Assign searches to workload pools
Before you can assign searches to workload pools, you must configure and enable workload management. See Configure workload management.
Workload management lets you allocate system resources to individual search processes. To allocate resources to a search, you must assign the search to a workload pool. How you assign a search to a workload pool depends on whether the search is a scheduled search or an ad-hoc search.
Assign a scheduled search to a workload pool
You can assign a scheduled search to a workload pool using Splunk Web, CLI, or REST.
When you assign a scheduled search to a workload pool, the pool information is written to savedsearches.conf. For more information, see savedsearches.conf.spec.
Assign a scheduled search using Splunk Web
To assign a scheduled search to a workload pool using Splunk Web, follow these steps:
- Click on Settings > Searches, Reports, and Alerts.
- Find the specific saved search, and click Edit > Advanced Edit.
- In the Workload Pool field, enter the name of the pool.
- Click Save.
The workload pool information is written tolocal/savedsearches.confand the scheduled search runs in the specified pool.
Assign a scheduled search using the CLI
To assign a scheduled search to a workload pool, run the following CLI command:
./splunk add saved-search -name <search_name> -workload_pool <pool_name>
Assign a scheduled search using REST
Send a POST request to the saved/searches/{name} endpoint. For example:
curl -k -u admin:pass https://localhost:8089/services/searches/<search_name> -d workload_pool=<pool_name>
Assign an ad-hoc search to a workload pool
You can assign an ad-hoc search to a workload pool using Splunk Web, CLI, or REST.
To assign an ad-hoc search to a workload pool, a role must have both the list_workload_pools and select_workload_pools capabilities. See Set access controls for workload management.
Assign an ad-hoc search using Splunk Web
- In the Search bar, enter your ad-hoc search string.
- Select a workload pool from the menu.
- Run the search.
The ad-hoc search job runs in the specified workload pool.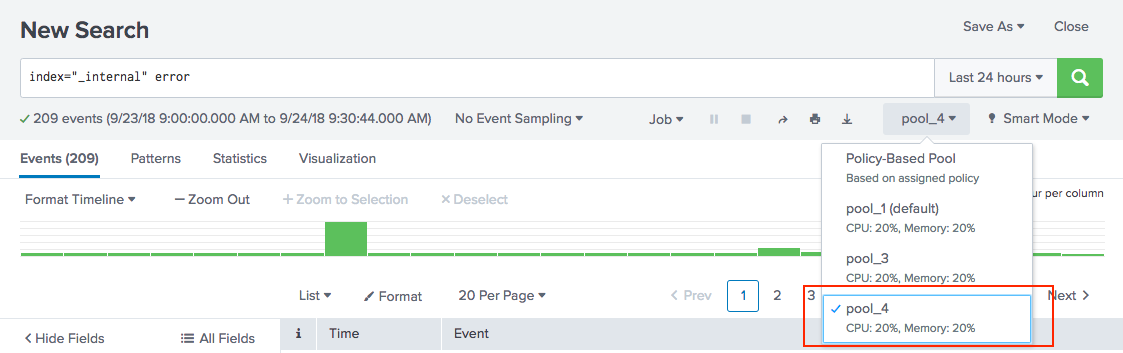
If you select Policy-Based Pool, workload management automatically assigns the search to a pool based on the ad-hoc search's context, such as app or role. If an explicit match for the search is not found, workload management assigns the search to the default pool.
The workload pool menu is only visible to roles that have
list_workload_poolsandselect_workload_poolscapabilities. - Click Job > Inspect Job > Search job properties.
- Confirm that the ad-hoc search ran in the specified pool. For example:
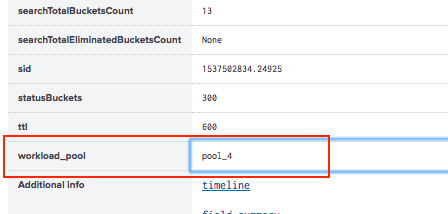
Assign an ad-hoc search using CLI
To assign an ad-hoc search, run the following CLI command:
./splunk search "index=_internal" -workload_pool=<pool_name>
Assign an ad-hoc search using REST
Send a POST request to the search/jobs endpoint. For example:
curl -k -u admin:pass https://localhost:8089/services/search/jobs -d search="search index=_internal" -d workload_pool=pool_1
Change the workload pool for a running search
You can re-assign an actively running search to a different workload pool using Splunk Web or REST. This applies to both scheduled searches and ad-hoc searches.
To change the workload pool for a running search, a role must have the list_workload_pools and select_workload_pools capabilities. See Set access controls for workload management.
Change workload pool using Splunk Web
- Click Activity > Jobs.
- For the specific running search, click Job > Edit Job Settings.
- Select a new pool from the Workload Pool menu.
Re-assigning an ad-hoc search on the Search bar triggers a new search process in the new pool. To continue running the same search process in a new pool, re-assign the search via the Job Activity page or REST endpoint.
Change workload pool using REST
Send a POST request to the search/jobs/{search_id}/control endpoint. For example:
curl -k -u admin:pass https://localhost:8089/services/search/jobs/{search_id}/control -d action=setworkloadpool -d workload_pool=<pool_name>
Search concurrency considerations in workload management
It's important that you consider concurrency-related constraints when you assign searches to workload pools.
Search concurrency limits in workload management
Splunk Enterprise enforces concurrent search limits globally. As a result, in the context of resource reservation in workload management, searches are not entirely isolated, and increasing search load in one workload pool can limit the number of searches you can run in other pools.
The following concurrent search quotas can impact search performance in workload management:
- Scheduler concurrency limits
- This limit determines the maximum number of searches that the scheduler can run concurrently. For detailed information, see How the scheduler determines concurrent search limits.
- User/role search quotas
- This quota determines the maximum number of historical searches allowable for a specific user/role. These quotas are configured with
srchJobsQuotaand related settings inauthorize.conf. See Authorize.conf.
To minimize search performance issues due to concurrent search limits, make sure adequate search quota is available.
For detailed information on how concurrent search quotas work in a search head cluster environment, see How the cluster handles concurrent search quotas.
Search priority in workload management
Search priority in workload management is determined by two main factors:
- Search scheduler priority
- When the total number of searches reaches the maximum concurrent search limit, the search scheduler runs additional searches in priority order as search quota becomes available. To ensure that important searches are not skipped, you can set a scheduled search to high-priority in the search scheduler. For more information, see Configure the priority of scheduled reports.
- Workload rules order
- Workload rules control access to resources in workload pools based on app or role. The order of a rule determines which apps or roles, and therefore which searches, have priority access to a workload pool. For more information, see Create workload rules.
To avoid skipped searches and other search concurrency issues due to search priority, make sure to assign high-priority searches to workload pools that provide sufficient resources.
| Set access controls for workload managment | Monitor workload management |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!