eventcount
Description
Returns the number of events in the specified indexes.
Syntax
The required syntax is in bold.
- | eventcount
- [index=<string>]...
- [summarize=<bool>]
- [report_size=<bool>]
- [list_vix=<bool>]
Required arguments
None.
Optional arguments
- index
- Syntax: index=<string>
- Description: A name of the index report on, or a wildcard matching many indexes to report on. You can specify this argument multiple times, for example
index=* index=_*. - Default: If no index is specified, the command returns information about the default index.
- list_vix
- Syntax: list_vix=<bool>
- Description: Specify whether or not to list virtual indexes. If
list_vix=false, the command does not list virtual indexes. - Default: true
- report_size
- Syntax: report_size=<bool>
- Description: Specify whether or not to report the index size. If
report_size=true, the command returns the index size in bytes. - Default: false
- summarize
- Syntax: summarize=<bool>
- Description: Specifies whether or not to summarize events across all peers and indexes. If
summarize=false, the command splits the event counts by index and search peer. - Default: true
Usage
The eventcount command is a report-generating command. See Command types.
Generating commands use a leading pipe character and should be the first command in a search.
Specifying a time range has no effect on the results returned by the eventcount command. All of the events on the indexes you specify are counted.
Specifying indexes
You cannot specify indexes to exclude from the results. For example, index!=foo is not valid syntax.
You can specify the index argument multiple times. For example:
|eventcount summarize=false index=_audit index=main
Running in clustered environments
Do not use the eventcount command to count events for comparison in indexer clustered environments. When a search runs, the eventcount command checks all buckets, including replicated and primary buckets, across all indexers in a cluster. As a result, the search may return inaccurate event counts.
Examples
Example 1:
Display a count of the events in the default indexes from all of the search peers. A single count is returned.
| eventcount
Example 2:
Return the number of events in only the internal default indexes. Include the index size, in bytes, in the results.
| eventcount summarize=false index=_* report_size=true
The results appear on the Statistics tab and should be similar to the results shown in the following table.
| count | index | server | size_bytes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 52550 | _audit | buttercup-mbpr15.sv.splunk.com | 7217152 |
| 1423010 | _internal | buttercup-mbpr15.sv.splunk.com | 122138624 |
| 22626 | _introspection | buttercup-mbpr15.sv.splunk.com | 98619392 |
| 10 | _telemetry | buttercup-mbpr15.sv.splunk.com | 135168 |
| 0 | _thefishbucket | buttercup-mbpr15.sv.splunk.com | 0 |
When you specify summarize=false, the command returns three fields: count, index, and server. When you specify report_size=true, the command returns the size_bytes field. The values in the size_bytes field are not the same as the index size on disk.
Example 3:
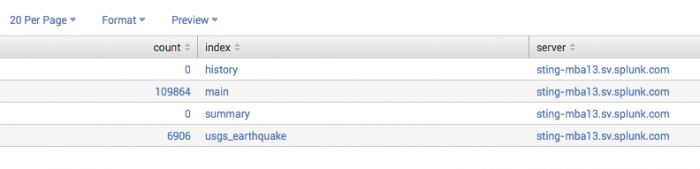
Return the event count for each index and server pair. Only the external indexes are returned.
| eventcount summarize=false index=*
To return the count all of the indexes including the internal indexes, you must specify the internal indexes separately from the external indexes:
| eventcount summarize=false index=* index=_*
See also
| eval | eventstats |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk Cloud Platform™: 9.2.2403, 8.2.2201, 8.2.2203, 8.2.2112, 8.2.2202, 9.0.2205, 9.0.2208, 9.0.2209, 9.0.2303, 9.0.2305, 9.1.2308, 9.1.2312
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!