About Splunk User Behavior Analytics
Splunk User Behavior Analytics (UBA) uses behavior modeling, peer-group analysis, and machine learning to uncover hidden threats in your environment. Splunk UBA automatically detects anomalous behavior from users, devices, and applications, combining those patterns into specific, actionable threats.
Investigate and respond to detected threats using a streamlined threat review workflow that provides visibility into anomalous activity and supporting evidence. Splunk UBA increases the effectiveness of your security analysts by helping them focus on threats and malicious activities with kill chain and geographical visualizations.
How does Splunk UBA work?
Splunk UBA ingests data from the Splunk platform, which includes Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud, and does the following to help you understand what users are doing in your environment. Splunk UBA generates threats by performing the following tasks:
- Normalize device and domain names, and associate all accounts identified in your HR data with a single human user.
- Perform identity resolution to find the real-time association between IP addresses, host names, and users, and also maintain these associations over time.
- Baseline the behavior of the users, devices, and apps in your environment across organizational units and peer groups.
- Use unsupervised machine learning algorithms to analyze the data for activity deviating from normal behavior. Splunk UBA uses anomaly detection rules and models to distill millions of events to a few hundred anomalies.
- Use threat rules and models to further distill anomalies down to a handful of threats. A single anomaly might not represent a legitimate threat in your environment. Over time, however, a series of anomalies can tell a story about a threat that must be investigated. Threat detection models can stitch together anomalies to provide an end-to-end story about a high-fidelity threat.
See Understand data flow in Splunk UBA in the Get Data into Splunk User Behavior Analytics manual for more details about how data moves through Splunk UBA.
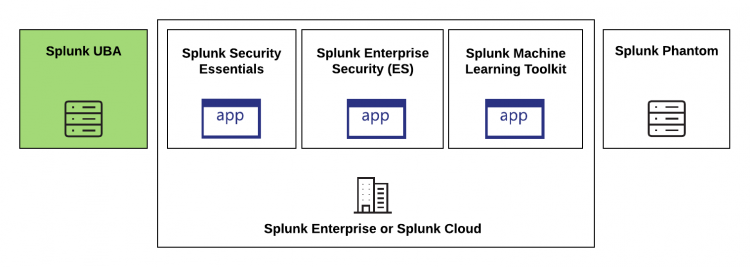
How does Splunk UBA work with other Splunk security products?
Splunk UBA gets its data from the Splunk platform. Unlike many Splunk security products which are apps installed on the Splunk platform, Splunk UBA must be installed on dedicated resources in the form of physical, on-premise servers or servers in your organization's managed cloud deployment. See System requirements for Splunk UBA in Install and Upgrade Splunk User Behavior Analytics.
Integrate Splunk UBA with the Splunk platform to perform the following tasks:
- When viewing anomaly details in Splunk UBA, you can return to Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud to view some of the raw events contributing to the anomaly raised in Splunk UBA. See Use event drilldown to review an anomaly's raw events.
- Send notable events from Splunk ES to Splunk UBA or send anomalies and threats from Splunk UBA to Splunk ES. The status of any notable events in Splunk ES and anomalies and threats in Splunk UBA that are shared between systems are synchronized to provide consistency and continuity in your investigations. This integration requires the Splunk Add-On for Splunk UBA. See About the Splunk add-on for Splunk UBA in the Send and Receive Data from the Splunk Platform manual.
See also
For more information about the other products in the Splunk security portfolio, see the product documentation.
| You want to do this | Documentation |
|---|---|
| Use Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud to aggregate logs and perform human-based analysis of rules, statistics, and correlation, as well as perform ad-hoc searches and pivots. | See:
|
| Start your security journey with Splunk Security Essentials to find the best content available in your environment and determine which solutions are the most effective. | See What's new in Splunk Security Essentials in the Splunk Security Essentials Release Notes. |
| Use Splunk Enterprise Security to orchestrate investigations, detections, and respond to security threats. | See:
|
| The Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) provides packaged Splunk Search Processing Language (SPL) search commands, macros, and visualizations. Use the MLTK to build custom machine learning solutions for any use case. | See About the Machine Learning Toolkit in the User Guide. |
| Use Splunk Phantom to automate your security workflow. | See About Splunk Phantom in Use Splunk Phantom. |
| Get started on the Splunk UBA home page |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® User Behavior Analytics: 5.0.0, 5.0.1, 5.0.2, 5.0.3, 5.0.4, 5.0.4.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!