Pull notable events from Splunk Enterprise Security to Splunk UBA
You can pull notable events from Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) into Splunk User Behavior Analytics (UBA).
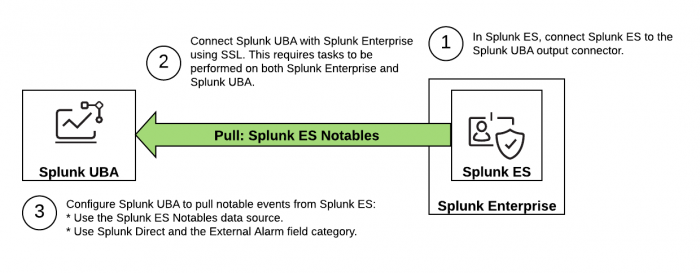
The following image summarizes the steps to configure a Splunk ES Notables or Splunk Direct data source to pull notable events from Splunk ES to Splunk UBA.
Perform the following tasks to set up the desired data source in Splunk UBA:
- In Splunk ES, set up Splunk UBA to receive notable events from Splunk ES.
- Connect Splunk UBA with Splunk Enterprise using SSL. See Configure the Splunk platform to receive data from the Splunk UBA output connector.
- Configure Splunk UBA to pull notable events from Splunk ES. Use one of the methods detailed in the Pull notable events from Splunk ES section.
Set up Splunk UBA to receive notable events from Splunk ES
In Splunk ES, set up a connection with Splunk User Behavior Analytics so that you can send and receive data.
Splunk Cloud Platform customers must contact Splunk Cloud Platform Support to perform the Splunk UBA setup.
- On the Splunk ES main menu, select Configure > UBA Setup.
- Select the tick-box for Identity Integration.
- Enter the Server Address and Port . Use the format of
https://server[:port]. - Click Save when done.
Pull notable events from Splunk ES
Use one of the following methods to pull notable events from Splunk ES to Splunk UBA:
- Pull notable events and risk events using the Splunk ES Notables data source
- Pull notable events using Splunk Direct
Pull notable events and risk events using the Splunk ES Notables data source
Use the Splunk ES Notables data source in Splunk UBA to integrate Splunk UBA with Splunk ES. Configure Splunk UBA to connect to the Splunk ES search head. The Splunk ES Notables data source automatically ingests notable events and risk events from Splunk ES and properly maps categories from Splunk ES Content Updates. If you have custom correlation searches in Splunk ES, make sure the category field is added correctly in the correlation search.
The category field must match one of the listed categories. The Splunk UBA external alarm model uses these events and category mappings to generate meaningful anomalies which can subsequently raise the appropriate threats. To view the list of anomaly categories, see Filter the anomaly table in Use Splunk User Behavior Analytics.
Notable events that are closed in Splunk ES are not ingested by Splunk UBA.
- In Splunk UBA, select Manage > Data Sources.
- Click New Data Source.
- In the SIEM Connectors category, click Splunk ES Notables.
- On the Connection screen, provide connection and authentication details to connect to Splunk Enterprise Security (ES), then click Next. The connection and authentication details are those of the Splunk ES search head and the management port.
The user must have permissions to access the notable events and risk indexes.
- On the Time Range screen, select Live and All Time, then click Next.
- On the Splunk Query screen, verify the SPL being used to retrieve the events and category mappings from Splunk ES, then click Next. If you need to modify the SPL, make sure
NOT (source="UEBA" OR source="UBA")is included in the final SPL to exclude Splunk UBA anomalies and threats. - On the Test Mode screen, click Test Mode to validate the data source before ingesting all events, then click Next. For more information about test mode, see Add data sources to Splunk UBA in test mode .
- Click OK.
Pull notable events using Splunk Direct
Use Splunk Direct to pull notable events from Splunk ES to Splunk UBA by configuring an external alarm data source. Write a custom query to handle the necessary data enrichment such as mapping the alarm category or severity.
- In Splunk ES, confirm that you get the desired notable events from the following query. The query analyzes notable events on Splunk ES that are not generated from Splunk UBA data sources and performs the proper mappings for the External Alarm category on Splunk UBA.
You will need this query in the following steps.
`notable` | search NOT (source="*UEBA*" OR source="*UBA*") | eval action=IF(action="deferred" OR action="blocked","blocked","allowed") | eval tag="attack,network,communicate", app='Authentication.app', dest_zone='dest_pci_domain', src_host='src_nt_host', src_zone='src_pci_domain' | eval severity="Critical",evcls=coalesce(signature,savedsearch_name,search_name) | eval signature=IF(isnull(signature),evcls,signature) | eval alarmCategories=CASE( like(lower(evcls),"%application%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%vulnerability%"),"ProductAttack", like(lower(evcls),"%intrusion%"),"SystemAttack", like(lower(evcls),"%data%loss%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%dlp%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%dlp%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%exfil%"),"Exfiltration", like(lower(evcls),"%malware%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%virus%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%botnet%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%backdoor%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%trojan%"),"MalwarePersistence", like(lower(evcls),"%malware%_operations") OR like(lower(evcls),"%cnc%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%callback%"),"MalwareActivity", like(lower(evcls),"%spam%") OR like(lower(evcls),"%phish%"),"MalwareInstall",1=1,"PolicyViolation") | eval user=IF(isnull(user) AND like(dest,"%@%"),dest,user), dest_ip=coalesce(dest_ip,'values(dest)'),eventtype=evcls, user=IF(like(user,"%wireless%"),"",user), src_ip=IF(isnull(src_ip) AND NOT like(src,"%@%"), src,src_ip), dest_ip=IF( like(dest_ip,"%@%"),'',dest_ip) | makemv delim="," tag | makemv delim=" " dest_ip | mvexpand dest_ip | fields action,alarmCategories,app,category,dest_host,dest_ip,dest_nt_domain, dest_zone,duration,eventtype,file_name,file_path,severity,signature, sourcetype,src_host,src_ip,src_zone,tag,url,user - In Splunk UBA, select Manage > Data Sources.
- Click New Data Source.
- In the SIEM Connectors category, click Splunk ES Notables.
- On the Connection screen, provide connection and authentication details to connect to Splunk Enterprise Security (ES), then click Next. The connection and authentication details are those of the Splunk ES search head and the management port.
The user must have permissions to access the notable events and risk indexes.
- On the Time Range screen, select Live and All Time, then click Next.
- On the Splunk Query screen, verify the SPL being used to retrieve the events and category mappings from Splunk ES, then click Next. If you need to modify the SPL, make sure NOT (source="UEBA" OR source="UBA") is included in the final SPL to exclude Splunk UBA anomalies and threats.
- On the Data Format page, select External Alarm as the field category. Keep the default values in the Splunk Field column.
- Enter the query that you verified at the beginning of this procedure again.
- Make sure Test Mode is not selected, and then click OK.
| Send Splunk UBA anomalies and threats to Splunk ES as notable events | Send Splunk UBA audit events to Splunk ES |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® User Behavior Analytics: 5.1.0, 5.1.0.1, 5.2.0, 5.2.1, 5.3.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!