Scope and precedence importing items
When items are exported from a source, those items are made public. However, to use those items you must have access to the module from which the items were exported. And, you must import those items into the module in which you want to use the exported items.
When importing items, it's important that you understand scope and precedence.
Scope
Scope defines which items are available for you to use from your current module. Your current module is the module in which you are actively creating searches.
The following list defines what is "in scope" for you to use from your current module:
| In scope | Description |
|---|---|
| Items in the current module | Any item created in a module is available for you to use inside that module. |
| items that are imported | Items that you have imported from other modules are available for you to use in searches in your current module. |
| Items in the namespace where the current module resides | Items, such as datasets, in a namespace are available for you to use in your current module without importing those items. |
Scope examples
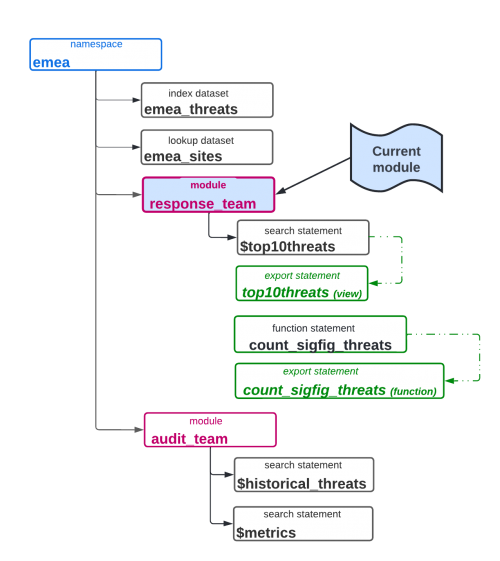
In the following image, your current module is the response_team module.
What you can use when the response_team module is the current module is described in the following table:
| Type of item | Items in scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Datasets |
|
Because the response_team module is in the emea namespace, you can use every dataset in the emea namespace.
|
| Statements |
|
|
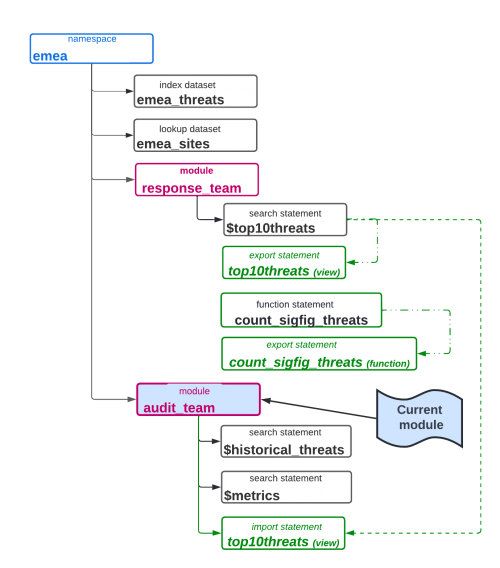
For comparison, suppose the current module is the audit_team module, as shown in this image:
Suppose your current module is the the audit_team module, and you have access to the response_team module. The following table describes what you can use while creating searches in the audit_team module:
| Type of Item | Items in scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Datasets |
|
|
| Statements |
|
|
Precedence
When you refer to an item in a search, such as the name of dataset, view, or function, SPL2 resolves the reference to the item by finding the matching item that is "in scope". See Scope.
If there are multiple items in scope that match the reference, for example if the items have the same name and are the same kind of item, then precedence rules determine which item to use.
Precedence rules
The following table shows the precedence rules order for items:
| Precedence order | Description |
|---|---|
| Local | Items created inside a module are local to that module and take precedence over items that are imported or built-in. |
| Imported | Imported items take precedence over built-in items. If there are naming conflicts, bulk imports and named imports behave differently.
|
| Namespace | For datasets only. |
| Built-in |
Precedence examples
Here are a few precedence examples:
Local items take precedence over imported items
Suppose you create a function called isError in a module. If the module also has an imported function called isError, then when the function is used in a search statement, the local isError function is used. The imported function is ignored. Local items take precedence over imported items.
Imported items take precedence over built-in items
Suppose you import a function called if into your module. When the function is used in a search statement, the imported if function is used instead of the built-in if function. The built-in function is ignored. Imported items take precedence over built-in items.
Different kinds of imported items with the same names do not cause a conflict
If one imported item is a function and the other imported item is a view, then even though the items have the same name there is no conflict because the items are different kinds of items. SPL2 determines which item to use based on how the item is used in the search. For example, where and how you specify functions in a search is different than where and how you can specify views.
Imported functions with the same name but a different number of arguments do not cause a conflict
If both imported items are functions with the same name but have a different number of arguments, the function that matches the arguments specified in your search is used. However, if both functions have the same number of arguments an error is returned.
If both items are imported using import *, then the last one imported is used no error is returned if they have the same number of arguments.
Avoiding precedence errors
To avoid precedence errors, you can use one of the following techniques:
- Rename an imported item
- Import items using a namespace alias.
For more information, see Naming conflicts when importing items.
See also
- Related information
- Importing items
- Specifying import paths
| Specifying import paths | Understanding SPL2 namespaces |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Cloud Services: current
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!