Use the Entities page in behavioral analytics service to begin your investigation for hidden and unknown threats. For example, suppose you are investigating a notable in Splunk Mission Control, and want to see if behavioral analytics service can provide additional insight or supporting evidence. The entity in question might have a low risk score, but you can examine the entity to see all the anomalies associated with that entity over time and uncover some abnormal behavior warranting further investigation. You can also begin an investigation in behavioral analytics service and create a notable in Splunk Mission Control if you discover sufficient evidence.
From Splunk Mission Control, click Investigation > Entities to access the behavioral analytics service Entities list and Treemap.
Entities are users or devices in your environment. See How to import assets and identities data from Splunk ES on Splunk Cloud Platform into behavioral analytics service for information about how this data gets into behavioral analytics service.
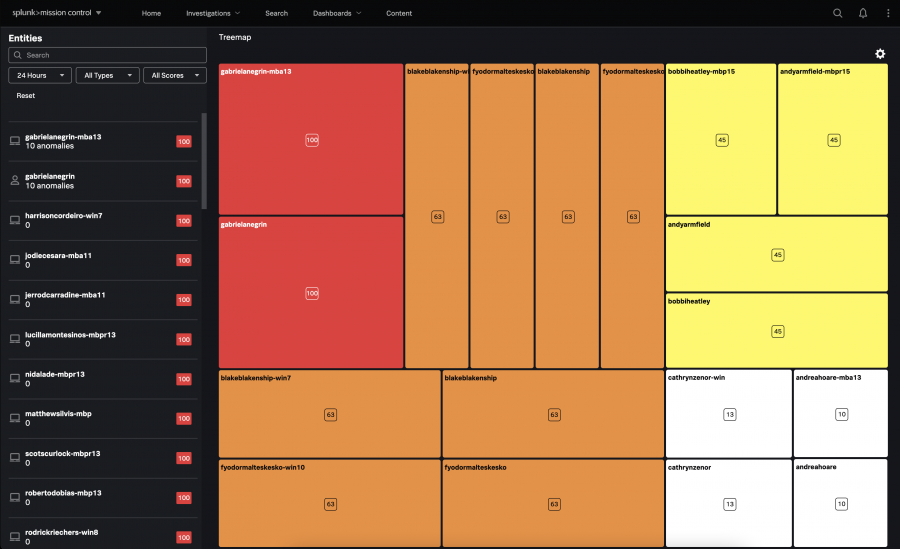
The entities with the highest risk score appear at the top of the Entities list. Use the Treemap to quickly identify the entities with the highest number of anomalies. The larger the box, the higher the number of anomalies associated with that entity.
View and filter the entities in the Entities list to begin a specific investigation
The Entities list shows you the entities being managed by behavioral analytics service in descending order by risk score. Entities with a risk score of 100 appear at the top of the list, and entities with a risk score of 0 appear at the bottom of the list. Note that only entities with a prior risk score greater than 0 and with a current risk score of 0 appear at the bottom of the Entities list. Entities with no prior risk or risk score do not appear on the Entities list.
Scroll through the list as needed to see entities with a lower risk score. See How behavioral analytics service calculates and maintains risk levels and risk scores for more information about the normalized entity risk scores.
Filter the entities you see on this page by type and score
You can filter the entities you see on this page by compute window, type, and score. For example, click All Scores and select Critical (91-100) so that only entities with a critical risk score appear on the Entities page. Further refine the list by clicking All Types and selecting Users so that devices do not appear on the page.
You can reset all filters to their default values to begin a new investigation by clicking Reset. By default, entities of all types and scores are listed based on risk scores computed from anomalies in the past 24 hours.
Filter the entities you see on this page by compute window
Behavioral analytics service standardizes all events to use UTC-7 time. By default, entities are ranked by their normalized risk scores based on anomalies detected in the past 24 hours. Select 7 Days to view the entities based on their normalized risk scores over the past 6 days plus back to 07:00:00 UTC on the seventh day.
- The 24 Hours compute window is a rolling window with a granularity of 1 hour.
- The 7 Days compute window is a rolling window with a granularity of 1 day.
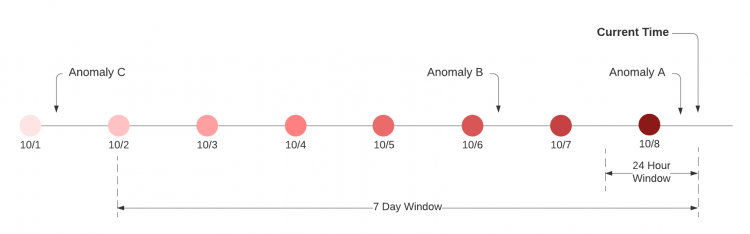
The following example shows the time windows considered for entity scoring using October 8 as the current date and 07:00:00 UTC as the current time:
The following table summarizes how the anomalies in the timeline are considered for entity scoring.
| Anomaly | Anomaly date and time | Is the anomaly considered for entity scoring? |
|---|---|---|
| Anomaly A | October 8, 04:00:00 UTC | Yes, if you select either 24 Hours or 7 Days as the compute window. |
| Anomaly B | October 6, 04:00:00 UTC |
|
| Anomaly C | October 1, 04:00:00 UTC | No for both compute windows. This anomaly is outside of both compute windows and is not considered in any entity scoring computation. |
Use the Treemap to quickly find the entities with the most anomalies
The Treemap provides an alternative visual and can help you quickly identify the entities in your organization with the highest number of anomalies.
The color of the box represents the risk score, and the size of the box represents the number of anomalies associated with the entity. If two entities have the same risk score but one entity has a larger box, the entity with the larger box has more anomalies associated with it than the entity with the smaller box. The entities with the highest risk score appear in the top-left portion of the treemap.
See How behavioral analytics service calculates and maintains risk levels and risk scores for more information about the normalized entity risk scores.
Click the gear icon to edit the treemap settings:
- Use the Density slider to restrict the number of entities shown in the treemap. For example, setting the slider to 20 causes fewer entities to show than setting the slider to 80.
- View the color key used in the treemap. The colors used in the severity levels match the colors used in Splunk Mission Control.
Color Corresponding risk level Corresponding risk score Red Critical 91 - 100 Orange High 61 - 90 Yellow Medium 31 - 60 White Low 0 - 30
View details about a specific entity
You can drill down to view details for any entity by performing one of the following tasks:
- Click on any entity in the entity list. Click on the entity to open the entity details in the same browser tab, or use command + click on MacOS or Ctrl + click on Windows to open the entity details in a new tab.
- Click on any entity in the treemap, then click View details. Click View details to open the entity details in the same browser tab, or use command + click on MacOS or Ctrl + click on Windows to open the entity details in a new tab.
| Generate a sample detection in behavioral analytics service | Drill down to view entity details in behavioral analytics service |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security: 7.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!