About subsearches
Using subsearches
A subsearch is a search within a primary, or outer, search. When a search contains a subsearch, the subsearch is run first.
Subsearches must be enclosed in square brackets in the primary search.
Consider the following search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase [search sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip] | stats count, dc(productId), values(productId) by clientip
The subsearch portion of the search is enclosed in square brackets.
[search sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip]
The first command in a subsearch must be a generating command such as search, eventcount, or tstats. For a list of generating commands, see Command types in the Search Reference.
How subsearches work
A subsearch looks for a single piece of information that is then added as a criteria, or argument, to the primary search. You use a subsearch because the single piece of information that you are looking for is dynamic. The single piece of information might change every time you run the subsearch.
For example, you want to return all of the events from the host that was the most active in the last hour. The host that was the most active might be different from hour to hour. You need to identify the most active host before you can return the events from that host.
Break this search down into two parts.
- The most active host in the last hour. This is the subsearch.
- The events from that host. This is the primary search.
You could run two searches to obtain the list of events. The following search identifies the most active host in the last hour.
sourcetype=syslog earliest=-1h | top limit=1 host | fields host
This search returns only one host value. Assume that the result is the host named crashy. To return all of the events from the host crashy, you need to run a second search.
sourcetype=syslog host=crashy
The drawback to running two searches is that you cannot setup reports and dashboard panels to run automatically. You must run the first search to identify the piece of information that you need, and then run the second search with that piece of information.
You can combine these two searches into one search that includes a subsearch.
sourcetype=syslog [search sourcetype=syslog earliest=-1h | top limit=1 host | fields + host]
The subsearch is in square brackets and is run first. The subsearch in this example identifies the most active host in the last hour. The result of the subsearch is then provided as a criteria for the main search. The main search returns the events for the host.
Time ranges and subsearches
Time ranges that you specify directly in a search apply only to the main search. The time ranges specified in the main search do not apply to subsearches. Likewise, a time range specified in a subsearch applies only to that subsearch. The time range does not apply to the main search or any other subsearch.
Time ranges selected from the Time Range Picker apply to the main search and to subsearches.
When to use subsearches
Subsearches are mainly used for two purposes:
- Parameterize one search, using the output of another search. The example, described above, of searching for the most active host in the last hour is a an example of this use of a subsearch.
- Run a separate search and add the output to the first search using the
appendcommand.
A subsearch can be used only where the explicit action that you are trying to accomplish is with the search and not a transformation of the data. For example, you cannot use a subsearch with "sourcetype=top | multikv", because the multikv command does not expect a subsearch as an argument. Certain commands, such as append and join can accept a subsearch as an argument.
Multiple subsearches in a search string
You can use more than one subsearch in a search.
If a search has a set of nested subsearches, the inner most subsearch is run first, followed by the next inner subsearch, working out to the outermost subsearch and then the primary search.
For example, you have the following search.
index=* OR index=_* | [search index=* | stats count by component | [search index=* | stats count by user | [search index=* | stats by ipaddress]]]
The order in which the search is processed is:
search index=* | stats by ipaddresssearch index=* | stats count by usersearch index=* | stats count by component- (An implied search command)
index=* OR index=_*(and the results of the nested subsearches)
Here is another example.
index=foo error [ search index=bar baz [search index=* | stats count by user | search count>100] | stats count by host ]
Be certain to analyze your search syntax when you find yourself using subsearches frequently. It is often possible to rewrite the search and omit the subsearch.
If the subsearches are sequential instead of nested, the subsearch farthest to the left, or beginning of the search, is run first. Then working towards the right, or end of the search, the next subsearch is run. When all of the subsearches are run, then the primary search is run.
For example, you have the following search.
index=* OR index=_* | [search index=* | stats count by customerID] | [search index=* | stats by productName]
The order in which the search is processes is:
search index=* | stats by customerIDsearch index=* | stats count by productName- (An implied search command)
index=* OR index=_*(the results of the subsearches)
Subsearch examples
These examples show you the difference between searching your data with and without a subsearch.
Example: Find the most frequent shopper and what they purchased
| This example uses the sample dataset from the Search Tutorial, but should work with any format of Apache Web access log. Download the data set from this topic in the Search Tutorial and follow the instructions to upload the data to your Splunk deployment. |
Let's find the single most frequent shopper on the Buttercup Games online store, and what that shopper has purchased. If the tutorial data uploaded, use the these steps to follow along with this example.
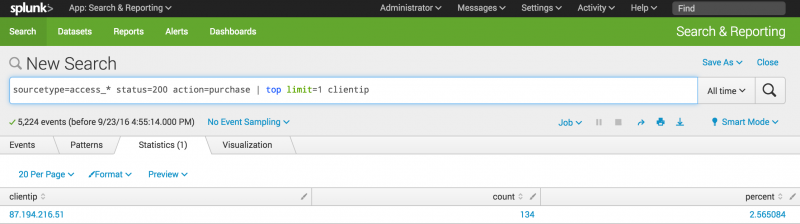
- To find the shopper who accessed the online shop the most, use this search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip
- The
limit=1argument specifies to return 1 value. Theclientipargument specifies the field to return.
- This search returns one
clientipvalue, which you will use to identify the VIP shopper. Thetopcommand also returns two other columns, count and percent. The count is the number of events that have thisclientip. The percent is the percentage of events that have thisclientip.
- You now need to run another search to determine how many different products the VIP shopper has purchased.
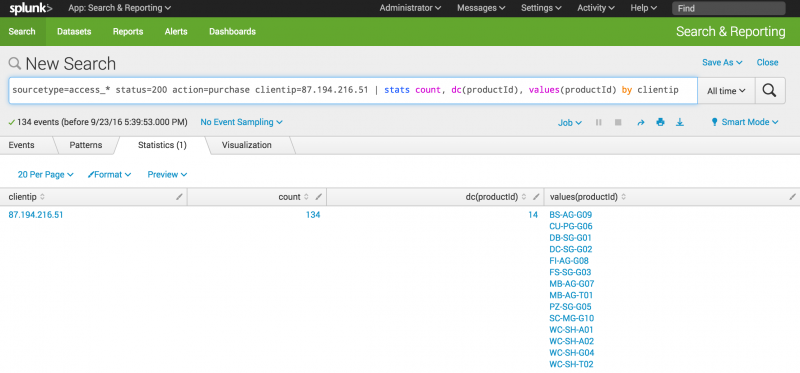
- Use the
statscommand to count the purchases by this VIP customer.sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase clientip=87.194.216.51 | stats count, dc(productId), values(productId) by clientip
- This search uses the
count()function to return the total count of the purchases for the shopper. Thedc()function is the distinct_count function. Use this function to count the number of different, or unique, products that the shopper bought. Thevaluesargument is used to display the actual product IDs in the results.
- The drawback to this approach is that you have to run two searches each time you want to build this table. The top purchaser is not likely to be the same person for any given time range.
- Let's try using a subsearch instead. Our first requirement is to identify the single most frequent shopper on the Buttercup Games online store.
- Copy and paste the following search into the Search bar and run the search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip
- This search returns the clientip for the most frequent shopper,
clientip=87.194.216.51. This search is almost identical to the search in Step 1. Because thetopcommand returns the count and percent fields, thetablecommand is used to keep only theclientipvalue.
- The search to identify the most frequent shopper becomes the subsearch for the search to determine what the shopper has purchased. Because you are searching the same data, the beginning of the main search is identical to the beginning of the subsearch.
- A subsearch is enclosed in square brackets [ ] and processed first when the search is parsed.
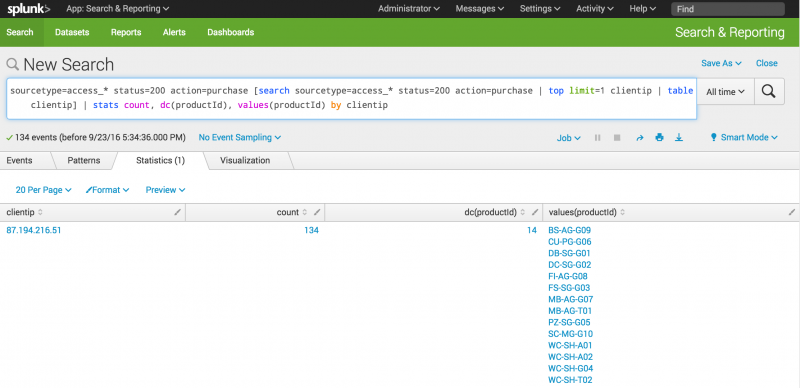
- Copy and paste the following search into the Search bar and run the search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase [search sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip] | stats count, dc(productId), values(productId) by clientip
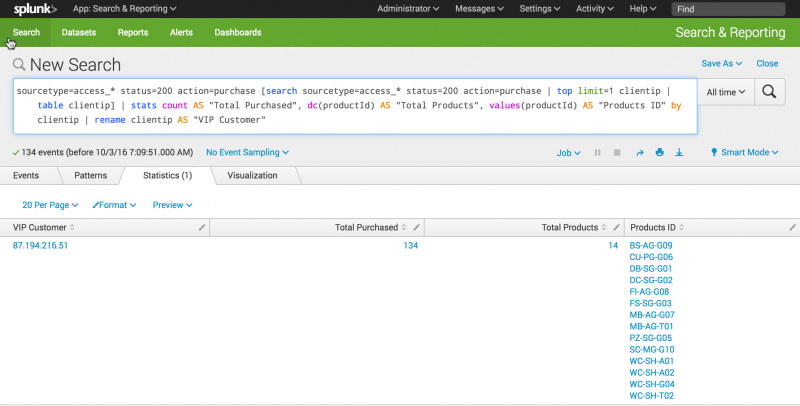
You rename columns by using the AS operator on the fields in your search. If the rename that you want to use contains a space, you must enclose the rename in quotation marks.Column Rename count Total Purchased dc(productId) Total Products values(productId) Products ID clientip VIP Customer - To rename the fields, copy and paste the following search into the Search bar and run the search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase [search sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip] | stats count AS "Total Purchased", dc(productId) AS "Total Products", values(productId) AS "Products ID" by clientip | rename clientip AS "VIP Customer"
Subsearch performance considerations
A subsearch can be a performance drain if the search returns a large number of results.
Consider this search.
sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase [search sourcetype=access_* status=200 action=purchase | top limit=1 clientip | table clientip] | stats count, dc(productId), values(productId) by clientip
The performance of this subsearch depends on how many distinct IP addresses match status=200 action=purchase. If there are thousands of distinct IP addresses, the top command has to keep track of all of them before the top 1 is returned, impacting performance.
Additionally, by default subsearches return a maximum of 10,000 results and have a maximum runtime of 60 seconds. In large production environments it is quite possible that the subsearch in this example will timeout before it completes.
There are several alternatives you can use to control the results:
- Try to rewrite the query to limit the number of events the subsearch must process.
- You can change the number of results that the format command operates over inline with your search by appending the
formatcommand to the end of your subsearch.
...| format maxresults = <integer>
- For more information, see the
formatcommand in the Search Reference.
- For more information, see the
If you are using Splunk Enterprise, you can also control the subsearch by editing settings in the limits.conf file. See How to edit a configuration file. Edit the settings for the runtime and maximum number of results returned.
[subsearch]
maxout = <integer>
- Maximum number of results to return from a subsearch.
- This value cannot be greater than or equal to 10500.
- Defaults to 10000.
maxtime = <integer>
- Maximum number of seconds to run a subsearch before finalizing
- Defaults to 60.
ttl = <integer>
- Time to cache a given subsearch's results, in seconds.
- Do not set this below 120 seconds.
- Defaults to 300.
After running a search you can click the Job menu and select Inspect Job to open the Search Job Inspector. Scroll down to the remoteSearch component, and you can see what the actual query that resulted from your subsearch. For more information, see View search job properties in this manual.
Output settings for subsearch commands
By default, subsearches return a maximum of 10,000 results. You will see variations in the actual number of output results because every command can change what the default maxout is when the command invokes a subsearch. Additionally, the default applies to subsearches that are intended to be expanded into a search expression, which is not the case for some commands such as join, append, and appendcols.
- For example, the
appendcommand can override the default maximum if themaxresultrowsargument is specified, unless you specifymaxoutas an argument to theappendcommand. - The output limit of the
joincommand is controlled bysubsearch_maxoutin thelimits.conffile. This defaults to 50,000 events.
Answers
Have questions? Visit Splunk Answers and see what questions and answers the Splunk community has about using subsearches.
| Use time to find nearby events | Use subsearch to correlate events |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.0.0, 7.0.1, 7.0.2, 7.0.3, 7.0.4, 7.0.5, 7.0.6, 7.0.7, 7.0.8, 7.0.9, 7.0.10, 7.0.11, 7.0.13
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!