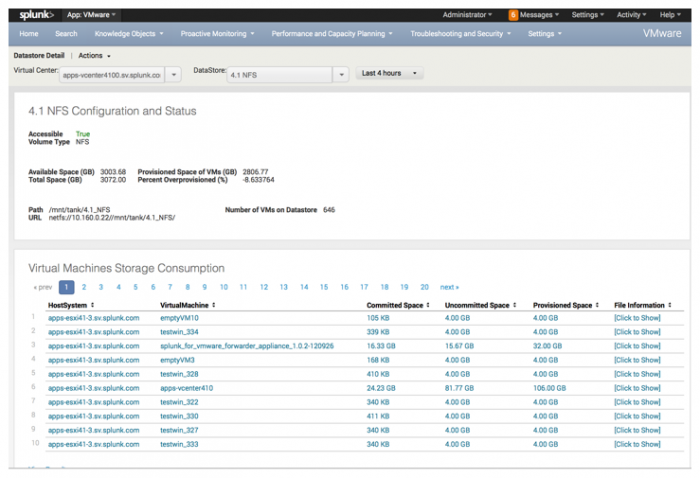
Datastore Detail
On the Datastore Detail dashboard you can access information about the storage layer in your environment. Using this dashboard you can:
- Monitor the most important performance metrics such as latency and IOPS for the connected datastore, at the filer and at the volume level.
- Correlate virtual machine performance with storage performance (specifically NetApp storage).
- Reduce the time it takes to identify a problem if storage performance degradation affects all of the hosts or some of the virtual machines on a particular datastore.
Display datastore details
Look at the details for a specific datastore either by using the drop-down lists to select a specific datastore, or drill down from another dashboard in the app to automatically populate the dashboard.
Use the drop-down lists to select:
- a virtual center.
- a datastore.
- a time range.
The panels in the dashboard populate with data about the datastore you selected.
Look at the configuration and status of the datastore
On this panel you can get information about the state of the datastore, such as:
- If the datastore is accessible.
- The volume type, for example, an NFS volume.
- The available space and total space, in GB, on the datastore.
- The space provisioned, in GB, for a virtual machine, and the percent overprovisioned.
- The path to the datastore and the associated URL.
- The number of virtual machines on the datastore.
The following search is used to populate the panel:
sourcetype="ontap:volume" (source=volume-get-iter OR source=volume-list-info-iter-start) | eval name=coalesce(name, "volume-id-attributes.name") | stats values(name) as volname by host | lookup dnslookup clienthost AS host OUTPUT clientip AS ip | mvexpand volname | table * | join type=inner ip, volname [search sourcetype=vmware:inv:datastore changeSet.info.nas.type="NFS" earliest=-24h latest=now | rename changeSet.info.nas.name as name, changeSet.info.nas.remotePath as path, changeSet.info.nas.remoteHost as filer, host as vcenter | dedup path, filer | rex field=path ".+/(?<volname>[^/]+)" | lookup dnslookup clienthost AS filer OUTPUT clientip AS ip | table name, moid, path, filer, ip, volname, vcenter] | rename name as "Datastore name", path as "Path", volname as Volume, filer as "Filer (VMware data)", host as Filer, ip as IP, vcenter as VCenter | search moid=$name.moid$
Get the Datastore Filer Latency rate
look here to quickly see whether storage latency is a contributing factor to reduced performance in your environment. Spikes in latency rates indicate that you need to investigate more.
Filer latency rates are measured by monitoring performance metrics that track average reads and writes to the filer. Measuring latency is important to prevent performance problems in the application layer.
The following search is used to populate the panel:
| `tstats` avg(read_latency_average), avg(write_latency_average), avg(other_latency_average) from netapp_perf_volume groupby _time span=2m, host | search [search `SystemHostname($filer[0].Filer$)`] | timechart avg(read_latency_average), avg(write_latency_average), avg(other_latency_average) by host | rename avg(read_latency_average) AS read_latency, avg(write_latency_average) AS write_latency, avg(other_latency_average) AS other_latency | eval read_latency=read_latency/1000 | eval write_latency=write_latency/1000 | eval other_latency=other_latency/1000
Get the Datastore Filer IOPS rate
Look at this panel to monitor filer IOPS if you are concerned about latency in your environment. You can get poor virtual machine performance if your virtual machines do not have enough I/O per second (IOPS), or network throughput.
The following search is used to populate the panel:
| `tstats` avg(read_ops_rate), avg(write_ops_rate), avg(other_ops_rate), avg(total_ops_rate) from netapp_perf_system groupby _time span=5m, host | search [search `SystemHostname($filer[0].Filer$)`] | timechart limit=5 avg(read_ops_rate), avg(write_ops_rate), avg(other_ops_rate), avg(total_ops_rate) by host
Get the Datastore Volume Latency rate
On this panel you can measure volume latency rates by monitoring performance metrics that track average reads and writes to the volume on the disk.
The following search is used to populate the panel:
sourcetype=ontap:perf source=VolumePerfHandler host=$volume[0].Filer$ objname=$volume[0].Volume$ | timechart limit=5 first(eval(avg_latency_average/1000)) as avg_latency_average first(eval(other_latency_average/1000)) as avg_latency_average first(eval(write_latency_average/1000)) as write_latency_average first(eval(read_latency_average/1000)) as read_latency_average by objname
Get the Datastore Volume IOPS rate
In this panel you can monitor volume IOPS if you are concerned about latency in your environment. You can get poor virtual machine performance if your virtual machines do not have enough I/O per second (IOPS).
The following search is used to populate the panel:
sourcetype=ontap:perf source=VolumePerfHandler host=$volume[0].Filer$ objname=$volume[0].Volume$ | timechart limit=5 first(total_ops_rate) as total_ops_rate first(write_ops_rate) as write_ops_rate first(read_ops_rate) as read_ops_rate first(other_ops_rate) as other_ops_rate by objname
Correlate VMware data with NetApp ONTAP storage data
Issues in the storage layer can impact the performance of virtual machines in your environment. You can correlate issues in your VMware infrastructure with NetApp storage issues using the Datastore Detail dashboard. This correlation feature enables you to better troubleshoot problems in your infrastructure and identify where the problems exist between the VMware hosts and your NetApp ONTAP filers.
For example, if virtual machines on an NFS datastore named "ISO" in the Splunk App for VMware cause a problem in your environment, you can drill down to the filer and the specific volume in the Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP and look at the performance information for the datastore known in your VMware environment as "ISO".
Correlation Requirements
To correlate VMware data with NetApp ONTAP data, you must have the following apps installed in your environment:
- The Splunk App for VMware.
- The Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP.
The correlation feature enables you to drill down from a dashboard in the Splunk App for VMware to the Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP and get specific filer and volume performance information.
For more information about installation and configuration of the apps, see their respective Installation and Configuration Guides, the "Splunk App for VMware Installation Guide" and the "Deploy and Use the Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP" manual.
Required sourcetypes
The following sourcetypes must be present for this dashboard to populate:
- The ontap:volume and ontap:perf sourcetypes must be present to get information about the volumes in the NetApp ONTAP environment.
- The vmware:inv:datastore sourcetype must be present to get information about the NFS volumes in the VMware environment.
Display Filer volume level details
Drill down from the filer to the datastore level to see details for a specific filer volume.
To display volume level details:
- In the Datastore Filer Latency rate panel, click a filer name.
- The Filer View dashboard of the Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP is displayed.
- Look at the specific storage controllers that have an impact on the performance of your environment.
For information on this dashboard, see "Filer View" in the Deploy and Use the Splunk App for NetApp Data ONTAP manual.
| Cluster Detail | Performance of Hosts and VMs |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for VMware (EOL): 3.1, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4, 3.2.0, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.3.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!