About the Search app
The Search & Reporting app, referred to as the Search app, is the application that you use to search and create reports on your data.
This topic describes the views and elements that comprise the Search app.
Open the Search app
1. From Splunk Home, click Search & Reporting in the Apps panel. This opens the Search Summary view in the Search & Reporting app.
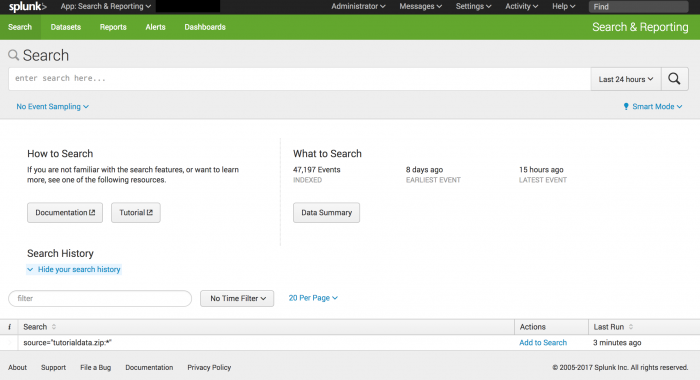
The Search summary view
Before you run a search, the Search summary view displays the following elements: App bar, Search bar, Time range picker, How to Search panel, What to Search panel, and the Search History.
The elements that are specific to the Search summary view are the How to Search and What to Search panels, and the Search History. These elements are described in the following table. The other elements are described in the The New Search view section later in this topic.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| How to Search | Links you to the Search Tutorial and Search Manual to learn about how to write searches. |
| What to Search | Displays a summary of the data that is installed on this Splunk instance and that you are authorized to view. Click Data Summary to open the Data Summary dialog box to see the hosts, sources, and source types in your data. |
| Search History | Lets you view and interact with your history of searches. The search history presents an expandable table of your past searches, which you can search and filter with keywords or time. The search history appears after you run your first search. For more information, see Search History. |
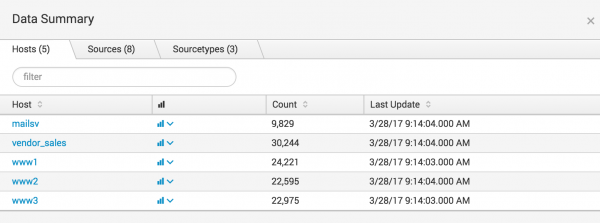
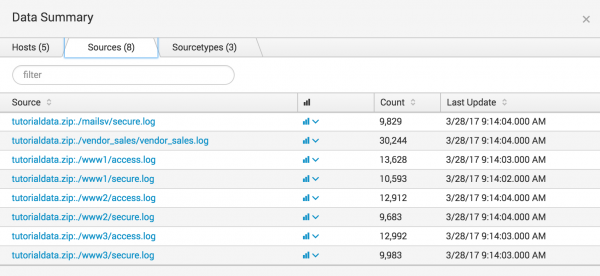
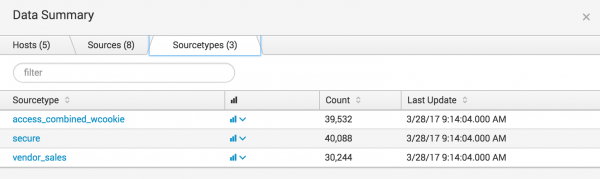
Data summary
The Data Summary dialog box shows three tabs: Hosts, Sources, Sourcetypes. These tabs represent searchable fields in your data.
Host
The host of an event is the host name, IP address, or fully qualified domain name of the network machine from which the event originated. In a distributed environment, you can use the host field to search data from specific machines.
Source
The source of an event is the file or directory path, network port, or script from which the event originated.
Source type
The source type of an event tells you what kind of data it is, usually based on how it is formatted. This classification lets you search for the same type of data across multiple sources and hosts.
In this example, source types are:
- access_combined_wcookie: Apache web server logs
- secure: Secure server logs
- vendor_sales: Global sales vendors
For information about which source type is assigned to your data, see "Why source types matter" in the Getting Data In manual.
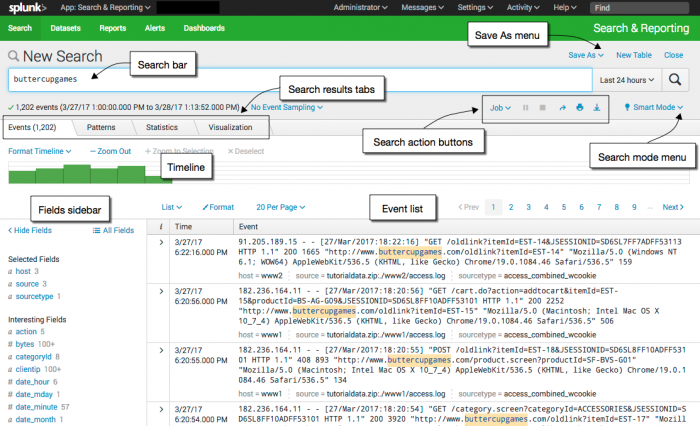
The New Search view
The New Search view opens after you run a search or when you click the Search tab to start a new search. The App bar, Search bar, and Time range picker are still available in this view. Additionally, this view contains many more elements: search action buttons and search mode selector; counts of events; job status bar; and tabs for Events, Patterns, Statistics, and Visualizations.
You can type index=_internal in the Search bar and press Enter to look at the events from the internal log files on your Splunk instance.
If you followed the steps
to get data into your Splunk deployment in the Search Tutorial, you can type buttercupgames in the Search bar and press Enter to search for the "buttercupgames" keyword in your events.
In this view, the App bar, Search bar and Time range picker are also available. The New Search view contains many more elements such as search action buttons, a search mode selector, counts of events, a job status bar, and results tabs for Events, Patterns, Statistics, and Visualizations.
App bar
Use the App bar to navigate between the different views in the Search & Reporting app: Search, Pivot, Reports, Alerts, and Dashboards. There are entire manuals devoted to these other capabilities.
Search bar
Use the search bar to specify your search criteria in Splunk Web. Type your search string and press Enter, or click the Search icon which is on the right side of the search bar.
Time range picker
Time is the single most important search parameter that you specify.
Use the time range picker to retrieve events over a specific time period. For real-time searches you can specify a window over which to retrieve events. For historical searches, you can restrict your search by specifying a relative time range such as 15 minutes ago, Yesterday, and so on. You can also restrict your searches using a specific date and time range. The time range picker has many preset time ranges that you can select from, but you can also type a custom time range.
For more information, see "About searching with time."
Timeline
The timeline is a visual representation of the number of events that occur at each point in time in your results. Peaks or valleys in the timeline can indicate spikes in activity or server downtime. The timeline options are located above the timeline. You can zoom in, zoom out, and change the scale of the chart.
When you click a point on the timeline or use on of the timeline options, the display of the timeline changes based on the events returned from your search. A new search is not run.
Search actions
There are a wide range of search actions you can perform, including working with your search Jobs, saving, sharing, exporting, and printing your search results.
For more information, see:
Search mode
You can use the search mode selector to provide a search experience that fits your needs. The modes are Smart (default), Fast, and Verbose.
For more information, see "Search modes".
Fields sidebar
To the left of the events list is the Fields sidebar. As events are retrieved that match your search, the Fields sidebar shows the Selected Fields and Interesting Fields in the events. These are the fields that the Splunk software extracts from your data.
When you first run a search the Selected Fields list contains the default fields host, source, and sourcetype. The default fields appear in every event.
Interesting Fields are fields that appear in at least 20% of the events.
Next to the field name is a count of how many distinct values there are in that field. Click on any field name to show more information about that field.
| Search with Splunk Web, CLI, or REST API | Anatomy of a search |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.0.0, 7.0.1, 7.0.2, 7.0.3, 7.0.4, 7.0.5, 7.0.6, 7.0.7, 7.0.8, 7.0.9, 7.0.10, 7.0.11, 7.0.13
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!