Manage Splunk Phantom users
View the Users page to see the users configured on your Splunk Phantom instance, add new users, or edit existing users.
Perform the following steps to access the Users page:
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
Default users and types of users
On a new Splunk Phantom instance, the following default users are available:
- Admin: This is the default admin account and cannot be disabled or deleted. The admin user is not counted towards the seat count of a seat-based license.
- Automation: The automation user is not counted towards the seat count of a seat-based license.
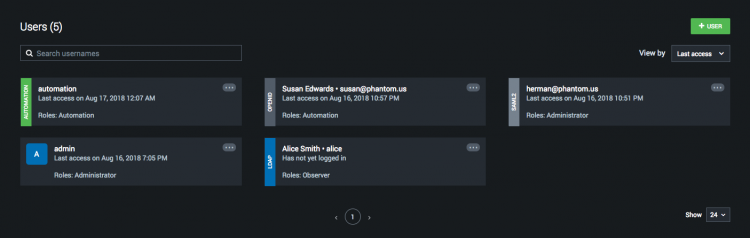
An information card is shown for each user and contains information such as the user's full name, username last access data, and roles. The card for local interactive users contains an icon showing the user's initials or custom icon. The card for all other types of users contains a colored ribbon indicating the user type.
The example below shows one of each type of user that can be configured in Splunk Phantom:
In this example, we can see the following information:
- The admin user is a local interactive user, and this user's card contains an icon with the letter "A". The other user cards show a vertical ribbon indicating the user type.
- Users like Alice Smith and Susan Edwards have provided first and last names which are displayed next to their usernames. Alice logs in with the short username, alice, while Susan logs in with the email-style username, susan@phantom.us. The format of the username used depends on the identity provider being used.
The automation user is a default internal service account used by Splunk Phantom for running automated playbooks and asset actions, such as data ingestion. The automation user and any other automation type users do not have passwords and can't log into the Splunk Phantom web interface. However they do provide REST authentication tokens that can be used to read and write data to the REST backend and perform useful activities. For information on how to use the REST API and authentication tokens, see Using the Splunk Phantom REST API reference in the Splunk Phantom REST API Reference.
Customize what you see on the Users page
Customize the information you see on the Users page:
- Click the drop-down list in the Show field to view more or fewer user cards at a time. By default, 24 user cards are shown.
- Use the filter in the View by field to sort the users by first name, last name, username, last accessed, and last created.
- Click on the ellipsis (...) icon in the upper-right corner of each user card for additional options, such as viewing the user's effective permissions, editing the user, or deleting the user.
Configure user permissions
All user permissions in Splunk Phantom are derived from the user's role. To grant permissions to a user, you assign a role with the desired permission. Only the default admin user can have special, hard-coded permissions outside of any roles.
Perform the following steps to view the permissions for a user:
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
- Click on a user card and review the roles assigned to this user in the Roles field.
Users with multiple roles have the sum of all the permissions allowed by those roles.
See Manage roles and permissions in Splunk Phantom for more information about Splunk Phantom roles and the permissions provided by each role.
Add users to Splunk Phantom
You can add users to Splunk Phantom from the Splunk Phantom web interface. These user accounts can access Splunk Phantom but not the operating system of the virtual appliance. The user can be authenticated locally by Splunk Phantom, or by using LDAP, OpenID, or SAML2. In the case of LDAP, OpenID, and SAML2, the user account can be created in Splunk Phantom or created automatically during the user's initial login. In order for accounts to be automatically created, a group mapping to a Splunk Phantom role must be configured. See Configuring single sign-on authentication for Splunk Phantom.
Create a local Splunk Phantom user
Perform the following tasks to add a local Splunk Phantom user. The user is authenticated by the Splunk Phantom instance.
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
- Click + User.
- Verify that the User type is set to Local.
- Enter a username in the Username field.
- Enter a password in the Password field.
- (Optional) Complete the other fields on the screen, such as first and last name, email address, title, time zone, and location. If two factor authentication is enabled, also provide the Duo username. See Secure Splunk Phantom using two factor authentication.
- Click Create.
Create an LDAP, OpenID, or SAML2 Splunk Phantom user
Perform the following steps to add a user who is authenticated using single sign-on (SSO). Before you do this, make sure you have single sign-on enabled. See Configuring single sign-on authentication for Splunk Phantom.
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
- Click + User.
- In the User type field, select the SSO provider. Only the configured and enabled SSO providers are available to choose from.
- Enter the username in the Username field.
- (Optional) Complete the other fields on the screen, such as time zone and roles. If two factor authentication is enabled, also provide the Duo username. See Secure Splunk Phantom using two factor authentication.
- Click Create.
Create an automation user in Splunk Phantom
Perform the following steps to add an automation user in Splunk Phantom:
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
- Click + User.
- In the User type field, select Automation.
- Enter the username in the Username field.
- (Optional) In the Allowed IPs field, specify the IP addresses allowed to connect as this user. You can specify individual IP addresses, CIDR ranges, or any to allow all IP addresses.
- (Optional) Enter a default label for this user. Any containers that get created by this user use this label if another label is not specified.
- (Optional) If multi-tenancy is enabled, select the default tenant in the Default Tenant field.
- (Optional) The Automation role is provided to automation users by default. See Manage roles and permissions in Splunk Phantom for more information about the permissions granted by each role.
- Click Create.
Edit an automation user to view the REST API authorization token and associated assets
Click an existing automation user on the Users page to view the following information:
- The REST API authorization token, which is used to authenticate the user for access to the REST API. See Using the Splunk Phantom REST API reference in the Splunk Phantom REST API Reference manual.
- The assets associated with this user.
- The automation user is used to test connectivity with the listed assets, and also for ingesting data. Use the automation user configuration to set the permissions of the asset when the asset is running on its own.
- When the asset is not performing test connectivity or data ingestion, it is running with the permissions of the user performing the action. If the asset is being run from a playbook, the asset has the permissions of the playbook user.
- You can assign assets to an automation user during asset configuration. If you assigned an automation user to an asset, the asset appears in the automation user's card. See Configure automation users for a Splunk Phantom asset.
Disable an existing Splunk Phantom user
Disable a user in Splunk Phantom to prevent that user from logging in or accessing the system. Disabling a user does not delete the user account.
To disable an existing Splunk Phantom user, perform the following steps:
- From the main menu, select Administration.
- Select User Management > Users.
- Click the ellipsis (...) icon for the user you want to disable, and select Edit.
- Click the Disabled checkbox.
- Click Save.
| Use authorized users to grant authorized access | Manage roles and permissions in Splunk Phantom |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Phantom (Legacy): 4.9, 4.10, 4.10.1, 4.10.2, 4.10.3, 4.10.4, 4.10.6, 4.10.7
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!