Configure Linux systemd for workload management
Before you can configure workload management on Linux distributions running systemd, you must configure systemd to manage splunkd as a service by creating a unit file that defines a cgroup hierarchy.
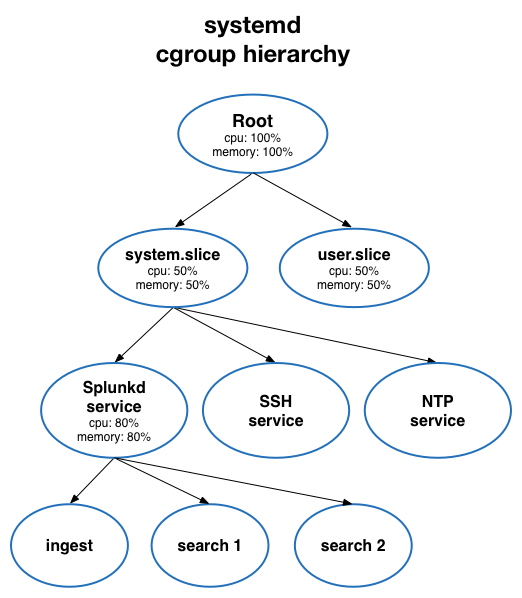
The following diagram illustrates the cgroup hierarchy under systemd:
For more information, see cgroups.
You must configure cpu and memory cgroups for workload management on all search heads and indexers.
Configure systemd to manage splunkd as a service
There are two ways to configure systemd to manage splunkd as a service:
Configuring systemd using enable boot-start requires Splunk Enterprise version 7.2.2 or later.
Permissions requirements for systemd
systemd has the following permissions requirements:
- Non-root users must have super user permissions to manually configure
systemdon Linux. - Non-root users must have super user permissions to run
start,stop,restartcommands undersystemd.
For instructions on how to create a new user with super user permissions, see your Linux documentation. The specific steps can vary depending on the Linux distribution.
You must use sudo to run systemctl start|stop|restart. If you do not use sudo, you must authenticate. For example:
==== AUTHENTICATING FOR org.freedesktop.systemd1.manage-units === Authentication is required to manage system services or units. Multiple identities can be used for authentication: 1. <username_1> 2. <username_2> Choose identity to authenticate as (1-2): 2 Password: ==== AUTHENTICATION COMPLETE ===
Configure systemd manually
Follow these steps to configure systemd to manage splunkd as a service:
-
Confirm that your Linux machine is running
systemd. See Is Linux running systemd? -
Before you create, delete, or modify the
systemdunit file, you must stopsplunkd:$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk stop
-
If you enabled Splunk software to start at boot using
enable boot-start, rundisable boot-startto remove both thesplunkinitscript from/etc/init.dand its symbolic links.sudo $SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk disable boot-start
-
Open the
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/splunk-launch.conffile and note the value ofSPLUNK_SERVER_NAME. The default value isSplunkd. -
In the
/etc/systemd/systemdirectory, create a unit file named<SPLUNK_SERVER_NAME>.service, such asSplunkd.service.You can change the
SPLUNK_SERVER_NAMEto any name you choose by directly editing thesplunk-launch.conffile. -
Add the following content to the
<SPLUNK_SERVER_NAME>.serviceunit file:[Unit] After=network.target [Service] Type=simple Restart=always ExecStart=/home/<username>/splunk/bin/splunk _internal_launch_under_systemd LimitNOFILE=65536 SuccessExitStatus=51 52 RestartPreventExitStatus=51 RestartForceExitStatus=52 KillMode=mixed KillSignal=SIGINT TimeoutStopSec=10min User=<username> Delegate=true MemoryLimit=<value> CPUShares=1024 PermissionsStartOnly=true ExecStartPost=/bin/bash -c "chown -R <username>:<username> /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/%n" ExecStartPost=/bin/bash -c "chown -R <username>:<username> /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/%n" [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Regarding these lines in the unit file:
ExecStartPost=/bin/bash -c "chown -R <username>:<username> /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/%n" ExecStartPost=/bin/bash -c "chown -R <username>:<username> /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/%n"
if a group does not exist on they system with the name <username>, the
splunkdservice will not start. To workaround this issue, manually update the unit file with the correct group name.The
MemoryLimitvalue should be set to the total system memory available in bytes. TheMemoryLimitvalue will not update if the total available system memory changes. To update theMemoryLimitvalue in the unit file, manually edit the unit file value and run thesystemctl daemon-reloadcommand to reload systemd.The following unit file properties are set specifically for Splunk workload management:
Type=simple
Restart=always
Delegate=true
Do not change these values unless you are familiar withsystemdor receive guidance from Splunk support.Do not use the following unit file properties. These properties can cause
splunkdto fail on restart.
RemainAfterExit=yes
ExecStopFor more information, see Systemd unit file properties.
-
Reload the unit file.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
-
Start
splunkdas asystemdservice.sudo systemctl start Splunkd.service
-
Verify that
splunkdis running as asystemdservice:sudo systemctl status <SPLUNK_SERVER_NAME>.service
When you create the
splunkdservice,systemdcreates corresponding CPU and Memory cgroups in these locations:CPU: /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/system.slice/<SPLUNK_SERVER_NAME>.service Memory: /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/<SPLUNK_SERVER_NAME>.service
- For distributed deployments, repeat steps 1-9 on all search heads and indexers.
systemd unit file properties
The following table lists the unit file properties you must specify to run splunkd as a service under systemd:
| Property | Expected Value |
|---|---|
| Restart | always |
| Type | simple |
| ExecStart | $SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk _internal_launch_under_systemd
|
| ExecStartPost | chown -R <USER>:<GROUP of USER>/sys/fs/cgroup/<cpu or memory>/system.slice/%n"
|
| Delegate | True |
| SuccessExitStatus | 51 52 |
| RestartPreventExitStatus | 51 |
| RestartForceExitStatus | 52 |
| RemainAfterExit | no (default) |
| MemoryLimit | Example: 12G |
| CPUShares | Example: 8192. (Allowed range is 2 to 262144. Default is 1024.) |
| User, Group | <Splunk Owner> <Splunk Group> |
For more information on systemd unit file properties, see Service unit configuration.
Manage clusters under systemd
When managing an indexer cluster under systemd:
You must use the sudo command to start, stop, and restart the cluster master or individual peer nodes using systemctl start|stop|restart commands. You do not need sudo to perform a rolling restart using the splunk rolling-restart cluster-peers command, or to take a peer offline using the splunk offline command.
When managing a search head cluster under systemd:
You must use the sudo command to start, stop, and restart cluster members using systemctl start|stop|restart commands. You do not need sudo to perform a rolling restart using the splunk rolling-restart shcluster-members command, or to remove a cluster member using the splunk remove shcluster-members command.
Next step
After you set up cgroups on your Linux operating system, you can configure workload management in Splunk Enterprise. See Configure workload management.
| Set up Linux for workload management | Configure Linux systems not running systemd |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!