Overview of maintenance windows in ITSI
Maintenance windows allow for IT Service Intelligence (ITSI) knowledge objects to enter a maintenance state. This state is intended to silence alarms about machines that don't require active monitoring.
It's a best practice to schedule maintenance windows with a 15- to 30-minute time buffer before and after you start and stop your maintenance work. This gives the system an opportunity to catch up with the maintenance state and reduces the chances of ITSI generating false positives during maintenance operations.
For example, if a server will be shut down for maintenance at 1:00PM and restarted at 5:00PM, the ideal maintenance window is 12:30PM to 5:30PM. The 15- to 30-minute time buffer is a rough estimate based on 15 minutes being the time period over which most KPIs are configured to search data and identify alert triggers.
Maintenance windows apply to services and entities. For instructions on putting a service or entity into maintenance mode, see Schedule maintenance downtime in ITSI.
Manage maintenance windows through the REST API
The Maintenance Service Interface encapsulates operations on maintenance windows in ITSI. Use this interface to perform CRUD operations on maintenance windows in your environment. For more information, see Maintenance Services Interface in the IT Service Intelligence REST API Reference manual.
Maintenance mode and service dependencies
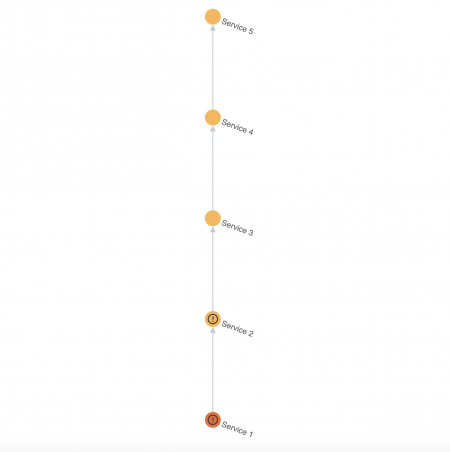
If you want a service to be in maintenance mode, you need to put all services it depends on in maintenance mode as well, if their ServiceHealthScore KPIs are included as dependencies. This rule applies even if you only want to put a single service in maintenance mode. For example, the following topology tree shows that Service 5 depends on Service 4, Service 4 depends on Service 3, and so on:
If you want to put Service 3 in maintenance mode, and it depends on the ServiceHealthScore KPI of services 1 and 2, then those services must be put in maintenance mode as well. The same applies to Service 5, which depends on the health scores of all the other services. You need to put services 1, 2, 3, and 4 in maintenance mode in order for Service 5 to be in maintenance mode.
For an explanation of how dependencies are visually represented in the service tree, see Use the Service Analyzer tree view in ITSI in the Service Insights Manual.
For instructions to add dependencies to a service, see Add service dependencies in ITSI in the Service Insights manual.
Impact of services in maintenance mode
Maintenance windows can have an impact on associated KPIs, service health score calculations, and other ITSI features.
Consider the following when you put a service into maintenance mode:
- All KPIs within that service are automatically put into maintenance mode.
- ITSI ignores search results from KPIs in maintenance mode for the purpose of service health score calculation for the duration of the maintenance window.
- Maintenance windows don't affect adaptive threshold calculations. Search results from KPIs in maintenance mode don't count when looking back at past data to calculate threshold values.
Impact of entities in maintenance mode
Consider the following when you put an entity into maintenance mode:
- If the entity has no KPIs running searches against it, there is no impact on service health scores.
- If the entity has one or more KPIs running searches against it, all search results from all KPIs running against that entity are ignored for the purpose of service health score calculation.
- If a KPI is split by entity, for example if the same KPI is running against two different entities, and one entity is in maintenance mode and one is not, search results generated by the KPI running against the entity in maintenance mode are ignored for the purpose of health score calculation. Search results generated by the same KPI running against the entity that's not in maintenance mode are included as usual in the service health score calculation.
- You can put an entity in full or partial maintenance mode without it being explicitly put into maintenance mode, if a service that contains the entity is put in maintenance mode.
Impact on dashboards
Services, entities, and KPIs that are fully or partially impacted by a maintenance window appear in a dark gray color on pages that display health scores, including service analyzers, service and entity details pages, glass tables, multi-KPI alerts, and deep dives.
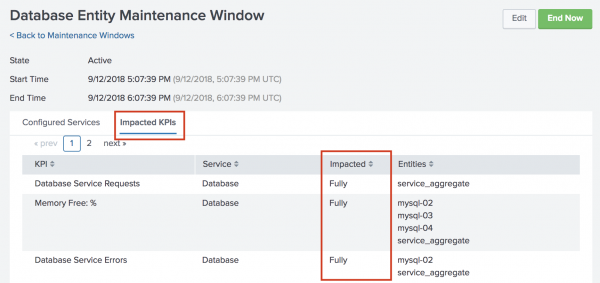
View impacted KPIs
You can view the impact of a maintenance window on associated KPIs.
- Click Configuration > Maintenance Windows.
- Select a maintenance window to see the specific services or entities impacted by it.
- Click Impacted KPIs to see a list of KPIs impacted by the maintenance window. KPIs that are split by entity, and thus are currently running searches against other entities that are not in maintenance mode, are listed as partially impacted. KPIs that aren't split by entity are listed as fullyimpacted.
| Create teams in ITSI | Schedule maintenance downtime in ITSI |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® IT Service Intelligence: 4.11.0, 4.11.1, 4.11.2, 4.11.3, 4.11.4, 4.11.5, 4.11.6, 4.12.0 Cloud only, 4.12.1 Cloud only, 4.12.2 Cloud only, 4.13.0, 4.13.1, 4.13.2, 4.13.3, 4.14.0 Cloud only, 4.14.1 Cloud only, 4.14.2 Cloud only, 4.15.0, 4.15.1, 4.15.2, 4.15.3, 4.16.0 Cloud only, 4.17.0, 4.17.1, 4.18.0, 4.18.1, 4.19.0, 4.19.1, 4.19.2, 4.19.3, 4.19.4, 4.20.0, 4.20.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!