Troubleshoot the Splunk App for Anomaly Detection
The following are issues you might experience when using the Splunk App for Anomaly Detection and how to resolve them. If you don't see the information you need, you can ask your question and get answers through community support at Splunk Answers.
You see a "Splunk App for Anomaly Detection requires the [PSC/MLTK] add-on to be installed" banner
Cause
You are not running the required version(s) of the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) app or the Python for Scientific Computing (PSC) add-on.
Solution
Update MLTK or PSC to the required version(s). See, Version dependencies for the Splunk App for Anomaly Detection.
The app is lagging or hanging when you try to add or manage jobs
Cause
You are not running the required version(s) of the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) app or the Python for Scientific Computing (PSC) add-on.
Solution
Update MLTK or PSC to the required version(s). See, Version dependencies for the Splunk App for Anomaly Detection.
Data health diagnostics detects issues
Cause
When you select the numeric field on which you'd like to detect anomalies, the app runs a health diagnostic. If you data is missing values or rows, or the data has unevenly spaced timestamps, the data quality icon shows as red.
Solution
Perform some cleanup on your data and query again. You can leverage commands like fillnull to fill in missing or non-numeric values. You can use aggregation such as the bin command to create evenly-spaced temporal data.
The full dataset doesn't show up in the listed results or on plot
Cause
The app truncates the time series at ten-thousand data points.
Solution
Trim your data to only the most interesting ten-thousand data points, or run the data in batches.
The time range selected in time range picker is not being applied to output of inputlookup
Cause
The time range picker doesn't apply to the inputlookup command in this app.
Solution
Switch to a search instead, or consider using the head or tail commands:
- For the syntax of the
headcommand, see head in the Search Reference. - For the syntax of the
tailcommand, see tail in the Search Reference.
You can also choose to edit your lookup to only include data from the time range you're interested in analyzing for anomalies.
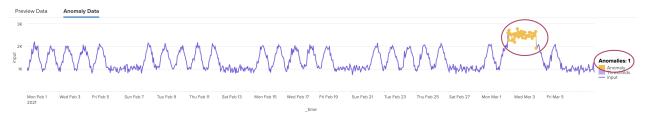
The Anomalies count to the right of the anomaly plot does not match the number of yellow dots in the plot or number of rows in the anomaly results table
Cause
This is expected behavior. Adjacent anomalous points are counted as a single anomalous interval.
| Support for the Splunk App for Anomaly Detection |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for Anomaly Detection: 1.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!