About VMware
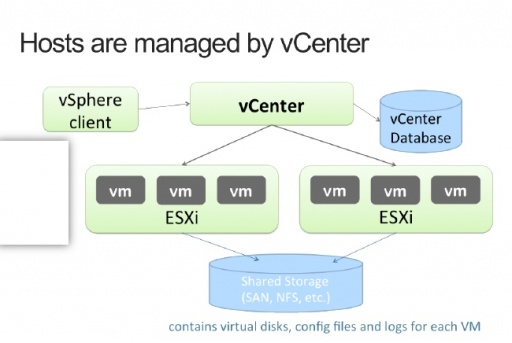
A VMware environment consists of a vCenter management console managing the VMs and ESX/I hosts (physical hosts) in a virtual environment. vCenter manages all the configuration tasks for the managed resources to enable them to support the day-to-day business applications. As a VMware administrator you can set alarms and events to automatically notify you of changes in your environment (such as a virtual machines being moved or hosts failing), you can manage clusters (groups of hosts managed as single entities), and data centers (groups of physical resources such as hosts, virtual machines, networks, and data stores).
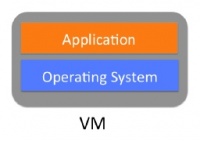
In VMware a virtual machine runs on a physical server. The hypervisor take on the responsibility of the OS and manages the interaction between the virtual machines and the physical hardware.
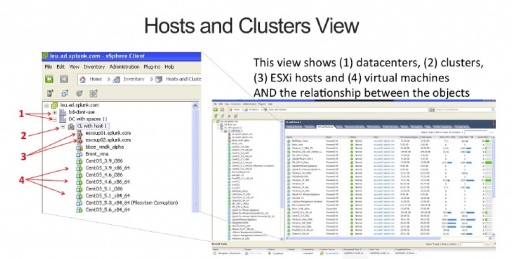
In data centers the names for the physical resources (hosts, virtual machines, networks, and data stores) must be unique. The cluster resources (such as CPU, memory) are managed by vCenter. In a cluster, a virtual machine can be moved between ESX/I hosts by vCenter for many reasons such as to load balance and reduce the demand on a particular resource or If a Host fails, a VM can be moved to restart it.
vSphere client is the windows based desktop administration console. Use this console to access your managed resurces in your VMware environment.
| Requirements for collecting data | About Splunk for VMware |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for VMware (EOL): 1.0, 1.0.1, 1.0.2, 1.0.3, 2.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!