Configure the fit and apply commands
The MLSPL.conf file controls the resources used by the Machine Learning Toolkit. Here, users with Admin level access can configure the default settings for all algorithms or for specific ones. As of version 4.0.0 of the toolkit, the MLSPL.conf file can be changed within toolkit itself, under the new tab called Settings. The file settings can also still be changed as before through the command line interface. This document covers both methods.
The MLSPL.conf file default settings are set to prevent the overloading of a search head. Users are encouraged to understand these MLSPL.conf file settings before making any changes.
Machine learning requires compute resources and disk space. Each algorithm has a different performance cost, complicated by the number of selected input fields and events processed. Ensure you know the impact of making changes to the algorithm settings by adding the ML-SPL Performance App for the Machine Learning Toolkit to your setup via Splunkbase.
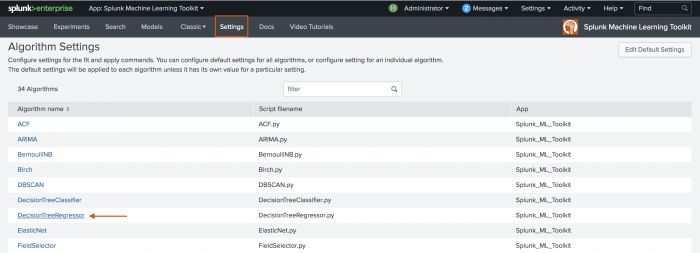
Configure through the Settings tab
Configure the fit and apply commands by setting properties in the mlspl.conf configuration file via the Settings tab within the Machine Learning Toolkit.
- Select the name of the algorithm of which you wish to view or alter settings.
The Edit Default Settings button option changes the master list of settings, rather than those of any individual algorithm. Use this option judiciously.
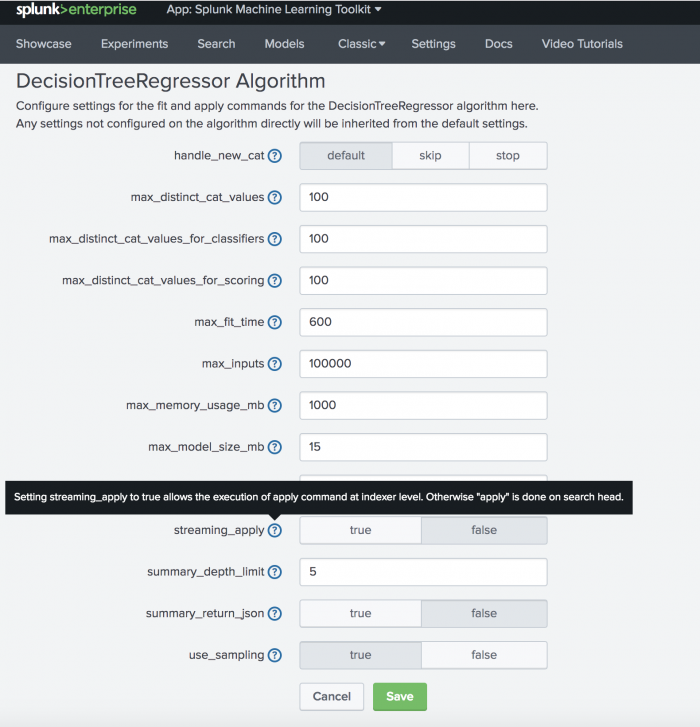
- From the specific algorithm page, adjust the available fields as desired. See the table below for setting details, or hover over any setting name to view more information from within the toolkit.
- Click the green Save button when done.
Repeat these steps for any of the other listed algorithms.
Setting descriptions
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
handle_new_cat |
default | Action to perform when new value(s) for categorical variable/ explanatory variable is encountered in partial_fit. Default sets all values of the column that correspond to the new categorical value to zeroes. Skip skips over rows that contain the new value(s) and raises a warning. Stop stops the operation by raising an error.
|
max_distinct_cat_values |
100 | The maximum number of distinct values in a categorical feature field, or input field, that will be used in one-hot encoding. One-hot encoding is when you convert categorical values to numeric values. If the number of distinct values exceeds this limit, the field will be dropped, or excluded from analysis, and a warning appears. |
max_distinct_cat_values_for_classifiers |
100 | The maximum number of distinct values in a categorical field that is the target, or output, variable in a classifier algorithm. |
max_distinct_cat_values_for_scoring |
100 | Determines the upper limit for the number of distinct values in a categorical field that is the target (or response) variable in a scoring method. If the number of distinct values exceeds this limit, the field will be dropped (with an appropriate error message). |
max_fit_time |
600 | The maximum time, in seconds, to spend in the "fit" phase of an algorithm. This setting does not relate to the other phases of a search such as retrieving events from an index. |
max_inputs |
100000 | The maximum number of events an algorithm considers when fitting a model. If this limit is exceeded and use_sampling is true, the fit command downsamples its input using the Reservoir Sampling algorithm before fitting a model. If use_sampling is false and this limit is exceeded, the fit command throws an error.
|
max_memory_usage_mb |
1000 | The maximum allowed memory usage, in megabytes, by the fit command while fitting a model.
|
max_model_size_mb |
15 | The maximum allowed size of a model, in megabytes, created by the fit command. Some algorithms (e.g. SVM and RandomForest) might create unusually large models, which can lead to performance problems with bundle replication.
|
max_score_time |
600 | The maximum time, in seconds, to spend in the "score" phase of an algorithm. |
streaming_apply |
false | Setting streaming_apply to true allows the execution of apply command at indexer level. Otherwise apply is done on search head.
|
use_sampling |
true | Indicates whether to use Reservoir Sampling for data sets that exceed max_inputs or to instead throw an error.
|
A reboot of Splunk is required in order to put any setting changes into effect.
Configure using the command line interface
Configure the fit and apply commands by setting properties in the mlspl.conf configuration file located in the default directory:
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/Splunk_ML_Toolkit/default/mlspl.conf
In this file, you can specify default settings for all algorithms, or for an individual algorithm. To apply global settings, use the [default] stanza and algorithm-specific settings in a stanza named for the algorithm, for example, [LinearRegression] for the LinearRegression algorithm. Be aware that not all global settings can be set or overwritten in an algorithm-specific section. For details, see How to copy and edit a configuration file.
To avoid losing your configuration file changes when you upgrade the app, create a copy of the mlspl.conf file with only the modified stanzas and settings, then save it to $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/Splunk_ML_Toolkit/local/
Setting descriptions
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
max_inputs |
100000 | The maximum number of events an algorithm considers when fitting a model. If this limit is exceeded and use_sampling is true, the fit command downsamples its input using the Reservoir Sampling algorithm before fitting a model. If use_sampling is false and this limit is exceeded, the fit command throws an error.
|
use_sampling |
true | Indicates whether to use Reservoir Sampling for data sets that exceed max_inputs or to instead throw an error.
|
max_fit_time |
600 | The maximum time, in seconds, to spend in the "fit" phase of an algorithm. This setting does not relate to the other phases of a search such as retrieving events from an index. |
max_memory_usage_mb |
1000 | The maximum allowed memory usage, in megabytes, by the fit command while fitting a model.
|
max_model_size_mb |
15 | The maximum allowed size of a model, in megabytes, created by the fit command. Some algorithms (e.g. SVM and RandomForest) might create unusually large models, which can lead to performance problems with bundle replication.
|
max_distinct_cat_values |
100 | The maximum number of distinct values in a categorical feature field, or input field, that will be used in one-hot encoding. One-hot encoding is when you convert categorical values to numeric values. If the number of distinct values exceeds this limit, the field will be dropped, or excluded from analysis, and a warning appears. |
max_distinct_cat_values_for_classifiers |
100 | The maximum number of distinct values in a categorical field that is the target, or output, variable in a classifier algorithm. |
A reboot of Splunk is required in order to put any setting changes into effect.
| Configure permissions for ML-SPL commands | Using the score command |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Machine Learning Toolkit: 4.0.0, 4.1.0, 4.2.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!