Configure deployment clients
This topic explains how to set up deployment clients to receive content from a deployment server. In most cases, you just need to specify the deployment server that you want the client to connect to.
Even though this step occurs on the deployment clients, not the deployment server itself, it is an essential part of the overall configuration of the deployment server system.
Important: The deployment server cannot be a deployment client of itself. If it is, the following error will appear in splunkd.log: "This DC shares a Splunk instance with its DS: unsupported configuration". This has the potential to lead to situations where the deployment clients lose their ability to contact the deployment server.
Specify the deployment server
On each client, you must specify the deployment server it will connect to. You do this by configuring the client's deploymentclient.conf file. Each deployment client must have a unique network hostname.
There are three ways to configure this file:
- Use the CLI. See "Use the CLI", later in this topic.
- Edit the file directly. See "Edit deploymentclient.conf", later in this topic.
- For Windows universal forwarders only: Configure a Windows forwarder as a deployment client during the installation process. See the following Universal Forwarder manual topics:
Important: Do not use the deployment server to push deploymentclient.conf updates to the deployment clients. Doing so can potentially lead to situations where the deployment clients lose their ability to contact the deployment server.
Use the CLI
On the deployment client, run these CLI commands:
splunk set deploy-poll <IP_address/hostname>:<management_port> splunk restart
Use the IP_address/hostname and management_port of the deployment server you want the client to connect with.
For example:
splunk set deploy-poll deploymentserver.splunk.mycompany.com:8089 splunk restart
Edit deploymentclient.conf
You can also directly create and edit a deploymentclient.conf file in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local.
Syntax
The deploymentclient.conf file requires two stanzas:
| Stanza | What it's for |
|---|---|
[deployment-client]
|
Configures a number of attributes, including where to find new or updated content. You do not usually need to change the default values for this stanza. |
[target-broker:deploymentServer]
|
Specifies the location of this client's deployment server. deploymentServer is the default name for a deployment server. You must specify the deployment server under this stanza.
|
This file has a large number of optional attributes, but for most deployments, you only need to set the targetUri attribute under the [target-broker:deploymentServer] stanza. This attribute specifies the client's deployment server. Here's the attribute's syntax:
| Attribute | What it's for | Default |
|---|---|---|
targetUri
|
Specifies the deployment server connection information.
Set to |
n/a |
For a complete list of deploymentclient.conf attributes, see the deploymentclient.conf specification file in the Admin manual.
Important: You must restart the deployment client for the change to take effect.
Example
Here is a typical client configuration:
[deployment-client] [target-broker:deploymentServer] targetUri = deploymentserver.splunk.mycompany.com:8089
As is usually the case, this example accepts the default values for nearly all attributes. The one attribute that you must set, the location of the deployment server, has a value of deploymentserver.splunk.mycompany.com:8089.
Use the REST API to reload and restart
You can use the REST API to reload and restart after configuring a deployment client. See deployment/client/{name}/reload in the REST API Reference Manual.
Set a client name
You can assign each deployment client a client name. The deployment server can filter on client names, as described in "Set up client filters".
By default, the client name is set to the deployment client's GUID. If you plan to use the client name in filtering, it's recommended that you explicitly set it to some reasonable and readable name.
Important: Client names should be unique.
To configure a client name, set the clientName attribute in deploymentclient.conf to the chosen name. For example:
[deployment-client] ... clientName = Fflanda-LINUX1
Restart the deployment client for the configuration change to take effect.
Get deployment client information
You can find information about the deployment client from two locations:
- On the deployment client itself
- On the deployment server
View status from the deployment client
You can view the status of a deployment client from Splunk Web:
1. Click the Settings link at the top of Splunk Web. A window pops up with links to the set of system interfaces.
2. Select Server settings in the System section.
3. Choose Deployment client settings. This takes you to a read-only screen that provides some information about the client:
- Its deployment server.
- Its server classes and apps.
- Its status.
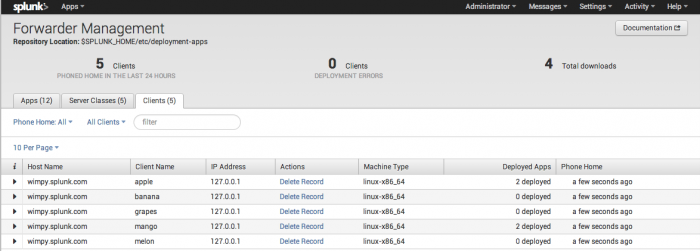
View clients from the deployment server
Once you configure and restart the client, it will initiate a handshake process with the specified deployment server. The deployment server adds it to its list of clients under the Clients tab of the forwarder management interface. For example:
Disable a deployment client
To disable a deployment client, run this CLI command on the deployment client:
splunk disable deploy-client
Upgrade a deployment client
You upgrade a client in the usual way, according to whether the client is a universal forwarder or a full Splunk Enterprise instance. The fact that an instance is a deployment client does not make any difference in how you perform the upgrade.
However, after you upgrade the client, the client will appear twice in the client list that the deployment server maintains and presents through the forwarder management interface. To eliminate the duplicate listing, you must restart the deployment server after a client upgrade.
| Plan a deployment | Create deployment apps |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.1.9, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.2.6, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.3.4
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!