Splunk Stream on-premise deployment architecture
To deploy Splunk Stream you install three Stream components on your Splunk software.
| Product name | Installation package name | Installed file name |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk App for Stream | splunk_app_stream
|
splunk_app_stream/
|
| Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders | Splunk_TA_stream
|
Splunk_TA_stream/
|
| Splunk Add-on for Stream Wire Data | Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data
|
Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data/
|
Splunk Stream also provides Independent Stream Forwarders (ISF). ISF installation is packaged as a binary file <streamfwd> in the Splunk App for Stream package.
For more about Splunk Stream components, see Splunk Stream installation package overview in this manual.
Splunk Stream supports most deployment architectures:
- Managed Splunk Cloud deployments
- Distributed deployment configurations, including deployment servers and indexer clusters
- Single instance deployments, where a single instance of Splunk Enterprise is both the indexer and the search head
- Independent Stream Forwarders (ISF) on compatible Linux machines
Single instance deployment
When you install Splunk Stream on a single Splunk Enterprise instance, that instance serves as both search head and indexer and provides both search and storage capability. A single instance deployment can support one or two users running concurrent searches, which is ideal for a small test environment. For single instance installation instructions, see Install Splunk Stream on a single instance in this manual.
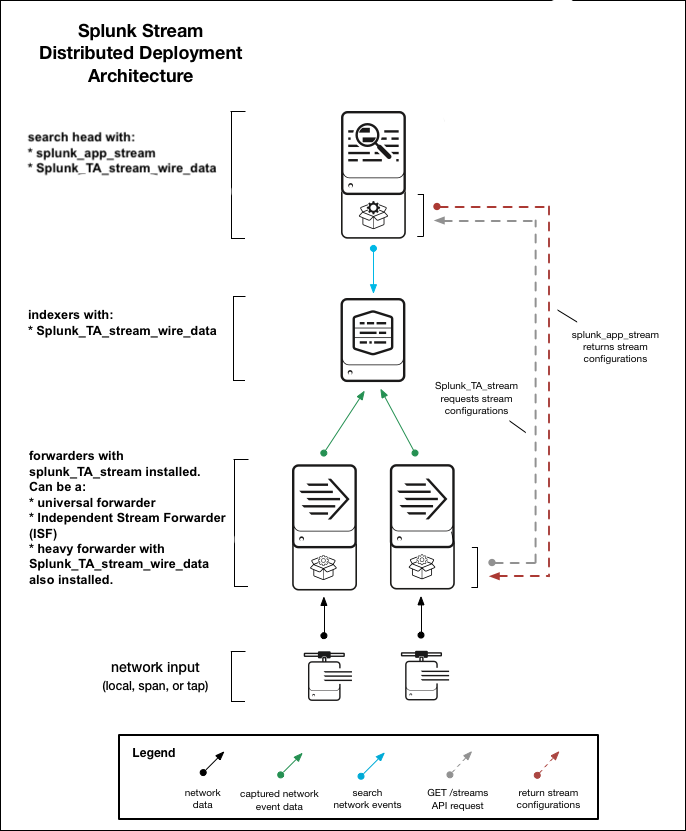
Distributed Splunk Stream deployment
A Splunk Stream distributed deployment can capture network event data from multiple network devices, including NICs, switches, and routers. A distributed deployment can be used in medium and large enterprise network infrastructures. For distributed installation instructions, see Install Splunk Stream in a distributed environment in this manual.
A distributed deployment for Splunk Stream includes the following deployment locations and Splunk Stream components:
| Splunk deployment location | Splunk Stream component |
|---|---|
| search heads | The Splunk App for Stream (splunk_app_stream) and Splunk Add-on for Stream Wire data (Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data) must be installed on search heads.
You can optionally install Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders ( |
| indexers | Splunk Add-on for Stream Wire Data (Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data) must be installed on all indexers for searching and parsing. Splunk Add-on for Stream Wire Data contains both search and index time knowledge objects.
|
| universal forwarders | The Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders (Splunk_TA_stream) must be installed on universal forwarders where you want to capture network data. For dedicated wire capture in Linux environments without a universal forwarder, use the Independent Stream Forwarder (ISF). For more information, see Network collection architectures in this manual
|
| heavy forwarder | If you use a heavy forwarder in your Splunk Stream configuration, the Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders (Splunk_TA_stream) must be installed on universal or heavy forwarders where you want to capture network data. You must also install the Add-on for Stream Wire Data (Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data) on your heavy forwarder wherever that index performs pipeline processing.
|
| deployment server | Use the Splunk deployment server to distribute The Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders package (Splunk_TA_stream) to universal forwarders across a distributed deployment. When you upgrade to a new version of Splunk Stream, the deployment server detects whether a new version of The Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders exists. If a new version is found, all universal forwarders subscribed as deployment clients pull and install the new version of the add-on. For more information, see
|
| Independent Stream Forwarder (ISF) | The ISF is a standalone Stream forwarder. The ISF sends captured network data to Splunk using the HTTP event collector, and does not require a Splunk universal forwarder to collect wire data. It is helpful in networks and deployments where a universal forwarder cannot be installed. See Install an Independent Stream Forwarder |
How a distributed Splunk Stream deployment works
In a typical distributed deployment, the Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders is installed on universal forwarders as Splunk_TA_Stream. Once installed, the forwarder captures network event data on local NICs, such as each node of a subnet environment, or from a network SPAN or TAP. For more information about data collection, see Network collection architectures in this manual.
The network data that a Stream forwarder captures depends on the specific protocols and fields that you select when you configure a stream using the Configure Streams UI that the Splunk App for Stream provides when you install it. The Stream forwarder sends that captured event data to indexers using the Splunk Add-on for Stream Wire Data (Splunk_TA_stream_wire_data).
Splunk_TA_stream/local/inputs.conf stores the location of the Splunk App for Stream (splunk_app_stream) installation, . The Stream forwarder uses this location to ping the Splunk App For Stream over HTTP port 8000. If the Stream forwarder detects a change in the Splunk Stream configuration, the Stream forwarder sends an API request to the endpoint to get the latest configuration data.
For more information about configuring the Splunk Add-on for Stream Forwarders, see Configure Stream Forwarders in this manual.
| Splunk Stream installation package overview | Splunk Stream for Cloud deployment architecture |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk Stream™: 7.3.0, 7.4.0, 8.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!