Plan and scale your Splunk UBA deployment
Install Splunk UBA in a single-server or distributed deployment architecture. A distributed deployment helps you scale your Splunk UBA installation.
Scaling your deployment
A distributed Splunk UBA deployment scales horizontally with streaming and batch servers. Because the nodes in a distributed Splunk UBA deployment perform a high number of computations among them and require fast network connections, do not deploy Splunk UBA across different geographical locations. If you have multiple sites, configure a duplicate Splunk UBA cluster as a warm standby system. See Configure warm standby in Splunk UBA in the Administer Splunk User Behavior Analytics manual.
Use the parameters below to guide you in properly sizing your Splunk UBA deployment. Exceeding the limits will have a negative impact on performance and can result in events being dropped and not processed.
- The Max events per second capacity represents the peak events rate processed by Splunk UBA when ingesting data from Splunk Enterprise.
- The Max Number of accounts represents the total number of accounts monitored by Splunk UBA, such as user, admin, system, or service accounts.
- The Max Number of devices represents the total number of devices monitored by Splunk UBA.
- The Max number of data sources represents the total number of data source connectors configured on Splunk UBA to ingest data from Splunk Enterprise.
| Size of cluster | Max events per second capacity | Max Number of accounts | Max Number of devices | Max number of data sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 node | 4K | up to 50K | up to 100K | 6 |
| 3 nodes | 12K | up to 50K | up to 200K | 10 |
| 5 nodes | 20K | up to 200K | up to 300K | 12 |
| 7 nodes | 28K | up to 350K | up to 500K | 24 |
| 10 nodes | 40K-45K | up to 350K | up to 500K | 32 |
| 20 nodes | 75K-80K | up to 750K | up to 1 Million | 64 |
Engage Splunk engineering if the requirements for your environment exceed the limits listed in the table above.
After Splunk UBA is operational, you must perform regular maintenance of your Splunk UBA deployment by managing the number of threats and anomalies in your system. See Manage the number of threats and anomalies in your environment for information about the maximum number of threats and anomalies that should be in your system based on your deployment size.
Sizing and deployment example
Below is an example of how to determine the proper deployment for a particular environment:
- Use the following
tstatsquery on Splunk Enterprise. This query obtains the EPS statistics for the last 30 days.| tstats count as eps where index=* earliest=-30d@d groupby index, sourcetype _time span=1s | stats count as NumSeconds max(eps) perc99(eps) perc90(eps) avg(eps) as avg_eps by index, sourcetype | addinfo | eval PercentageOfTimeWithData = NumSeconds / (info_max_time - info_min_time) | fields - NumSeconds info* | eval EffectiveAverage = avg_eps * PercentageOfTimeWithData | fieldformat PercentageOfTimeWithData = round(PercentageOfTimeWithData*100,2) . "%" - Export the results to a CSV file. See Export search results in the Splunk Enterprise Search Manual for options and instructions.
- Using a spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel, open the CSV file and remove all rows that have data sources that will not be ingested into Splunk UBA. See Which data sources do I need? in the Get Data into Splunk User Behavior Analytics manual to determine the data sources you need to configure. The data sources you need will vary depending on your environment and the content you want to see in Splunk UBA.
- Get a total of the EPS in the 99% and 90% columns. Base your sizing requirements on the 99% column to get the added benefit of providing a cushion of extra nodes.
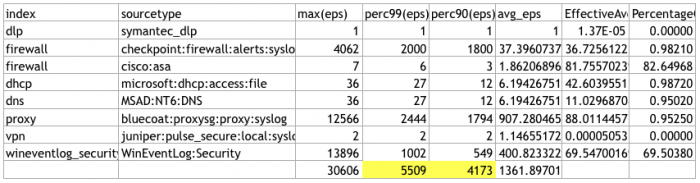
This example has a total EPS in the 99% column over 5,000 and fewer than 10 data sources, meaning that a 3-node deployment is sufficient.
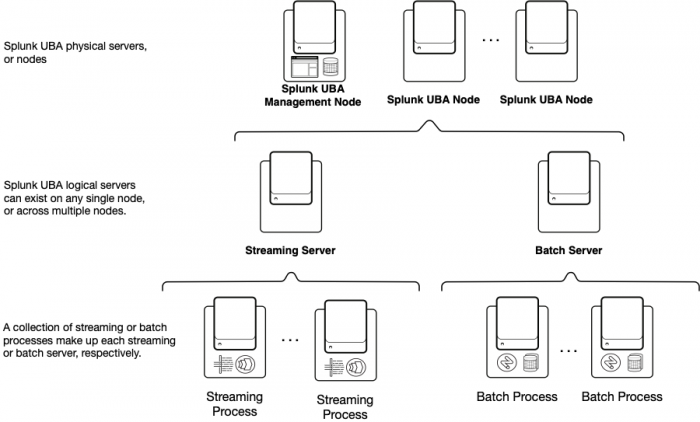
Splunk UBA deployment architecture
To scale Splunk UBA in a distributed deployment, Splunk UBA assigns each physical server, or node, in a cluster to a specific task. Each node then has specific services installed to support that task. The specific services installed on each node can vary depending on the size of your cluster. For example, in a 7-node deployment, Spark services are installed on node 7 only, while Hadoop services are installed on all nodes except for node 3.
- See Monitor the health of your Splunk UBA deployment in Administer Splunk User Behavior Analytics for more information about each type of service.
- See Where services run in Splunk UBA in Administer Splunk User Behavior Analytics for more information about finding where services are running in your Splunk UBA deployment.
In a single-node deployment, all services provided by the streaming and batch servers exist on the same node.
All nodes in your Splunk UBA deployment must meet the System requirements for Splunk UBA.
| Server | Description |
|---|---|
| Management server | The management server hosts the Splunk UBA web interface. You only need one management server.
|
| Streaming server | Streaming servers are logical servers consisting of a collection of related streaming processes. A streaming server can exist on any single Splunk UBA node or across multiple nodes.
|
| Batch server | Batch servers are logical servers consisting of a collection of related batch processes. A batch server can exist on any single Splunk UBA node or across multiple nodes.
|
| Splunk UBA installation checklist | System requirements for Splunk UBA |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® User Behavior Analytics: 5.0.0, 5.0.1, 5.0.2, 5.0.3, 5.0.4, 5.0.4.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!