Enable detections from Analytic Stories
Before you enable a detection, you must first manually test the search and make some customizations.
For example, if you're interested in common Azure-related security issues, you can start by filtering on known use cases for cloud security or look for a keyword called "Azure".
Follow these steps to enable detections from analytic stories:
- From the Splunk Enterprise Security menu bar, select Configure > Content > Use Case Library.
- From the use cases filters on the left, select Cloud Security.
- If you choose to search for an analytic story such as Azure Active Directory Account Takeover, select the greater than ( >) symbol to expand the display.
You can see the detection searches that are related to this use case. - Select the name of the analytic story. In this example, select Azure Active Directory Account Takeover.
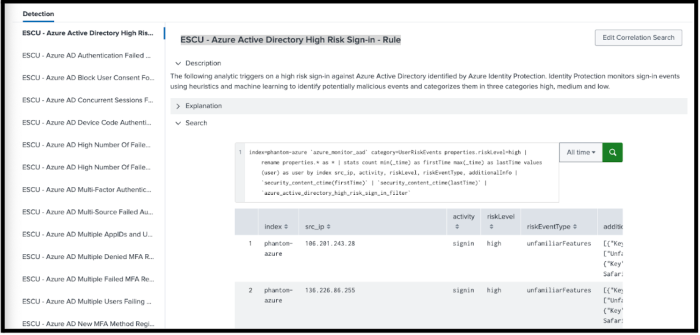
The Analytic Story Details page opens for the analytic story and you can see all the detection searches. - From the Detection section, select a search, such as ESCU - Azure Active Directory High Risk Sign-in - Rule.
- From the Search section, select the greater than (>) symbol to expand the display.
- Revise the time picker to last 7 days and select Search.
- From the How to Implement section, select the greater than (>) symbol to expand the display for tips on implementation.
- From the Known False Positives section, select the greater than (>) symbol to expand the display for tips on when the results might not indicate a problem.
| Status of detection analytics | Turn on the detection |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security Content Update: 3.22.0, 3.23.0, 3.24.0, 3.25.0, 3.26.0, 3.27.0, 3.28.0, 3.29.0, 3.30.0, 3.31.0, 3.32.0, 3.33.0, 3.34.0, 3.35.0, 3.36.0, 3.37.0, 3.38.0, 3.39.0, 3.40.0, 3.41.0, 3.42.0, 3.43.0, 3.44.0, 3.45.0, 3.46.0, 3.47.0, 3.48.0, 3.49.0, 3.50.0, 3.51.0, 3.52.0, 3.53.0, 3.54.0, 3.55.0, 3.56.0, 3.57.0, 3.58.0, 3.59.0, 3.60.0, 3.61.0, 3.62.0, 3.63.0, 3.64.0, 4.0.0, 4.0.1, 4.1.0, 4.2.0, 4.3.0, 4.4.0, 4.5.0, 4.6.0, 4.7.0, 4.8.0, 4.9.0, 4.10.0, 4.11.1, 4.12.0, 4.13.0, 4.14.0, 4.15.0, 4.16.0, 4.17.0, 4.18.0, 4.19.0, 4.20.0, 4.21.0, 4.22.0, 4.23.0, 4.24.0, 4.25.0, 4.26.0, 4.27.0, 4.28.0, 4.29.0, 4.30.0, 4.31.0, 4.31.1, 4.32.0, 4.33.0, 4.34.0, 4.35.0, 4.36.0, 4.37.0, 4.38.0, 4.39.0, 4.40.0, 4.41.0, 4.42.0, 4.43.0, 4.44.0, 5.0.0, 5.1.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!