Chart overview
Select a chart type to show one or more data dimensions in a results set. Learn how charts visualize data series.
For a quick glance at common charts and common chart use case commands, you can view the Splunk Dashboards Quick Reference guide by clicking the link in Getting started.
Select a chart
You can select a chart depending on the number of data dimensions that you want to visualize. For example, use a pie chart to show how values combine in a single field. A bubble chart can show relationships between multiple fields in a data set.
| Chart type | Description |
|---|---|
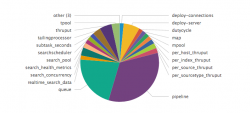
| Pie | Shows a single dimension. Pie slice size represents the density or frequency of values in a field. |
| Column and bar
|
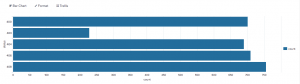
Represent one or more dimensions in a results set. These charts plot data on two axes. Each axis represents a results field. Column and bar charts can compare values and fields. |
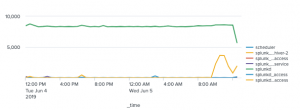
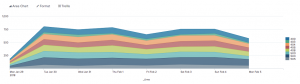
| Line and area | Line charts can show value changes over time. Area charts show changes in an aggregated value over time. |
| Scatter and bubble | Represent multiple dimensions in a results set. These charts plot data on two axes. Data point appearance, size, and/or distribution show additional patterns or relationships. |
Get started
The following topics show you how to build and configure charts.
| Table column Simple XML | Data for charts |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.1.0, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.1.5, 7.1.6, 7.1.7, 7.1.8, 7.1.9, 7.1.10, 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10, 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9, 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.2, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.1.5, 8.1.6, 8.1.7, 8.1.8, 8.1.9, 8.1.10, 8.1.11, 8.1.12, 8.1.13, 8.1.14, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.2.4, 8.2.5, 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.1.9, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.2.6, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.3.4, 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2



 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!