Configure the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory
The Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory is a bundle of commands written in Python. New for version 2.0, the add-on no longer requires an installation of Java on the machines that run it.
Configuring the add-on in the UI on the search head cluster replicates the configuration on every search head.
Configure the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory
Use Splunk Web to configure the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory.
If you have upgraded from a previous version, you must visit the Configuration page once to save your existing configuration in the new format. From then on, make any changes in this page.
If you have not used the add-on, use the Configuration page to add and remove configurations.
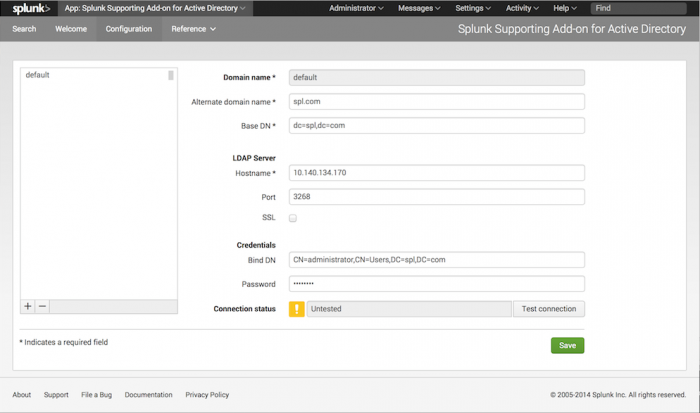
Configure the add-on with Splunk Web
The Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory has a configuration page that you can access from Splunk Web.
To use the configuration page, activate the add-on by selecting it from the "App" menu in the upper left corner of the screen. Then, after the add-on loads, select "Configuration" from the menu.
Add a domain
To add a domain using the Configuration page:
1. In the lower left corner of the domain list pane, click the "+" sign.
2. In the Domain Name field, type in the name of the domain that you want the add-on to get data for.
3. In the Alternate domain name field, type in an alternate representation of the domain in NetBIOS format. Make sure that the Alternate domain name is specified in UPPERCASE format.
Example: SPLUNK
4. In the Base DN field, type in the same domain in LDAP notation.
Example: DC=spl,DC=com
5. In the LDAP Server: Hostname field, type in the name or IP address of the host that the add-on should connect to for this domain.
6. In the LDAP Server: Port field, type in the port that the add-on should connect to on the LDAP server.
Note: When configuring the 'default' connection, use port 3268 (for plain text) or 3269 (for SSL) connections. This tells the add-on to connect to the Global Catalog, which is faster, but might not return all attributes. For other domain connections, use port 389 (for plain text) or 636 (for SSL)
7. If you want the server to use SSL to connect, click the SSL checkbox.
8. In the Credentials: Bind DN field, enter the username that the add-on should use to connect to the LDAP server you specified previously, in LDAP notation.
Example: CN=Splunk Searcher,CN=Users,DC=spl,DC=com
Note: You can also enter the name in the following formats:
- User Principal Name (UPN), such as 'user@splunk.com'
- Security Account Manager (SAM) account name, such as 'splunk\username'
- Base Distinguished Name (DN).
9. In the Credentials: Password field, enter the password for that user.
10. Optionally, you can test whether or not the add-on can make a valid connection. To do so, click the Test connection button.
A window appears while the add-on attempts to connect to the LDAP server and retrieve information. If the test succeeds, the window displays results. If no results display, then the test has failed and you must correct your settings before attempting to test the connection again.
11. Click Save to save your changes.
Remove a domain
To remove a domain:
1. In the domain list pane, click the domain that you want to remove.
2. Click the "-" button at the bottom of the pane.
3. Click the Save button to save the changes.
Configure the add-on for use on a heavy forwarder
Though the add-on is not required on the heavy forwarder, configure the add-on on the forwarding instance to run a saved search. For example, you can run the LDAP query as a saved search to get continuous data of Active Directory.
1. Configure the receiving instance
To configure forwarding and receiving, see Enable forwarding on a Splunk Enterprise instance and Enable a receiver in the Splunk Enterprise Forwarding Data manual.
- Configure receiving on the host(s) that you want to receive the forwarded data.
- Create an index for the forwarded data to reside in.
2. Configure SA-LDAPsearch on the forwarding instance
- Configure forwarding on the instance that runs the add-on.
- Configure the add-on to connect to an Active Directory domain controller or Global Catalog. See Configure the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory.
- On the forwarder, create an index with the same name as the receiving index in step 2 of Configure the receiving instance.
- (Optional) To forward data to a particular destination index, see Filter data by target index in the Splunk Enterprise Forwarding Data manual.
3. Run and save the search
- On the heavy forwarder, navigate to the Search & Reporting app.
- Type in a valid command(s) for the add-on, but do not invoke the search yet.
See The LDAP search commands chapter for proper syntax for the LDAP search commands. - At the end of the search, add
| collect index=<index>, where<index>is the index that you created. - Run the search.
- Save the search as a report.
- Give the report a name and a description, then click Save.
- Schedule the report. See Schedule reports in the Splunk Enterprise Reporting manual.
- Confirm that you see events on the receiving indexer.
Where to find the events on the receiver
The events that you forward appear in the index that you created on the receiving indexer with the host field set to the name of the host that originated the LDAP search and a source type of stash. You can search the index that you created on the receiving instance to see all of the forwarded events.
If you do not see the events on the receiving indexer, confirm that:
- You have created an index on both the heavy forwarder and the receiving indexer, and that the index names match.
- The forwarding instance is a heavy forwarder. A universal forwarder cannot route data based on destination index.
- You have configured the
forwardedindexfilter to forward data destined for the index you created. - You pipe the results of your LDAP search to the
collectcommand and specify the index you created.
Configure the add-on to push a base-64 encoded password to all search-heads in a distributed environment
Here's how to configure the add-on on the deployer and push a base-64 encoded password to all search heads in a distributed environment. The add-on isn't required on the indexers unless you're using the indexers as search peers. Don't configure the add-on from the UI because it will store the encrypted password, and won't push it to the search head clusters and indexer cluster.
- Login to the deployer machine using SSH or remote desktop.
- Go to $SPLUNK_HOME$/etc/shcluster/apps.
- Install the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory if you have not already, and go to the "SA-ldapsearch" add-on directory.
- Create a local folder if it doesn't already exist, and go to it.
- Verify there should not be any ldap.conf or password.conf file. If it exists, delete it.
- Create a new ldap.conf file and open it in edit mode.
- Add a default stanza with a proper value in that file.
[default] alternatedomain = <value> basedn = <value> binddn = <value> port = <value> server = <value> ssl = 0 password =
- Prepend the base-64 encoded password with {64}. For example:
password = {64}aAbBcCdDd= - Push the add-on to search head clusters using this command:
splunk apply shcluster-bundle -target https://<SH_captain_IP>:8089
Configure the add-on to send data to Splunk Cloud
When you configure the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory for use with Splunk Cloud, configure a heavy forwarder to send data to the Splunk Cloud instance. This requires installing the add-on on a heavy forwarder that is configured to forward data to that Splunk Cloud instance. The procedure is similar to configuring the add-on to use a heavy forwarder, but there are additional steps required to get the Splunk Cloud instance to accept data from the forwarder. See Introduction to Getting Data In in the Splunk Cloud Platform Admin Manual.
If you're Configuring SA-ldapsearch on the search head in a cloud environment, then it must have the connectivity between the LDAP server and the search head.
Configure Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) settings for the add-on with ssl.conf
You can use the ssl.conf file to override SSL settings on the Splunk Enterprise instance that runs the add-on.
The settings in ssl.conf apply only to the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory and override settings that you have defined in server.conf on the instance. You can specify any valid attributes within the [sslconfig] stanza of server.conf. See the server.conf spec file. A list of common attributes follows:
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| caCertFile = <filename> | File name (relative to 'caPath') of the root CA (Certificate Authority) certificate store. Must refer to a PEM format file containing one or more root CA certificates concatenated together. | cacert.pem
|
| sslVersions = <versions_list> | A comma-separated list of SSL versions to support for incoming connections. The versions available are "ssl3", "tls1.0", "tls1.1", and "tls1.2". The special version "*" selects all supported versions. The version "tls" selects all versions tls1.0 or newer. If you prefix a version is with "-" you remove it from the list.
SSLv2 is always disabled; "-ssl2" is accepted in the version list but does nothing. When configured in FIPS mode, ssl3 is always disabled regardless of this configuration. |
*,-ssl2 (anything newer than SSLv2).
|
| sslVerifyServerCert = true|false | Used by distributed search: when making a search request to another server in the search cluster. Used by distributed deployment clients when polling a deployment server.
If you set this to true, you should make sure that the server that is being connected to is a valid one (authenticated). Both the common name and the alternate name of the server are then checked for a match if they are specified in this configuration file. A certificate is considered verified if either name matches. |
false |
1. Open a shell or command prompt.
2. Change to the $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/SA-ldapsearch/local directory.
3. Create the ssl.conf file.
4. Add a single line [sslConfig] to the file.
5. Add valid key-value pairs to the file.
6. Save the file and close it.
7. Log into Splunk Web on the instance that runs the add-on.
8. Configure the add-on to add an LDAP domain. See Configure the add-on with Splunk Web.
Other uses
You can also create lookup tables with the report you save, depending on the LDAP commands you use. Lookup tables cannot be forwarded, however. To work around this limitation, you can:
- Copy the lookup table to the lookup directory on a search head or indexer.
- Import the lookup table into App Key Value Store.
| Install the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory | Upgrade the Splunk Supporting Add-on for Active Directory (SA-LDAPSearch) |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Supporting Add-on for Active Directory: 3.0.8
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!