What a Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure deployment looks like
This topic discusses the overall architecture of a Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure deployment.
Introduction
A Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure deployment consists of a Splunk Enterprise instance (that contains the index and runs Splunk Web, and that users access to view the app) and a number of universal forwarders--one for each Active Directory or Windows server you want to include in the deployment.
This setup procedure guides you through the install of nearly all components on one hosts. This means that:
- The host will act as the indexer to receive incoming data from forwarders.
- The host will act as a deployment server to manage forwarders and deploy apps and configurations.
- The host will act as a search head to host the app and view the incoming data.
Only the universal forwarders in this deployment will be on different hosts. This helps reduce confusion on what components need to be installed where. Once you have an understanding of how the app and its components work, you can read the topic on how to scale the deployment for increased performance on larger environments.
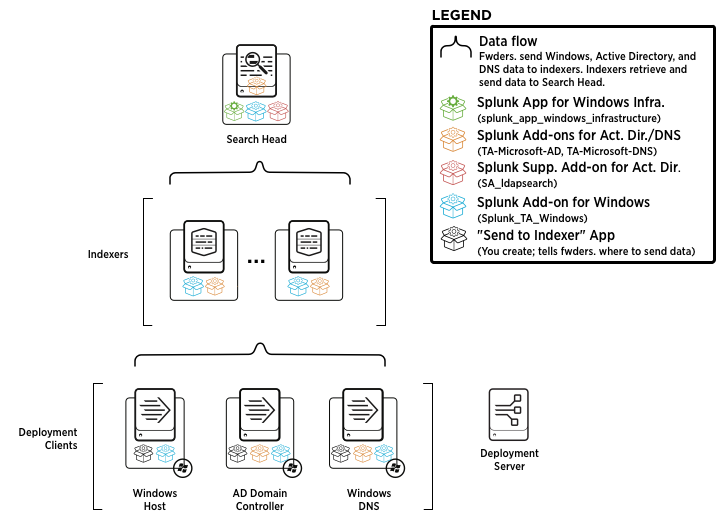
Deployment diagram
The diagram below depicts an example Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure deployment.
Get started
The next page details the installation of the first piece of your Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure deployment: setting up the indexer that will act as the hub for the entire operation.
If you're using TA-Windows v6.0.0, you don't need TA_AD and TA_DNS. TA_AD and TA_DNS are merged with TA-Windows v6.0.0.
| What data the Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure collects | How to deploy the Splunk App for Windows Infrastructure |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for Windows Infrastructure (EOL): 1.5.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!