msearch
Description
Returns a list of the individual metric data points in a specified metric index that match a provided filter. msearch returns metric data points in JSON format by default. The msearch command is designed to be used as a tool for the onboarding and troubleshooting of metrics data and the exploration of metrics indexes.
Do not use msearch for large-scaled searches of metrics data. Such searches will be very slow to complete. Use mstats for large metrics searches instead.
The msearch command cannot search data that was indexed prior to your upgrade to the 8.0.x version of the Splunk platform.
You can use the msearch command only if your role has the run_msearch capability. See Define roles on the Splunk platform with capabilities in Securing Splunk Enterprise.
Syntax
msearch [filter=<string>] [<index-opt>]... [splunk_server=<wc-string>] [splunk_server_group=<wc-string>]... [earliest=<time-specifier>] [latest=<time-specifier>]
Required arguments
None. By default all types of terms are returned.
Optional arguments
- chunk_size
- Syntax: chunk_size=<unsigned-integer>
- Description: Advanced option. This argument controls how many metric time series are retrieved at a time from a single time-series index file (
.tsidxfile) when the Splunk software processes searches. Lower this setting from its default only when you find a particularmsearchsearch is using too much memory, or when it infrequently returns events. This can happen when a search groups by excessively high-cardinality dimensions (dimensions with very large amounts of distinct values). In such situations, a lowerchunk_sizevalue can makemsearchsearches more responsive, but potentially slower to complete. A higherchunk_size, on the other hand, can help long-running searches to complete faster, with the potential tradeoff of causing the search to be less responsive. Formsearch,chunk_sizecannot be set lower than 10.
- For more information about this setting, see Use chunk_size to regulate msearch performance.
- Default: 1000
The default value for the the
chunk_sizeargument is set by thechunk_sizesetting for the[msearch]stanza inlimits.conf.
- earliest
- Syntax: earliest=<time-specifier>
- Description: Specify the earliest
_timefor the time range of your search. You can specify an exact time (earliest="11/5/2016:20:00:00") or a relative time (earliest=-horearliest=@w0).
- filter
- Syntax: filter= "<string>"
- Description: An arbitrary boolean expression over the dimension or
metric_name.
- index-opt
- Syntax: index=<index-name> (index=<index-name>)...
- Description: Limits the search to results from one or more indexes. You can use wildcard characters (*). To match non-internal indexes, use
index=*. To match internal indexes, useindex=_*.
- latest
- Syntax: latest=<time-specifier>
- Description: Specify the latest time for the
_timerange of your search. You can specify an exact time (latest="11/12/2016:20:00:00") or a relative time (latest=-30morlatest=@w6).
- splunk_server
- Syntax: splunk_server=<wc-string>
- Description: Specifies the distributed search peer from which to return results. If you are using Splunk Enterprise, you can specify only one
splunk_serverargument. However, you can use a wildcard when you specify the server name to indicate multiple servers. For example, you can specifysplunk_server=peer01orsplunk_server=peer*. Uselocalto refer to the search head.
- splunk_server_group
- Syntax: splunk_server_group=<wc-string>
- Description: Limits the results to one or more server groups. If you are using Splunk Cloud, omit this parameter. You can specify a wildcard character in the string to indicate multiple server groups.
Usage
This search command generates a list of individual metric data points from a specified metric index that match a provided filter. The filter can be any arbitrary boolean expression over the dimensions or the metric_name. Specify earliest and latest to override the time range picker settings.
The msearch command is designed to display individual metric data points in JSON format. If you want to aggregate metric data points, use the mstats command.
All metrics search commands are case sensitive. This means, for example, that msearch treats as the following as three distinct values of metric_name: cap.gear, CAP.GEAR, and Cap.Gear.
Use chunk_size to regulate msearch performance
If you find that msearch is slow or unresponsive, use chunk_size to regulate its behavior. Reduce the chunk_size to make the search more responsive with the potential tradeoff of making the search slower to complete. Raise the chunk_size to help the msearch search to complete faster, with the potential tradeoff of making it less responsive.
Examples
1. Return data points that match a specific filter
This search returns individual data points from the _metrics index that match a specific filter.
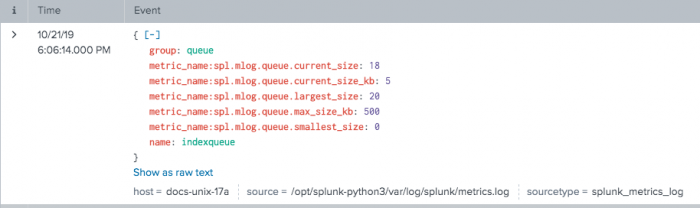
| msearch index=_metrics filter="group=queue name=indexqueue metric_name=*.current_size"
Here is an example of a JSON-formatted result of the above search.
2. Return individual data points from the metrics index
| msearch index=_metrics
3. Lower chunk_size to improve msearch performance
The following search lowers chunk_size so that it returns 100 metric time series worth of metric data points in batches from tsidx files that belong to the _metrics index. Ordinarily it would return 1000 metric time series in batches.
| msearch index=_metrics chunk_size=100
See also
| meventcollect | mstats |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!