What a Splunk App for Unix and Linux deployment looks like
This topic explains the overall architecture of a Splunk App for Unix and Linux deployment.
For instructions on how to deploy the app, read "Install the Splunk App for Unix and Linux."
For instructions on how to deploy the add-on, read "Install the Splunk Add-on for Unix and Linux."
Overview
The Splunk App for Unix and Linux can be deployed in a number of ways. The most common way is to deploy a "central" Splunk instance that has indexers and search heads, contains the main Splunk App for Unix and Linux index, and runs Splunk Web.
The central Splunk instance can be one or more servers
A central Splunk instance can consist of one or more servers. In a single indexer setup, a Splunk App for Unix and Linux deployment collects data about itself. In a multiple-server configuration, you can deploy:
- At least one indexer that collects data from itself or other *nix servers
- One or more search heads that search the collected data and host the application.
You can distribute the central Splunk instance further by adding more indexers and search heads. This allows you to scale the deployment for additional incoming data volume.
The central Splunk instance can run on any Splunk-supported operating system
You can deploy the Splunk App for Unix and Linux on Windows search heads and use Windows indexers to index the data. In this scenario, the Windows indexers must receive data sent to them from *nix servers with universal forwarders installed. The Windows indexers cannot collect *nix data themselves.
The Splunk App for Unix and Linux can monitor many *nix servers at once
The Splunk App for Unix and Linux supports collecting data from hundreds of servers. There are many ways to configure the Splunk App for Unix and Linux, depending on your network's topology.
You monitor additional servers with your Splunk App for Unix and Linux deployment by:
- Installing universal forwarders on each *nix server you want to include in the environment.
- Configuring the forwarders to send data to the indexers in the central Splunk instance.
- Deploying the Splunk Add-on for Unix and Linux onto those forwarders.
You can use a deployment server to manage universal forwarder configurations and deploy the Splunk Add-on for Unix and Linux onto many *nix servers at once.
Example deployment
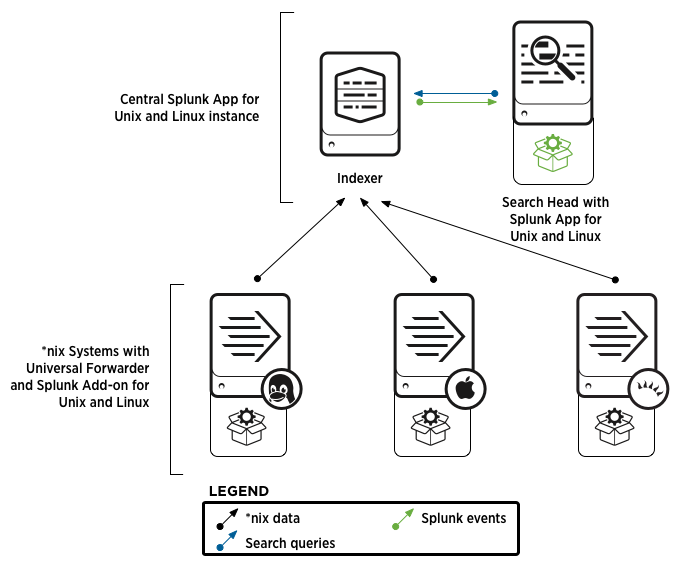
The diagram below depicts an example Splunk App for Unix and Linux deployment.
Each *nix server on your network gets a Splunk universal forwarder. On that forwarder, you install the Splunk Add-on for Unix and Linux which collects *nix data and sends it to the indexer(s) in the central Splunk App for Unix and Linux instance.
The central Splunk App for Unix and Linux instance has at least a search head (with the Splunk App for Unix and Linux installed on it) and an indexer. The indexer indexes the *nix data (as shown by the black arrows), and the search head searches the indexer for that data (as shown by the green arrow). The indexer returns events to the search head (blue arrow). Users log into the search head to use the app and see the data.
Splunk's Professional Services can help with questions and provide assistance with large or complex layouts.
| Other deployment considerations | Install the Splunk App for Unix and Linux |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for Unix and Linux (EOL): 5.2.5, 6.0.0, 6.0.1, 6.0.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!