For details, see:
Specify data in your playbook
Playbooks work with data values from the playbook's container, its artifact CEF values, the results of an action or playbook that was previously run, or static data. You specify this data using datapaths within most playbook blocks.
When you add a playbook block, you specify the datapath in the configuration panel for that block. After the initial configuration, select the block to open its configuration panel.
To specify the datapath, follow these steps:
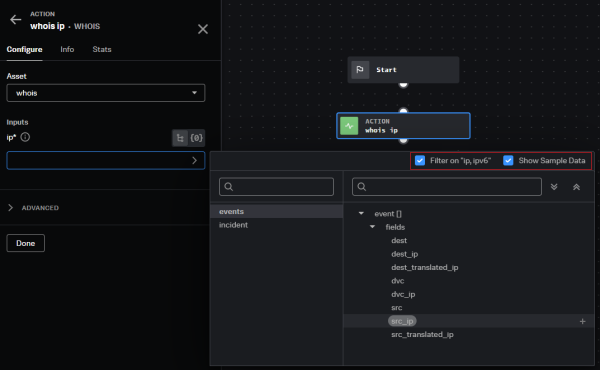
- In the playbook block configuration panel, select the parameter you want to specify. Available parameters are based on the type of block. For example, you might specify an if statement in a utility block or a
container_idfor an action block, shown in this figure. The datapath picker appears. - In the datapath picker, select the starting location for the data — including events, incident, and playbook. More specific data options display, based on your selection. Select the data type to use for your playbook input. Use the search field to help narrow down the list, if needed. In this example, we selected the Input
ip, then the starting locationevents, and then, from the event fields,src_ip. - For specific input data types, like IP, only appropriate data types display by default, indicated by the red box in the example screen. You can choose to clear the filter to show all possible data types.
- Data passed from an action block earlier in your playbook might have associated sample data, so you can see which types of data you might want to choose for your data path. Select or clear the Show sample data checkbox to view or hide sample data. The Show sample data checkbox appears only when you are selecting from an upstream action block's datapath. Sample data appears to illustrate what actual data might look like; you cannot select sample data.
- CEF values are described in more detail in Datapaths and CEF fields, later in this article.
- Within the datapath picker, you can use the
 icons to navigate results. You can also expand or collapse the lists by using the
icons to navigate results. You can also expand or collapse the lists by using the  icons.
icons. - After you complete your selections, the datapath displays in the parameter field.
- For multiple parameters, repeat this process for each additional parameter.
The datapath that appears in the parameter field might differ slightly from the names you selected in the datapath picker. This is due to internal mappings and is expected.
You can edit the generated datapath if you choose. For example, you might want to change the final section to point to a different variable. If you prefer, you can enter the datapath directly, without using the datapath picker. For details on the different sections of the datapath, see the next section, Datapath structure.
Datapath structure
Datapaths have the same general structure, shown in the figure below and described here. Datapaths with CEF fields are described in the next section, Datapaths and CEF fields.
![]()
- The name before the last colon describes the data's location. Examples include:
artifact,custom_function,playbook_input, and an action block name likerun_query_1. The datapath might contain multiple names before the last colon, that indicate block names in your playbook. - Everything after the last colon is the JSON-compatible structure for the data's location.
- Periods (.) denote moving down a layer into the data structure.
- Asterisks (*) denote arrays or lists. If the data is not an array or a list, there is no asterisk.
The example shown in the attached figure has the following specific structure:
artifactdenotes the object where the data is located- The asterisk (*) denotes that you are iterating through all artifacts, rather than just one.
- The period (.) moves you down one layer.
severityis the data for the artifact's metadata field calledseverity.
attempts to access the value at that location and return a list of values based on how many artifacts it searched. If that data path is empty, returns a list of None values.
Datapaths and CEF fields
Common Event Format (CEF) fields are a system of key-value pairs with data about artifacts. For details about CEF fields, see Create custom CEF fields in .
Datapaths with CEF fields are similar to other datapaths described in the previous section, but they include cef within the datapath and usually have at least two period separators.
![]()
The example shown in the figure has the following specific structure:
artifactdenotes the object where the data is located- The asterisk (*) denotes that you are iterating through all artifacts, rather than just one.
- The first period (.) moves you down one layer.
cefis the cef key, denoting a CEF field.- The second period (.) moves you down another layer into the data.
sourceHostNameis the key for the source's host name.
Splitting by commas and other delimiters
In Decision and Filter blocks, you might want to split datapath results into lists of values that you can evaluate. When configuring Decision and Filter blocks, you can choose whether you want to use a delimiter and, if so, specify the string you want to use as a delimiter. Use caution when splitting by commas, because some CEF fields might contain commas and cause unexpected results in a list. Because splitting by commas can yield confusing results, splitting by a delimiter is deprecated and is not active by default.
User-based datapaths
You can dynamically specify a user associated a playbook without knowing their name or id. For example, you might want to send a message to, or refer to, the user who initiated the current run of a playbook, rather than to a group or admin who might not know as much about the current playbook. For playbooks launched by automation, the result is automation.
Action, code, custom function, decision, and filter blocks
In the playbook block configuration, select playbook, then launching_user, then specify either the id or name of the user who launched the current run of this playbook.
Prompt blocks
In the prompt block User or Role configuration, specify the appropriate dynamic user or role:
- Event owner: The user or role the container is assigned to when the playbook is run
- Playbook run owner: The user who initiated the current run of this playbook.
Custom datapaths
If the datapath you need isn't available, create a custom datapath. This can happen when running actions with dynamic results. When you add a custom datapath, it is only available for the block you add it to.
To create a custom datapath, follow these steps:
- Hover over a datapath field title and select +.
- Enter the datapath name.
- Select either Key or List from the drop-down menu. Use Key to use one value, and use List to use a list of values. Using List adds a .* value to the datapath and it appears as <list_name [] > with datapaths nested below it in the datapath picker.
- To add more values to your List, select the + icon under the top value of the list.
- Select Save.
Example: Add a custom datapath to a playbook block
If you execute a "run query" action on the Splunk app in , the action result output includes a dynamic list of fields that are defined as part of the query that was run. These fields don't appear in the datapath selector, but you can add them by creating a custom datapath. In this instance, if the name of the action result output wasn't available, you can create the custom datapath action_result.data.*.hostname. As stated in the previous section, custom datapaths only appear in the block where they were added.
To create this example custom datapath in an action block, follow these steps:
- Add an action block to your playbook by dragging and dropping the half-circle icon attached to any existing block in the editor. Select an Action block from the menu that appears.
- Search for and select the action run query on the Splunk app in the By Action tab in the block.
- In the Configure tab for the block, enter the SPL query
host="web_application"to run a run query action on the Splunk app in . - Select the block you want to add the custom datapath to and select the datapath
run_query_1.After you make the selection, you see that the hostname isn't available, even though it was visible when running your query in Splunk. - Add the custom datapath
hostnameunderdata []. - Hover over the data field title and select +.
- Enter the datapath name
hostnameas a Key. - Select Save. The custom datapath appears in the list under
data []ashostname.
Datapaths and the Playbook API
For information on APIs involved with datapaths, see Understanding datapaths.
Specify data through the format method
In addition to using the datapath picker, you can specify your parameters by using the format method, in action, prompt, and format blocks. To use the format method, in the configuration panel, select the format button ![]() instead of the datapath button
instead of the datapath button ![]() . You will still specify the datapaths as described in this article, but then you will format them in a template. For details, see Customize the format of your playbook content.
. You will still specify the datapaths as described in this article, but then you will format them in a template. For details, see Customize the format of your playbook content.
| Determine your playbook flow in | Save a playbook so can access it |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® SOAR (On-premises): 6.1.0, 6.1.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!