For details, see:
Create a new playbook in
Using or starting with an existing playbook can save you time and effort. Before creating a new playbook, try to find an existing playbook that you can use or modify. See Find existing playbooks for your apps.
Perform the following tasks to create a new playbook in :
- Click the menu bar, then select Playbooks.
- Click + Playbook to create a new playbook.
- Select either the Automation or Input type playbook. Select an automation playbook to run a playbook automatically based on triggers. Automation playbooks can also have outputs, and can be used as sub-playbooks. Select an input playbook to accept configured inputs to run, and provide outputs. Input playbooks can only be used as sub-playbooks, and can't be triggered automatically as an independent playbook.
The Start and End blocks are pre-populated on the editor. All playbooks must start with the Start block. Regardless if playbooks end with the End block, the end/on_finish function is always called at the end of a playbook's execution.
Specify a name for the playbook.
- Playbooks in the same repository cannot have the same name. Playbooks in different repositories can have the same name.
- As a best practice, do not use personally identifiable information in the names of playbooks.
- Avoid using the slash character (/) in playbook names.
After you have created your playbook, you can click the auto-arrange playbook icon to align the blocks.
Use the zoom to fit icon, or click the icons with the plus and minus signs to zoom in or zoom out. For keyboard shortcuts, see Use keyboard shortcuts in the playbook editor.
Next, see Add a new block to your playbook for instructions on how to add a new block and begin constructing your playbook.
Add outputs to Automation and Input playbooks
You can add outputs to both Automation and Input playbooks. Automation playbooks can be run both independently and as a sub-playbook. Input playbooks can only be run as a sub-playbook. Outputs will be available to use by the parent playbook that calls a sub-playbook with outputs. To add outputs to a playbook, follow these steps:
- Create either an Automation or Input playbook. See the descriptions of these playbook types earlier in this article.
- Click the End block to access the output configuration panel.
- Enter a name for the output in the Output Variable Name field. The name can only contain A-Z, a-z, 0-9, spaces, or underscores. The name must be a valid Python identifier and cannot start with a zero.
- (Optional) Enter help text or a description in the HelpText/Description field. This appears as help text on the playbook listing page and when selecting a playbook to run as a sub-playbook.
- (Optional) Click the Output field and search for and select an Output datapath from the list. For details on specifying datapaths, see Specify data in your playbook. You can add multiple output datapaths per output.
- (Optional) Select a Data Type for the output. If you select a data type, downstream blocks can filter on data type to know whether the output is compatible or not. The Data Type automatically populates based on the first output datapath you selected.
- (Optional) Create a custom datapath if the datapath you need isn't available. When you add a custom datapath, it is only available for the block you add it to. For details on creating a custom datapath, see Custom datapaths in the Specify data in your playbook article.
- Click Done.
- Click Save.
- (Optional) Click + to add another output. You can add a maximum of 10 outputs per playbook.
- Add a block to your playbook. If you choose to add a playbook block, and the playbook has outputs, the Synchronous switch must be on to access the outputs. For more information, see Add a new block to your playbook.
- Enter a name for the playbook in the Playbook Name field.
- Click Save and enter a comment about the playbook.
After you save the playbook, it appears on the playbook listing page with the type and outputs listed.
Add inputs to an Input playbook
Use Input playbooks to pass data between playbooks and sub-playbooks. Input playbooks accept configured inputs to run, and can provide outputs. Input playbooks can only be used as sub-playbooks, and can't be triggered automatically as an independent playbook. As Input playbooks are only used as sub-playbooks, Input playbooks can be more prescriptive without having to accommodate for all types of data in the notable making playbooks easier to develop and reuse. To add inputs to an Input playbook, follow these steps:
- Create an Input playbook. See the descriptions of these playbook types earlier in this article.
- Click the Start block to access the input configuration panel.
- Enter a name for the input in the Input Variable Name field. The name can only contain A-Z, a-z, 0-9, spaces, or underscores. Input variable names must be unique.
- (Optional) Enter help text or a description in the HelpText/Description field. This appears as help text on the playbook listing page and when selecting an Input playbook to run as a sub-playbook.
- (Optional) Select a Data Type value from the list. The Data Type value you set is used to filter data when assigning data to a configured input.
- (Optional) Create a custom datapath if the datapath you need isn't available. When you add a custom datapath, it is only available for the block you add it to. For details on creating a custom datapath, see Custom datapaths in the Specify data in your playbook article.
- (Optional) Click + to add another input. You can add a maximum of 10 inputs to an Input playbook.
- Add a block to your playbook. For more information, see Add a new block to your playbook.
- After you have added a block, select playbook inputs in the datapath picker for the block, usually found in the Select Parameter field, and then select the input you want this block to use.
- Click Save.
- Enter a name for the playbook in the Playbook Name field.
- Click Save and enter a comment about the playbook.
After you save the playbook, it appears on the playbook listing page with the type and inputs listed.
Use an Input playbook as a sub-playbook
After you have created an Input playbook, you can run it as a sub-playbook from an Automation playbook to avoid having to copy and maintain code in different places.
- Create an Automation playbook.
- Drag and drop the half-circle icon attached to any existing block in the editor. Select a Playbook block from the menu that appears.
- Click the Input tab and select the playbook you want to run from the drop-down list.
- Click in the input fields and assign the inputs datapaths from the drop-down list. For details on specifying datapaths, see Specify data in your playbook.
- (Optional) Click the Info tab to view information about the playbook including the name, description, inputs, and outputs associated with the playbook.
- (Optional) Toggle the Synchronous switch on to make this playbook wait for the called playbook to complete running before continuing. If this switch is left off, the playbook finishes executing without waiting for the called playbook to complete and you won't be able to access the inputs.
- (Optional) Add any additional blocks to the playbook.
- Click Save.
For more information, see Run other playbooks inside your playbook in .
You cannot call sub-playbooks from Input playbooks.
Show input and output run data
After a playbook is executed, you can view the inputs and outputs for that playbook in the Investigation page or Activity panel.
To see the input and output run data, complete the following steps:
- Run a parent playbook with a sub-playbook that has inputs and outputs.
- Click the playbook name in the Investigation page or Activity panel.
- You'll see a "takeover" screen with information about the playbook run result, input, and output data
The results for a playbook without inputs and outputs still opens a takeover screen, but without any input and output results.
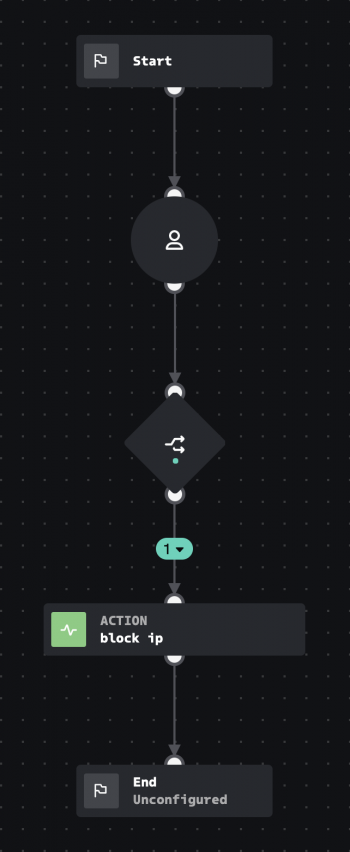
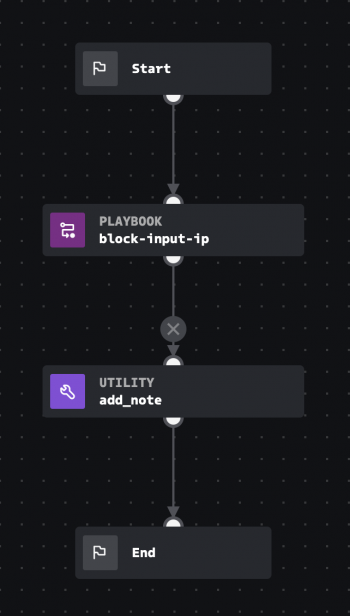
Example: Use inputs and outputs to block an IP address
Run an Input playbook as a sub-playbook to avoid having to copy and maintain code in different places. The following Input playbook uses an IP address as an input, and then a prompt block to ask a user whether to block the IP or not. A decision block is used next, where if the decision is to block the IP, then a block IP action block is used to block the IP and the playbook sets the status of the block IP action as an output.
In the following example, the Input playbook is used as a sub-playbook. The parent playbook passes the event src_ip datapath as an input to the sub-playbook, block-input-ip. The parent playbook then uses a utility block to add a note where the content of the note is the output of the block-input-ip playbook.
| Find existing playbooks | Add a new block to your playbook |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® SOAR (On-premises): 6.0.0, 6.0.1, 6.0.2, 6.1.0, 6.1.1, 6.2.0, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.3.0, 6.3.1, 6.4.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!