For details, see:
Configure forwarders to send SOAR data to your Splunk deployment
Starting in release 6.2.0, the embedded instance of Splunk Enterprise has been replaced with Universal Forwarders. These universal forwarders allow for better scaling, better performance, and reduced resource usage for getting your SOAR data into your Splunk deployment.
If your organization does not send your data to a Splunk Cloud Platform Deployment or Splunk Enterprise deployment, you do not need to configure forwarders.
Splunk SOAR (On-premises) includes the compatible, supported universal forwarder version. Do not upgrade to another universal forwarder version between Splunk SOAR releases.
After upgrading to Splunk SOAR (On-premises) release 6.2.0 or higher, you no longer require the user accounts phantomsearch and phantomdelete on your Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform deployment.
Support was added for new data types that you can send from 6.2.0 to Splunk Cloud Platform or your dedicated Splunk Enterprise deployment.
- Audit logs: Records of all activities in .
- Playbook run: Playbook performance metrics, including resource scoring data. See note at the end of this list.
- SOAR logs: Information about , based on app logs.
- Splunk Addon For Linux Logs: System logs from for use with Splunk IT Service Intelligence.
You will need to make sure that logging levels are set for the appropriate logs in order to forward useful information. For more information about configuring logs and logging levels see Configure the logging levels for Splunk SOAR (On-premises) daemons.
If you choose to forward the Playbook run data type, you must first create the phantom_playbook_run index in your destination Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform instance. See Create Events Indexes in the Splunk Enterprise documentation or Create a Splunk Cloud Platform events index in the Splunk Cloud Platform documentation.
Configure data forwarding
This section applies if you are forwarding data from to either an external instance of Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform.
You must complete these steps to ensure your data can be forwarded.
Configure a Universal Forwarder Credentials Package
If your organization forwards data to a Splunk Cloud Platform deployment, you need to use a Universal Forwarder Credentials Package to configure your forwarders.
To configure your forwarders with with a Universal Forwarder Credentials Package, follow these steps:
- In your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment, get a Universal Forwarder Credentials Package.
For details, see Install and configure the Splunk Cloud Platform universal forwarder credentials package in the Splunk Universal Forwarder documentation. - In Splunk Cloud Platform, select Apps, then Universal Forwarder.
- Select Download Universal Forwarder Credentials.
- Conditional: If your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment is in a restricted access category, you must request that TCP port 9997 be opened on your Splunk Cloud Platform.
- In , upload the credentials package from Step 1.
- From the Home menu, select Administration, then Administration Settings. Then select Forwarder Settings.
- Click the +Install Credentials Package button.
- Drag and drop, or click the large box to select and upload the Splunk Universal Forwarder Credentials Package associated with your Splunk Cloud Platform instance.
- In the Name field, type a name for your forwarder group (do not use the name
splunk). This name is displayed on the Forwarder Settings page. - Select all of the data types you want to forward to your Splunk Cloud Platform deployment. You must select at least one data type to forward.
- Make sure the Enabled slider button is in the on position.
- Click Save.
Configure forwarding to a Splunk Enterprise deployment
If your organization forwards data to a Splunk Enterprise deployment, you need to configure your forwarders. To configure data forwarding follow these steps:
- From the Home menu, select Administration, then Administration Settings. Then select Forwarder Settings.
- Select +New Group.
- In the Add a new forwarder group dialog do the following:
- In the Name field, type a name for your forwarder group. This name is displayed on the Forwarder Settings page.
- Conditional: If you use a TCP token to authenticate to your Splunk Enterprise deployment, add it to the Token field.
- In the Indexers field, add the address for your indexer.Click the Add Another if you have more indexers to add. You can remove an indexer from the list by using the - button at the end of the indexer's address field.
- Select the Data types you want to ingest into Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise.
- Make sure the Enabled slider button is in the on position.
- Click Save.
After you complete these steps, data will begin to stream from to your Splunk Enterprise deployment.
Configure transport layer security between your Splunk SOAR (On-premises) universal forwarder and the receiving indexer
You can now use transport layer security (TLS) certificates to secure connections between 's forwarders and the receiving indexers.
To add a TLS certificate, you will need a valid TLS certificate in your certificate bundle.
To use a certificate bundle it must include;
- the client certificate
- the matching private key
- the CA certificate that was used to sign the client certificate
- (Conditional) If the private key in your certificate bundle is encrypted, you will need the client certificate password.
For more information on preparing your TLS certificates for use with the Splunk platform, see How to prepare TLS certificates for use with the Splunk platform in Securing Splunk Enterprise.
To add a TLS certificate for your Universal Forwarder, or to edit the TLS configuration, do the following steps:
- From the Home menu, select Administration, Administration Settings, Forwarder Settings.
- On the Forwarder Settings page, click the edit icon on the right-hand end of the forwarder group's entry.
- Click the Certificate configuration tab.
- Add your client certificate bundle either by dragging and dropping it onto the box provided, or by clicking the box and navigating to the bundle on your filesystem.
- (Conditional) If your Client certificate bundle includes an encrypted private key, type your client certificate password in the Client certificate password box.
- Add your TLS certificate by dragging and dropping the certificate onto the box provided, or by clicking the box and navigating to the certificate on your filesystem.
- (Optional) Select options as needed:
- Verify server certificate
- Verify server name
- Use client SSL compression
- (Optional) If you use common names or Subject Alt names for your servers, add them as comma-separated lists to the Allowed common names or Allowed Subject Alt names fields.
- Click Save.
When a Universal Forwarder is configured with TLS certificates, the Forwarder Settings page displays the certificate expiration date in the Expiry column. Expired certificates have their dates and times displayed in red text.
Configure Splunk SOAR (On-premises) to forward information to ElasticSearch
When you configure to use an external instance of Elasticsearch, a copy of all indexed and searchable data is sent to the Elasticsearch instance.
Verify the following requirements before configuring the external Elasticsearch instance:
- If you are using SSL to secure your connection to the Elasticsearch instance, the SSL certificate is imported to the Splunk Phantom certificate store.
- You know the host name and port for the Elasticsearch instance.
- You know the username and password of an Elasticsearch user account, or the client certificate and client key.
Perform the following tasks to connect to an external Elasticsearch instance:
- From the main menu in , select Administration.
- Select Administration Settings.
- Select Forwarder Settings.
- Click the button labeled +Configure Elastic Search.
- On the Configure Elastic Search dialog, add the settings for your Elasticsearch instance:
- In the Host field, type the hostname and port for your Elasticsearch instance.
- In the Username field, type the username required to log in to your Elasticsearch instance.
- In the Password field, type the password required to log in to your Elasticsearch instance.
- Conditional: Select the Use SSL check box to enable SSL.
- Conditional: If your Elasticsearch instance is version 6 or higher, select the Use one index per section check box.
- Conditional: If you are using certificate-based authentication, select the Client Authentication check box.
- Type the name of the client certificate in the Client Certificate field. This certificate is often a file with the .pem extension.
- Type the name of the to client key in the Client Key field. This key is often a file with the .key extension.
- Data types for Elasticsearch are already configured for you.
- When you are finished, click the button labeled Save.
If you want to use a client certificate to connect to your Elasticsearch instance, provide the paths on the Splunk SOAR instance's operating system to the public and private keys. The private key, often a file with the .pem extension, is the Client Certificate. The public key, often a file with the .key extension, is the Client Key. Both files must be added to the Splunk SOAR (On-premises) Certificate store. See Splunk SOAR (On-premises) certificate store overview for more information on the Certificate Store.
Reindexing
You can reindex all of your data.
Reindexing will send all your SOAR data to your Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform deployment again, which can result in duplicated data. To prevent duplicates, make sure to delete existing objects from all forwarder groups before reindexing. See How indexing works in the Splunk Enterprise Managing Indexers and Clusters of Indexers manual.
To reindex your data, do these steps:
- From the Home menu, select Administration, Administration Settings, Forwarder Settings.
- From the Forwarder Settings screen, select the Reindex tab.
- Use the dropdown menu to select the data type you would like to reindex.
- (Optional) Set a start time from which to reindex data.
- Click Reindex.
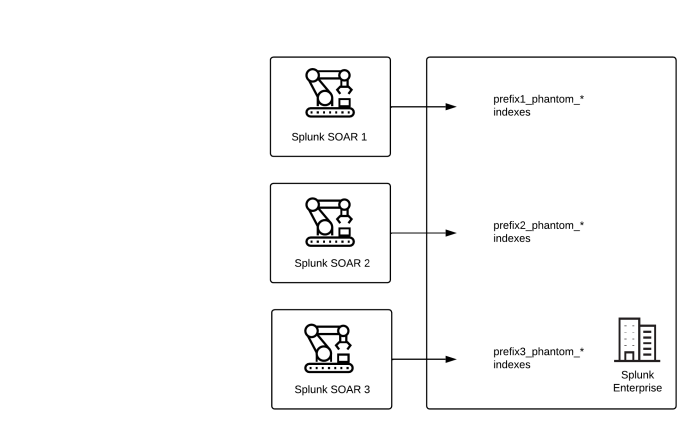
Define a custom index per instance
| This feature is deprecated. |
|---|
| Custom indexes for Splunk SOAR (On-premises) data is deprecated as of release 6.2.0. Existing custom indexes will remain, but no new custom indexes can be created.
Although this feature continues to function, it might be removed in a future version. |
If you have multiple instances in your environment, index prefixes are applied to the indexes in the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise created by the Splunk App for SOAR. For more information on indexes, see Set up remote search on a standalone Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise instance in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual.
Use the custom prefix to create separate indexes for each instance, which provides data separation and the ability to correlate each index with the appropriate instance.
Define a custom prefix with a standalone external Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise deployment
| This feature is deprecated. |
|---|
| Custom indexes for Splunk SOAR (On-premises) data is deprecated as of release 6.2.0. Existing custom indexes will remain, but no new custom indexes can be created.
Although this feature continues to function, it might be removed in a future version. |
Perform the following tasks on each Splunk SOAR instance to create a custom prefix for each instance with a standalone external Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise deployment for search:
- Verify that your instance is connected to the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise by setting up the search settings using a standalone external Splunk instance:
- Follow the instructions in Configure the service with Splunk App for SOAR in Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR.
- Make sure to click Test Connection at the end of the procedure and verify that and the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise are connected.
- Log in to the instance as the root user. In unprivileged environments, run the script as the specific user configured to run .
- On each instance, run the
set_preferencecommand:phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="<prefixstring>" --splunk-admin-username <splunkadminusername>
For example, to set a custom prefix called prefix1 using admin as the admin user for the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise:
phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="prefix1" --splunk-admin-username admin
Use an empty prefix string to remove a custom prefix. For example:
phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="" --splunk-admin-username admin
In Splunk SOAR clusters, the script updates the prefix for all nodes in the cluster.
- Users on the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise inherit index permissions from their roles. After creating the new indexes, you can update roles to give all users in the role access to the new indexes, or create new users and new roles to give access to the new indexes. This example shows how to edit the phantomsearch and phantomdelete roles to grant users access to the new indexes.
- From Splunk Web, select Settings > Roles.
- Click the name of the role you want to edit, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Check the boxes next to the names of the new indexes.
- Click Save.
- Perform this procedure again to grant access to the new indexes for the phantomdelete role.
- If you need additional custom roles to manage only the new indexes this example shows how to create them.
- From Splunk Web, select Settings > Roles.
- Click New Role.
- Type a name for the role.
- On the Inheritance tab, select the existing role you want your new role to inherit from, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Check the boxes next to the names of the new indexes.
- Uncheck the boxes next to the names of the indexes the new role should not be able to access.
- Click Create.
- Click the name of the role you want to edit, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Uncheck the boxes next to the names of the new indexes. This will prevent items managed by the new role from being repeated in indexes by phantomsearch.
- Click Save.
- Perform this procedure again to create a new role with access to the new indexes for the phantomdelete role. Custom roles used for deletions must inherit permissions from the phantomdelete role.
- After the prefix is created, update the Splunk administration for the HEC token to grant access to the new indexes. See Set up the HTTP Event Collector on the standalone Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise instance in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual for instructions.
- Perform this step if you are using a cluster. Run the following commands on each node in your cluster:
pkill --full add_to_searchindex <PHANTOM_HOME>/bin/phsvc restart uwsgi
- Reindex all indexes to search for the data created while using the new prefixes. See Reindex data in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual.
Define a custom prefix with a distributed external Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise deployment
| This feature is deprecated. |
|---|
| Custom indexes for Splunk SOAR (On-premises) data is deprecated as of release 6.2.0. Existing custom indexes will remain, but no new custom indexes can be created.
Although this feature continues to function, it might be removed in a future version. |
Perform the following tasks on each instance to create a custom prefix for each instance with a distributed external Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise deployment for search:
The custom prefix script is not supported for use with distributed deployments that are built in the Splunk Cloud Platform.
- Verify that your instance is connected to the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise by setting up the search settings using a distributed external Splunk instance:
- Follow the instructions in Set up remote search on a distributed Splunk Cloud Platform or Enterprise instance in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual.. The Splunk App for SOAR must be installed on all search heads in the cluster.
- Make sure to click Test Connection at the end of the procedure and verify that and the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise are connected.
- Log in to the instance as the root user. In unprivileged environments, run the script as the specific user configured to run .
- On each instance, run the
set_preferencecommand:phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="<prefixstring>" --splunk-admin-username <splunkadminusername>
For example, to set a custom prefix called prefix1 using admin as the admin user for the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise:
phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="prefix1" --splunk-admin-username admin
Use an empty prefix string to remove a custom prefix. For example:
phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix="" --splunk-admin-username admin
In Splunk SOAR clusters, the script updates the prefix for all nodes in the cluster.
Below is sample output from the command run in a unprivileged cluster with a distributed Splunk Enterprise deployment:
[phanru@phantom ~]$ phenv python -m manage set_preference --splunk-index-prefix prefix1 --splunk-admin-username admin Are you sure you wish to apply search index prefix prefix1 for this Phantom instance [yes/no]? yes Proceeding ... index configuration stored: /home/phanru/phantomcyber/tmp/indexes.conf Done! Next steps: - indexes.conf must be updated via splunk cluster manager node. - On Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise, edit permissions to allow the current or new HEC token to access new indexes. - On Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise, edit permissions to allow the current or new search/delete users to access new indexes. - If new HEC token or users are created, update the Phantom search settings. Run `pkill --full add_to_searchindex` on each Phantom cluster node Run `/home/phanru/phantomcyber/bin/phsvc restart uwsgi` on each Phantom cluster node - Rerun Test Connection. - All phantom search indexes must now be re-indexed.
Note the location of the newindexes.conffile created by the script. You will need this information in the next step. - Edit and save the contents of the new
indexes.conffile that was created by thephenv set_preference --splunk-index-prefixcommand. In our example, we can usecatto view and copy the contents of the<PHANTOM_HOME>/tmp/indexes.conffile. - In the manager node of the Splunk indexer cluster, append the contents of the new
indexes.conffile to the localindexes.conffile on the manager node, such as/opt/splunk/etc/manager-apps/_cluster/local/indexes.conf.As of Splunk Enterprise version 9.0, "master-apps" has been updated to "manager-apps".
- Run the following commands to push the new
indexes.confto the other indexers in the cluster and verify:/opt/splunk/bin/splunk apply cluster-bundle --answer-yes /opt/splunk/bin/splunk show cluster-bundle-status
- Users on the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise inherit index permissions from their roles. After creating the new indexes, you can update roles to give all users in the role access to the new indexes, or create new users and new roles to give access to the new indexes. This example shows how to edit the phantomsearch and phantomdelete roles to grant users access to the new indexes.
- From Splunk Web, select Settings > Roles.
- Click the name of the role you want to edit, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Check the boxes next to the names of the new indexes.
- Click Save.
- Perform this procedure again to grant access to the new indexes for the phantomdelete role.
- If you need additional custom roles to manage only the new indexes this example shows how to create them.
- From Splunk Web, select Settings > Roles.
- Click New Role.
- Type a name for the role.
- On the Inheritance tab, select the existing role you want your new role to inherit from, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Check the boxes next to the names of the new indexes.
- Uncheck the boxes next to the names of the indexes the new role should not be able to access.
- Click Create.
- Click the name of the role you want to edit, such as phantomsearch.
- Click the Indexes tab.
- Uncheck the boxes next to the names of the new indexes. This will prevent items managed by the new role from being repeated in indexes by phantomsearch.
- Click Save.
- Perform this procedure again to create a new role with access to the new indexes for the phantomdelete role. Custom roles used for deletions must inherit permissions from the phantomdelete role.
- After the prefix is created, update the Splunk administration for the HEC token to grant access to the new indexes. See Set up the HTTP Event Collector on the distributed Splunk Cloud Platform or Enterprise instance in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual for instructions.
- Perform this step if you are using a cluster. Run the following commands on each node in your cluster:
pkill --full add_to_searchindex <PHANTOM_HOME>/bin/phsvc restart uwsgi
- Reindex all indexes to search for the data created while using the new prefixes. See Reindex data in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual.
Use a custom prefix when you want to change your Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise instance
| This feature is deprecated. |
|---|
| Custom indexes for Splunk SOAR (On-premises) data is deprecated as of release 6.2.0. Existing custom indexes will remain, but no new custom indexes can be created.
Although this feature continues to function, it might be removed in a future version. |
If you have a situation where you want to use the same custom prefix on your instance with a different or new Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise instance, perform the following tasks:
- Follow the instructions in either Set up remote search on a standalone Splunk Cloud Platform or Enterprise instance or Set up remote search on a distributed Splunk Cloud Platform or Enterprise instance in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual to connect your instance with the Splunk Cloud Platform or Splunk Enterprise.
- Run the
set_preferencecommand to create the new prefix. - Update the Splunk administration for the HEC token to grant access to the new indexes.
- Reindex all indexes to search for the data created while using the new prefixes.
See Also
For more information about getting data into Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform see these additional resources.
- What data can I index? in the Splunk Enterprise Getting Data In manual.
- Use forwarders to get data into Splunk Cloud Platform in the Splunk Enterprise Getting Data In manual.
- Use forwarders to get data into Splunk Enterprise in the Splunk Enterprise Getting Data In manual.
- Set up the universal forwarder using Splunk SOAR version 6.2.0 and later in the Install and Configure Splunk App for SOAR manual.
- How to prepare TLS certificates for use with the Splunk platform in the Securing Splunk Enterprise manual.
| Configure search in | Configure Google Maps for visual geolocation data |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® SOAR (On-premises): 6.2.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!