About proactive Splunk component monitoring
Proactive component monitoring lets you view the health of Splunk Enterprise features from the output of a REST API endpoint. Individual features report their health status through a tree structure that provides a continuous, real-time view of the health of your deployment, without affecting your search load.
You can view feature health status information in the splunkd health report in Splunk Web. See View the splunkd health report.
You can also access feature health information programmatically from the server/health/splunkd endpoint. See Query the server/health/splunkd endpoint.
For detailed information on the splunkd process, see Splunk Enterprise Processes in the Installation Manual.
How the splunkd health report works
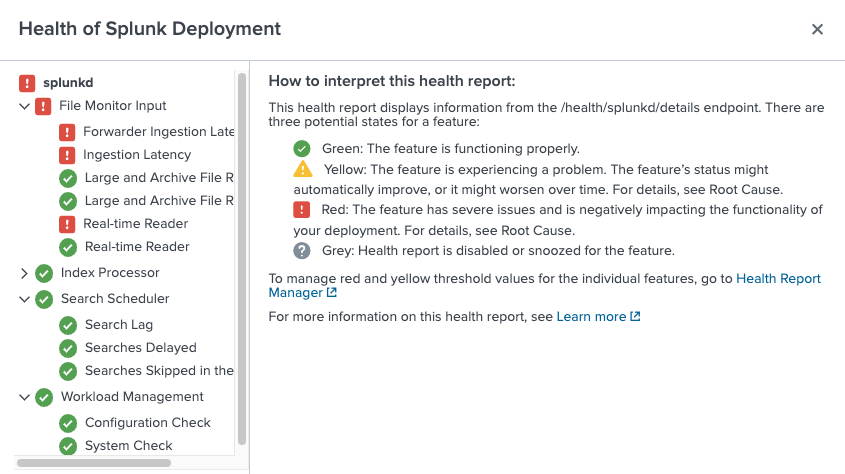
The Splunk Enterprise health report records the health status of splunkd in a tree structure, where leaf nodes represent particular Splunk Enterprise features, and intermediary nodes categorize the various features. Feature health status is color-coded in four states:
- Green: The feature is functioning properly.
- Yellow: The feature is experiencing a problem.
- Red: The feature has a severe issue and is negatively impacting the functionality of your deployment.
- Grey: Health report is disabled or snoozed for the feature.
The health status tree structure
The splunkd health status tree has the following nodes:
| Health status tree node | Description |
|---|---|
| splunkd | The top level node of the status tree shows the overall health status (color) of the splunkd process. The current status of splunkd indicates the state of the least healthy feature in the tree. The REST endpoint retrieves the instance health from the splunkd node.
|
| Feature categories | Feature categories represent the second level in the health status tree. Feature categories are logical groupings of features. For example, "BatchReader" and "TailReader" are features that form a logical grouping with the name "File Monitor Input". Feature categories act as buckets for groups and reflect the health status of the least healthy feature within the category. For example, if the health status of the "Search Lag" features is red, then the "Search Scheduler" category displays red. |
| Features | The next level in the status tree is feature nodes. Each node contains information on the health status of a particular feature. Each feature contains one or more indicators that determine the status of the feature. The overall health status of a feature is based on the least healthy color of any of its indicators. |
| Indicators | Indicators are the fundamental elements of the splunkd health report. These are the lowest levels of functionality that are tracked by each feature, and change colors as functionality changes. Indicator values are measured against red or yellow threshold values to determine the status of the feature. See What determines the status of a feature?
|
For a list of supported Splunk Enterprise features, see Supported features.
What determines the status of a feature?
The current status of a feature in the status tree depends on the value of its associated indicators. Indicators have configurable thresholds for yellow and red. When an indicator's value meets threshold conditions, the feature's status changes.
For information on how to configure indicator thresholds, see Set feature indicator thresholds.
For information on how to troubleshoot the root cause of feature status changes, see Investigate feature health status changes.
Default health status alerts
By default, each feature in the splunkd health report generates an alert when a status change occurs, for example from green to yellow, or yellow to red. You can enable/disable alerts for any feature and set up alert notifications via email, mobile, VictorOps, or PagerDuty in health.conf or via REST endpoint. For more information, see Configure health report alerts.
If you are monitoring a distributed deployment using the distributed health report, you can set up alert actions directly on the distributed health report's central instance. For more information, see Set up distributed health report alert actions.
View the splunkd health report
The splunkd health report in Splunk Web provides two options for viewing the health status of your deployment: a local health report view and a distributed health report view.
Local health report view
The local health report view shows the health status of your deployment from the viewpoint of the local instance on which you are monitoring. The features visible in the local health report depend on the type of component and your deployment architecture.
For example, when monitoring an indexer cluster environment, the cluster manager and peer nodes each show a different set of features contributing to the overall health of splunkd. The local health report is the default view.
Distributed health report view
The distributed health report view shows the health status of features across a distributed deployment. The distributed health report aggregates health status information from connected instances on a single central instance.
In Splunk Enterprise, search heads, search head cluster members, and cluster managers act as central instances. The distributed health report option appears only on central instances in the context of a distributed deployment.
The distributed health report is enabled by default on all search heads, search head cluster members, and cluster managers. You can disable the distributed health report on a particular instance to stop all features on that instance from reporting health status information to the splunkd health status tree. For more information, see Disable the distributed health report.
You can also disable individual features in either the local health report or distributed health report to prevent that feature from reporting health status information to the splunkd health status tree. For more information, see Disable a health report feature.
View distributed health report using REST API
You can view the health status of your distributed deployment using the Splunk REST API.
To view the overall health status of your distributed deployment, send an HTTP GET request to:
server/health/deployment
For endpoint details, see server/health/deployment in the REST API reference.
To view the health status of individual features reporting to the distributed health report (for example, indexers), send an HTTP GET request to:
server/health/deployment/details
For endpoint details, see server/health/deployment/details in the REST API reference.
| Forwarders | Requirements |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.4.0, 9.4.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!