What is an entity integration?
An entity integration is content within ITE Work that enables the automatic detection and discovery of entities, while also providing the vital metrics and related dashboards you need explore the health of those entities.
Entity integrations for a number of technologies are available as part of individual content packs in the Splunk App for Content Packs. After entities are detected, they become visible under the Infrastructure Overview menu. You can then use that information to observe and understand the performance of your entities. For more information, see Overview of creating custom content packs in ITSI.
Entities in ITE Work
An entity is an IT component that requires management to deliver an IT service. Each entity is uniquely identified by its specific attributes and relationships to other IT processes. Entities are usually hosts, but can also be items as diverse as cloud or virtual resources, network devices, applications, users, and cell towers.
ITE Work entities can be any of the following components:
- Physical, virtual, or cloud resources
- Network devices such as switches or routers
- AD and LDAP users
- Storage systems, volumes
- Operating systems or processes
- Software applications, such as database, web server, and business applications
- Application process instances
- Cell towers
Entities contain information ITE Work uses to associate services with information found in searches, imports, and integrations. You can use this entity information to filter items according to the entity definition.
An entity is similar to a "configuration item" in the ITIL framework, but an entity is never a service itself.
If you have a valid ITSI license installed, you can create entities before creating and configuring services. When you configure a service, you can specify entity matching rules based on entity aliases that automatically add the entities to your service.
Why use an entity integration?
Entity integrations support basic OS infrastructure monitoring and troubleshooting on top of Splunk core. Once integrated, entities provide you with a starting point for visualizing the data exposed through monitoring. Entities also provide an in-context drill-down workflow for the troubleshooting that you can do using dashboards.
How to create entities
There are a few ways to create entities in ITE Work:
- Manually create a single entity in ITE Work
- Manually import entities from a Splunk search in ITE Work
- Manually import entities from a CSV file in ITE Work
After you import entities, you can configure recurring imports to update existing entities and create new entities. For more information, see Set up a recurring import of entities in ITE Work.
Automatically create entities and collect data on a recurring basis with ITE Work entity integrations. These integrations are available:
- About the Unix and Linux entity integration in ITE Work
- About the Windows entity integration in ITE Work
- About the VMware vSphere entity integration in ITE Work
- About the Splunk Infrastructure Monitoring entity integration in ITE Work
All entities exist in the Global team. Only a user with write permissions to the Global team can create a single entity. Only a user with the itoa_admin role can import entities from CSV files or searches.
Modules, included only with ITSI, can help automatically discover entities. When a new server comes online, ITSI can automatically add it as an entity. Entity discovery occurs on a scheduled basis when you configure the modules included with ITSI. For more information about using modules to create entities, see ITSI module entity discovery in the ITSI Modules manual.
Analyze and monitor entities
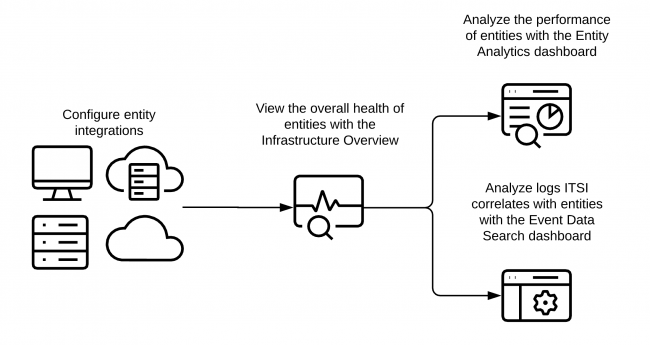
This diagram illustrates a basic entity integration workflow in ITE Work. Configure integrations to monitor hosts, containers, virtual infrastructures, and cloud services as entities with ITE Work.
After you import your entities, use the entity views available in ITE Work to analyze log data associated with an entity and track entity metrics.
| View | Description |
|---|---|
| About the Infrastructure Overview in ITE Work | Analyze health of entities across various platforms. |
| Event Data Search | Analyze logs ITE Work correlates with entities. |
| Entity Analytics | Analyze the performance of entities. |
Do more with services in ITSI
You can associate entities with services, included only with ITSI, to monitor your infrastructure at the service level. A service is a logical mapping of IT objects that applies to your business goals, such as a physical or virtual machine, an application, a process, or a business services. For more information, see Overview of creating services in ITSI in the ITSI Service Insights manual.
To associate an entity with a service, you have to define entity rules for that service. Entity rules filter KPI data to ensure that the service is only reading data from the entities associated with it. Create entity rules for the service to add entities with specific aliases, information, or titles to the service. For more information, see Define entity rules for a service in ITSI in the ITSI Service Insights manual.
| Configure the HTTP Event Collector to collect entity integration data in ITE Work |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® IT Essentials Work: 4.9.0, 4.9.1, 4.9.2, 4.9.3, 4.9.4, 4.9.5, 4.9.6, 4.10.0 Cloud only, 4.10.1 Cloud only, 4.10.2 Cloud only, 4.10.3 Cloud only, 4.10.4 Cloud only, 4.11.0, 4.11.1, 4.11.2, 4.11.3, 4.11.4, 4.11.6, 4.12.0 Cloud only, 4.12.2 Cloud only, 4.13.0, 4.13.1, 4.13.2, 4.13.3, 4.14.0 Cloud only, 4.14.1 Cloud only, 4.14.2 Cloud only, 4.15.0, 4.15.1, 4.15.2, 4.15.3, 4.16.0 Cloud only, 4.17.0, 4.17.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!