history
Description
Use this command to view your search history in the current application. This search history is presented as a set of events or as a table.
Syntax
| history [events=<bool>]
Required arguments
None.
Optional arguments
- events
- Syntax: events=<bool>
- Description: When you specify
events=true, the search history is returned as events. This invokes the event-oriented UI which allows for convenient highlighting, or field-inspection. When you specifyevents=false, the search history is returned in a table format for more convenient aggregate viewing. - Default: false
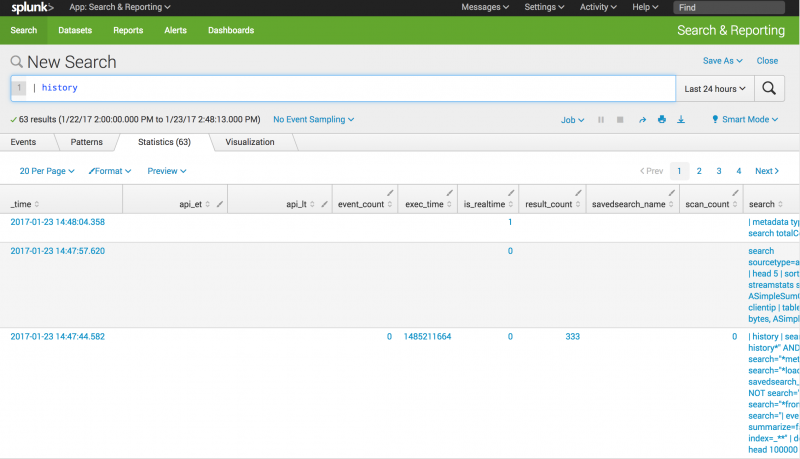
Fields returned when events=false.
Output field Description _timeThe time that the search was started. api_etThe earliest time of the API call, which is the earliest time for which events were requested. api_ltThe latest time of the API call, which is the latest time for which events were requested. event_countIf the search retrieved or generated events, the count of events returned with the search. exec_timeThe execution time of the search in integer quantity of seconds into the Unix epoch. is_realtimeIndicates whether the search was real-time (1) or historical (0). result_countIf the search is a transforming search, the count of results for the search. scan_countThe number of events retrieved from a Splunk index at a low level. searchThe search string. search_etThe earliest time set for the search to run. search_ltThe latest time set for the search to run. sidThe search job ID. splunk_serverThe host name of the machine where the search was run. statusThe status of the search. total_run_timeThe total time it took to run the search in seconds.
Usage
The history command is a generating command and should be the first command in the search. Generating commands use a leading pipe character.
The history command returns your search history only from the application where you run the command.
Examples
Return search history in a table
Return a table of the search history. You do not have to specify events=false, since that this the default setting.
| history
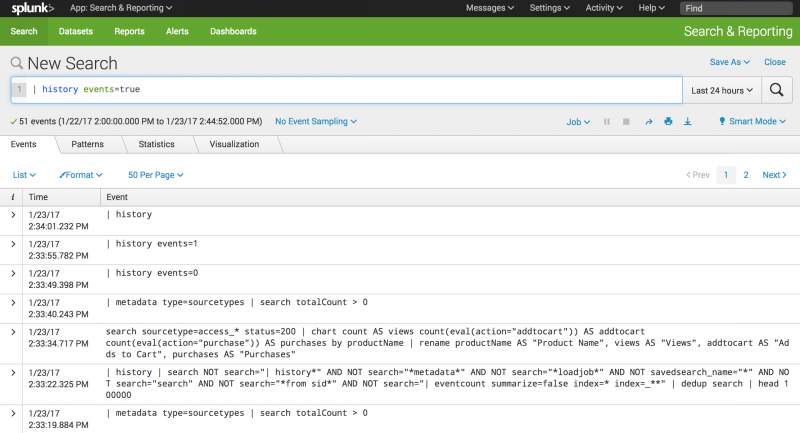
Return search history as events
Return the search history as a set of events.
| history events=true
See also
- Commands
- search
| highlight | iconify |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.0.0, 7.0.1, 7.0.2, 7.0.3, 7.0.4, 7.0.5, 7.0.6, 7.0.7, 7.0.8, 7.0.9, 7.0.10, 7.0.11, 7.0.13, 7.1.0, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.1.5, 7.1.6, 7.1.7, 7.1.8, 7.1.9, 7.1.10, 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10, 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9, 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.2, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.1.5, 8.1.6, 8.1.7, 8.1.8, 8.1.9, 8.1.10, 8.1.11, 8.1.12, 8.1.13, 8.1.14, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.2.4, 8.2.5, 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.1.9, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.2.6, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.3.4, 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!