterprise Security.
| Use the CIM to normalize data at search time | Use the CIM to validate your data |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Common Information Model Add-on: 5.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!