Create an add-on
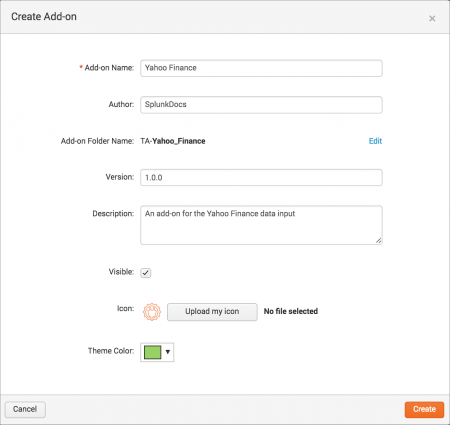
Click Create an add-on on the Add-on Builder home page, then specify the basic properties for your add-on. These settings also determine how your add-on appears in Splunk Web.
Set the following properties for your project:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Add-on Name | The name of the add-on. |
| Author | The author name, which appears with the add-on in Splunk Web. |
| Add-on Folder Name | The folder name for the add-on under $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/.
Add-on folder names have a prefix of "TA-", which is a requirement for Splunk Enterprise Security add-ons. For add-ons created by Splunk, the folder name prefix is "Splunk_TA_". To change the folder name suffix, click Edit. |
| Version | The version number of the add-on, which appears with the add-on in Splunk Web. |
| Description | The description of your add-on. |
| Visible | Indicates whether you want the add-on to be visible in the Splunk Web app list. By default, add-ons are not visible. However, if you create a setup page for your add-on, the Visible property will be enabled automatically. |
| Icon | Upload an image file to use as the icon for your add-on. The Add-on Builder creates a large version (72x72 pixels) and a small version (36x36 pixels) of the icon from this image. |
| Theme Color | The color to use for your add-on. |
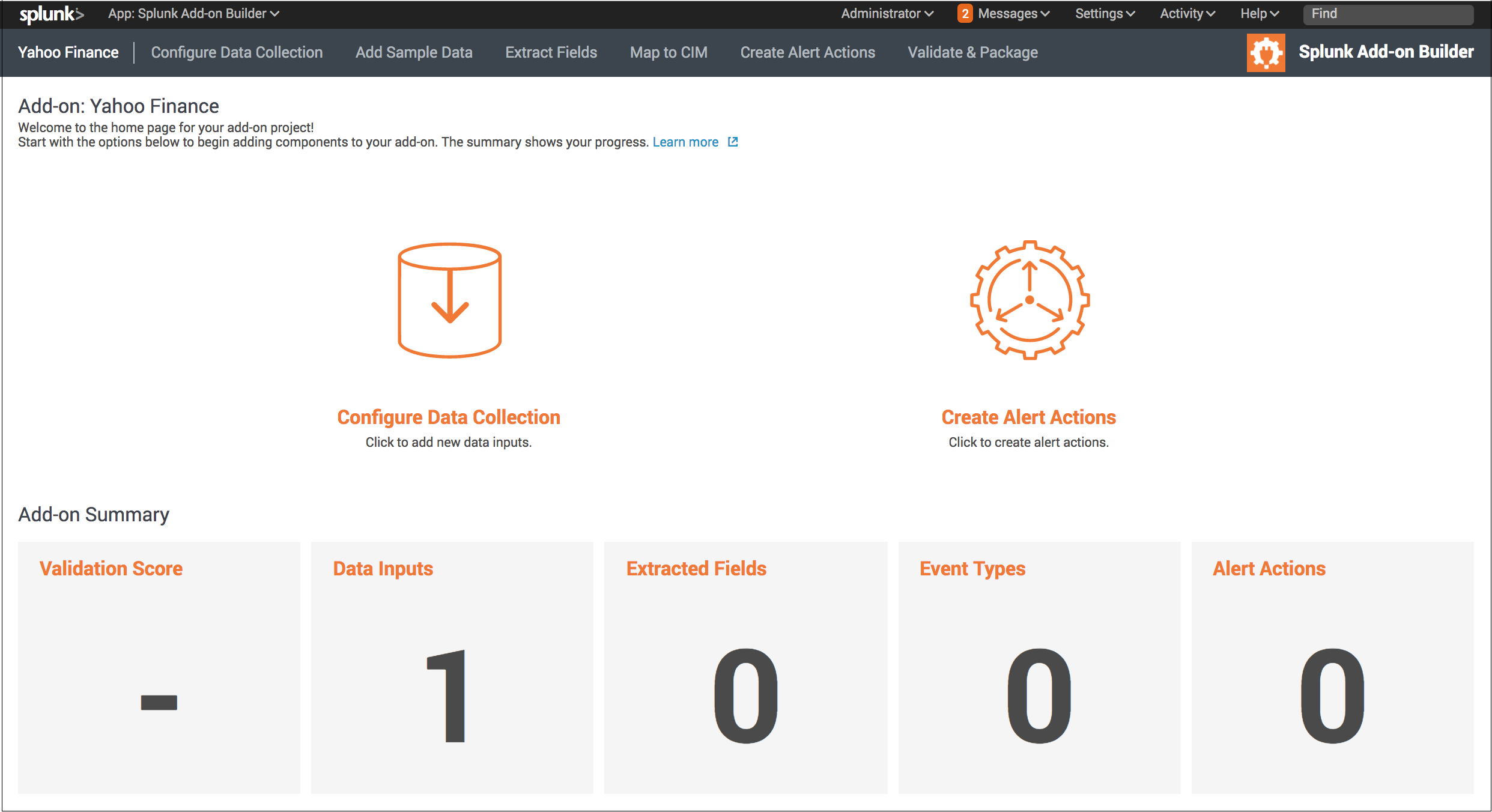
After you click Create to save your settings, the Splunk Add-on Builder displays a home page for your new add-on with the workflow for building it, including a summary of the objects you have configured.
Add-on Builder workflow
The following diagram shows the basic workflow in creating an add-on.
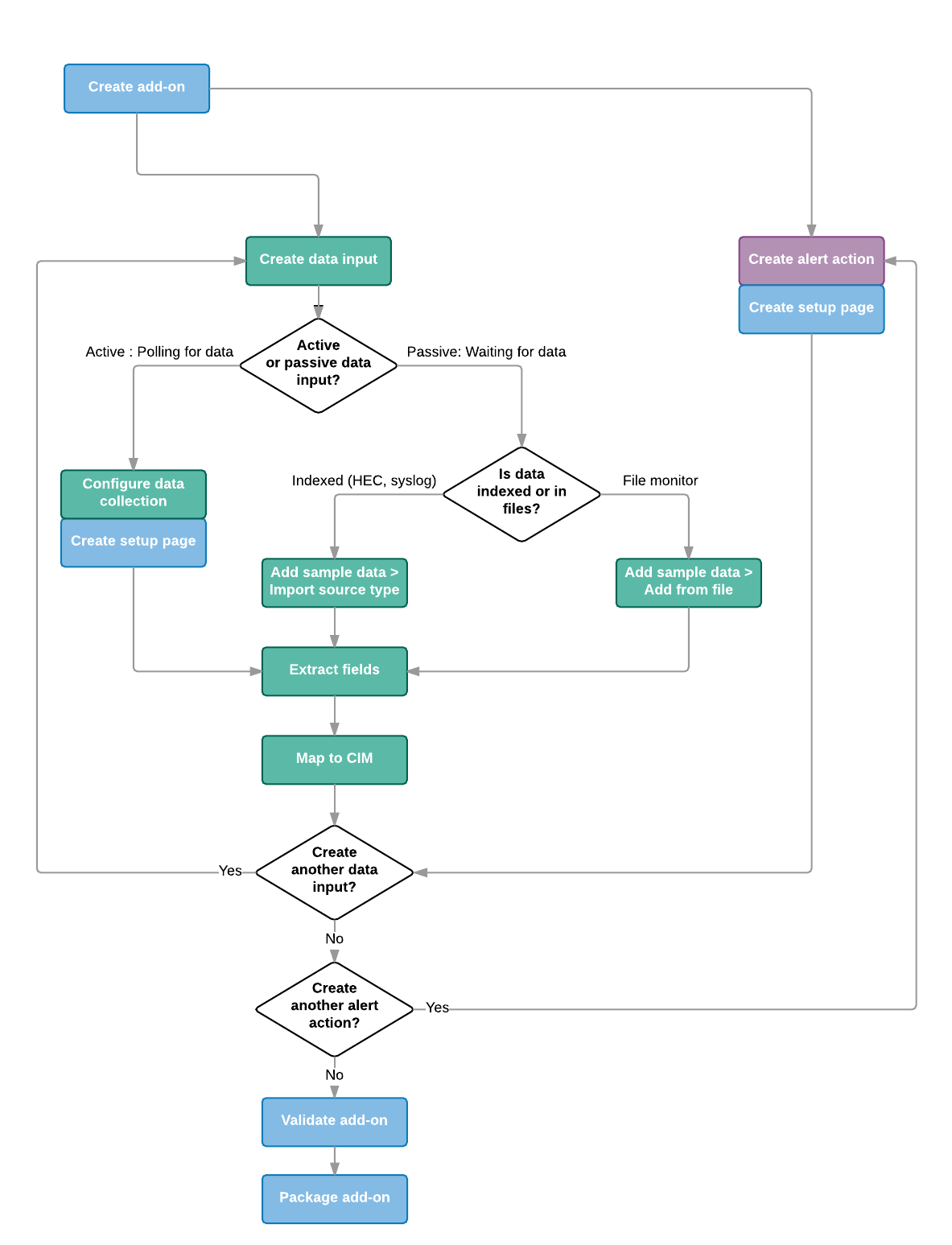
| Workflow action | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a data input | Get data into your add-on by configuring data inputs. |
| Configure data collection | Configure a data input using a REST API call, using a shell command, or writing Python code. |
| Create a setup page | Create a setup page for your add-on when you need to prompt users for information to run your add-on, including authentication. |
| Add sample data | If you already have data in Splunk, you can add sample data to your add-on so that you can add knowledge objects from it. You can import data from an existing source type or upload sample files. |
| Extract fields | Create field extractions from the data inputs you configured. |
| Map to CIM | Map the fields from the field extractions to the common information model (CIM). |
| Create alert actions | Create custom alert actions, including running an adaptive response action for Splunk Enterprise Security. |
| Validate the add-on | Validate the add-on for best practices, and test the modular/scripted inputs, field extractions, and CIM mappings. The Splunk Add-on Builder shows you any errors or warnings, along with recommendations about how to address them. |
| Package the add-on | Package the add-on when you are ready to install your add-on and use it. The result is a compressed file that contains a directory with the necessary configuration files. |
| Use the Splunk Add-on Builder | Configure data collection using a REST API call |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Add-on Builder: 2.1.0, 2.1.1, 2.1.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!