Machine Learning Toolkit Troubleshooting in Splunk Enterprise Security
Troubleshoot MLTK in Splunk Enterprise Security. There are some known issues and potential workarounds.
Error messages
MLTK errors are found in the mlspl.log file. The errors themselves are not necessarily enough to troubleshoot the issues. The Machine Learning Audit dashboard helps to correlate MLTK errors with the corresponding failed searches. See Machine Learning Audit Dashboard.
Testing and training models overwrites them
MLTK replaces the models with every run if you're not using partial_fit=true. Even if you are using partial_fit=true, MLTK updates the original model, which you might not want. You can test in your user space without overwriting or updating the original model. MLTK model names with the app: prefix are saved into the shared application namespace, for example: ./apps/SA-AccessProtection/lookups/failures_by_src_count_1d.csv. If you are the admin user and you revise the search to remove the app: prefix, then it will save in the admin user space, such as ./users/admin/SplunkEnterpriseSecuritySuite/lookups/recipients_by_src_1h.csv, and it will not overwrite the original. The user and app name spaces depend on the user that is logged in and the app currently running. You can also revise the name of the model to avoid overwriting the original while testing.
Original model name:
| tstats `summariesonly` count as failure from datamodel=Authentication.Authentication where Authentication.action="failure" by Authentication.src,_time span=1h | fit DensityFunction failure dist=norm into app:failures_by_src_count_1h
Model name revised to save in non-app space:
| tstats `summariesonly` count as failure from datamodel=Authentication.Authentication where Authentication.action="failure" by Authentication.src,_time span=1h | fit DensityFunction failure dist=norm into failures_by_src_count_1h
Model name revised to include testing:
| tstats `summariesonly` count as failure from datamodel=Authentication.Authentication where Authentication.action="failure" by Authentication.src,_time span=1h | fit DensityFunction failure dist=norm into app:testing_failures_by_src_count_1h
Maximum group limit
There is a limit of 1024 on the maximum number of groups that can be created when using the MLTK DensityFunction with a by clause. If you have custom searches that you're converting to MLTK, depending what you use to split your searches, the results will not display if the number of groups is too large to split with the by clause. To change the limit, change the value of the max_groups field in the DensityFunction stanza of the mlspl.conf file in the Machine Learning Toolkit app.
Example search
| tstats `summariesonly` count as dest_port_traffic_count from datamodel=Network_Traffic.All_Traffic by All_Traffic.dest_port,_time span=1d | `drop_dm_object_name("All_Traffic")` | fit DensityFunction dest_port_traffic_count by dest_port dist=norm into app:count_by_dest_port_1d
Example error message
Error in 'fit' command: Error while fitting "DensityFunction model: The number of groups cannot exceed <abc>; the current number of groups is <xyz>."
See the syntax constraints of the Density Function in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit User Guide.
CSV required
There's a lookup table file at $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/SA-Utils/lookups/qualitative_thresholds.csv that's required for using the qualitative_id thresholds. If the CSV file is missing, then you can't use the qualitative_id thresholds for extreme, high, medium, low, and minimal.
MLTK-backed key performance indicator errors
The Risk Analysis page shows risk scores that are "unable to load results" for up to one day after a risk modifier has been created.
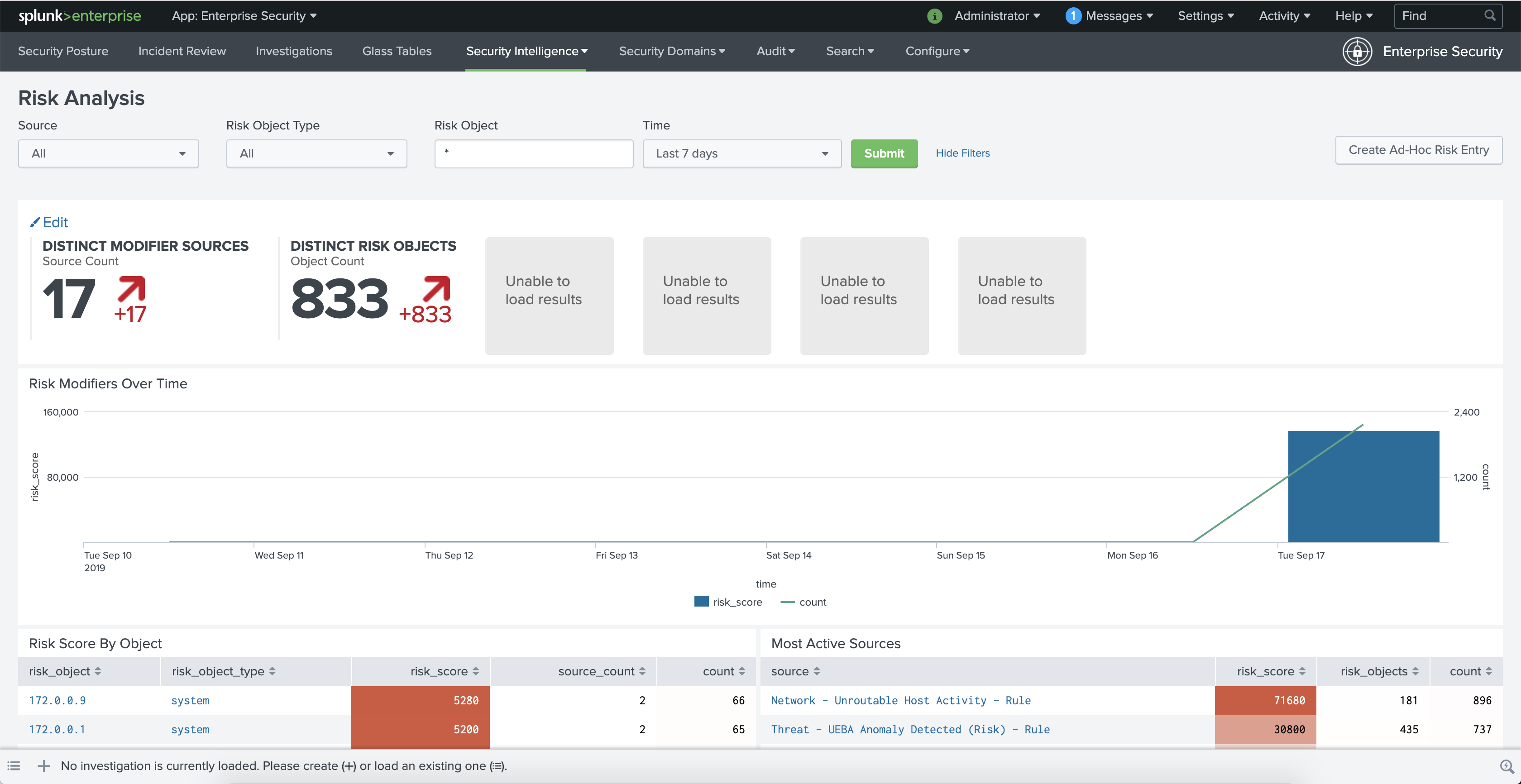
This occurs because the key security indicator searches have been updated to MLTK, and the corresponding MLTK models of these qualitative key indicators haven't been generated yet.
To load these results, manually run the following searches from Configure > Content > Content Management:
Risk - Median Object Risk Per Day - Model GenRisk - Total Risk By Risk Object Type Per Day - Model Gen
Python3, Python Scientific Computing, and MLTK compatibility issues during upgrade
Older versions of Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) are shipped with Splunk Enterprise Security, which may cause some upgrade issues. if you are upgrading to MLTK version 5.3 after you have already upgraded to Splunk Enterprise Security version 7.0, then MLTK version 5.3, Python Scientific Computing (PSC) app versions 3.0.0, and Python3 compatibility may be important considerations depending on whether you are using the partial_fit parameter as you update your searches for Python3.
However, if you are simply upgrading to Splunk Enterprise Security version 7.0, then MLTK version 5.3, Python Scientific Computing (PSC) app versions 3.0.0, and Python3 compatibility issues do not impact you.
MLTK models created by MLTK versions 5.2.2 and lower and packaged with Enterprise Security 7.0 are not compatible with MLTK versions 5.3.0 or higher. Therefore, you need to regenerate the MLTK models and re-run the MLTK searches when upgrading MLTK and Python Scientific App (PSC) to versions 5.3 and 3.0. Regenerating the models might take time to complete. You can regenerate the MLTK models manually or wait for Enterprise Security to start generating the models on the default schedule. The correlation search results may be inaccurate until the models have been regenerated.
Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) versions 5.3.0 and higher are compatible with the Python Scientific Computing (PSC) app versions 3.0.0 and higher. However, the MLTK models created by versions 5.2.2 and lower and packaged with Enterprise Security 7.0 are not compatible with MLTK versions 5.3.0 or higher. Additionally, when MLTK and Python Scientific App (PSC) are upgraded to versions 5.3 and 3.0 respectively, you might see an error that indicates the existing model app:median_object_risk_by_object_type_1d does not exist. Re-run the appropriate model generating search, say app:median_object_risk_by_object_type_1d after regenerating the model and the results are generated as expected. The MLTK searches may take some time to rebuild and may not provide accurate results until the MLTK searches get rebuilt. Additionally, the new MLTK search results may be different because new MLTK models are used.
if you upgrade to MLTK versions 5.3.0 and higher and use MLTK searches that have the condition partial_fit=true, you must delete the existing MLTK models and re-create the MLTK models so that you can train the MLTK searches with the appropriate historical context.
For more information on the impacted searches, see Machine Learning Toolkit Searches in Splunk Enterprise Security.
Also, see Update Splunk MLTK models for Python 3 in the Splunk Enterprise Python 3 Migration guide.
| Convert Extreme Searches to Machine Learning Toolkit in Splunk Enterprise Security |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security: 7.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!