Scenario: Wei creates an intelligence workflow in Splunk Mission Control to reduce false positives
The following scenario features Buttercup Games, a fictitious game company.
Buttercup Games recently released the latest version of its artificial intelligence gaming software. Wei, a security operations center (SOC) administrator at Buttercup Games, uses Threat Intelligence Management in Splunk Mission Control to detect and enrich security threats.
While monitoring the Buttercup Games software, Wei faces a high volume of false positives for IP addresses. False positives are security alerts that incorrectly indicate the presence of threats. To make more accurate detections, Wei decides to use an intelligence workflow in Splunk Mission Control to prioritize IP addresses by threat. Only company administrators can create and manage intelligence workflows, and because Wei is a SOC administrator at Buttercup Games, they can configure the workflow.
In this scenario, Wei uses Threat Intelligence Management in Splunk Mission Control to create an intelligence workflow that rules out false positives for IP addresses.
Wei creates an intelligence workflow
After navigating to Content and then Workflows in Splunk Mission Control, Wei follows these three steps to configure a new intelligence workflow.
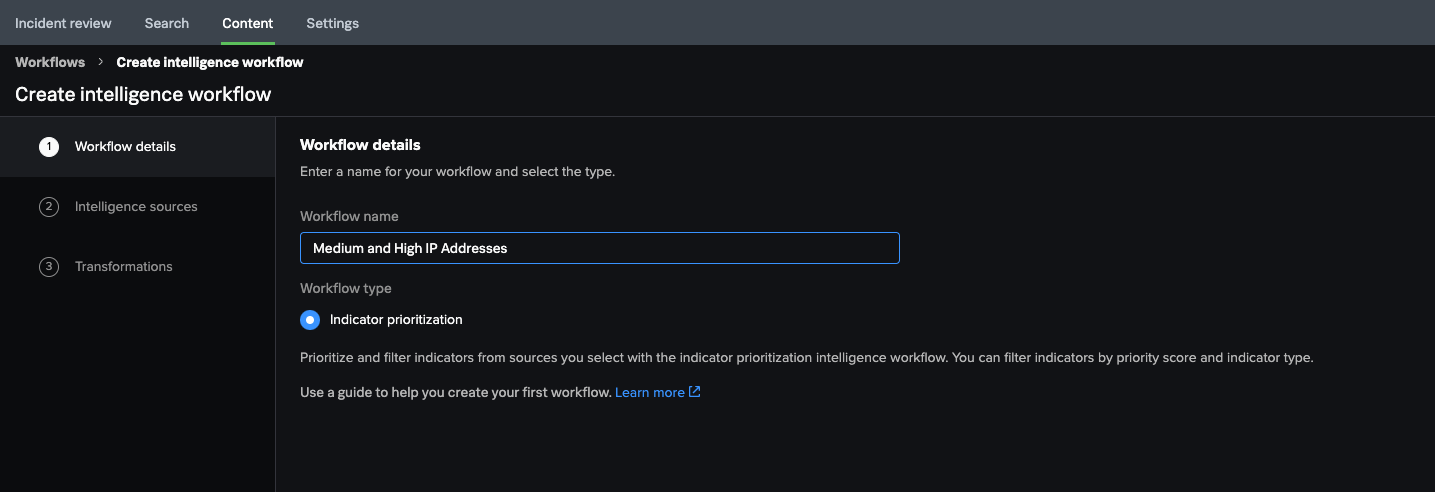
Wei provides details for the workflow
Wei names the workflow Medium and High IP Addresses and, to filter their internal event data by priority, selects Indicator prioritization for the workflow type.
Indicators are pieces of data that provide additional information about unusual, suspicious, or malicious cyber activity. In Wei's case, indicators include threat actors and malware associated with a malicious IP address.
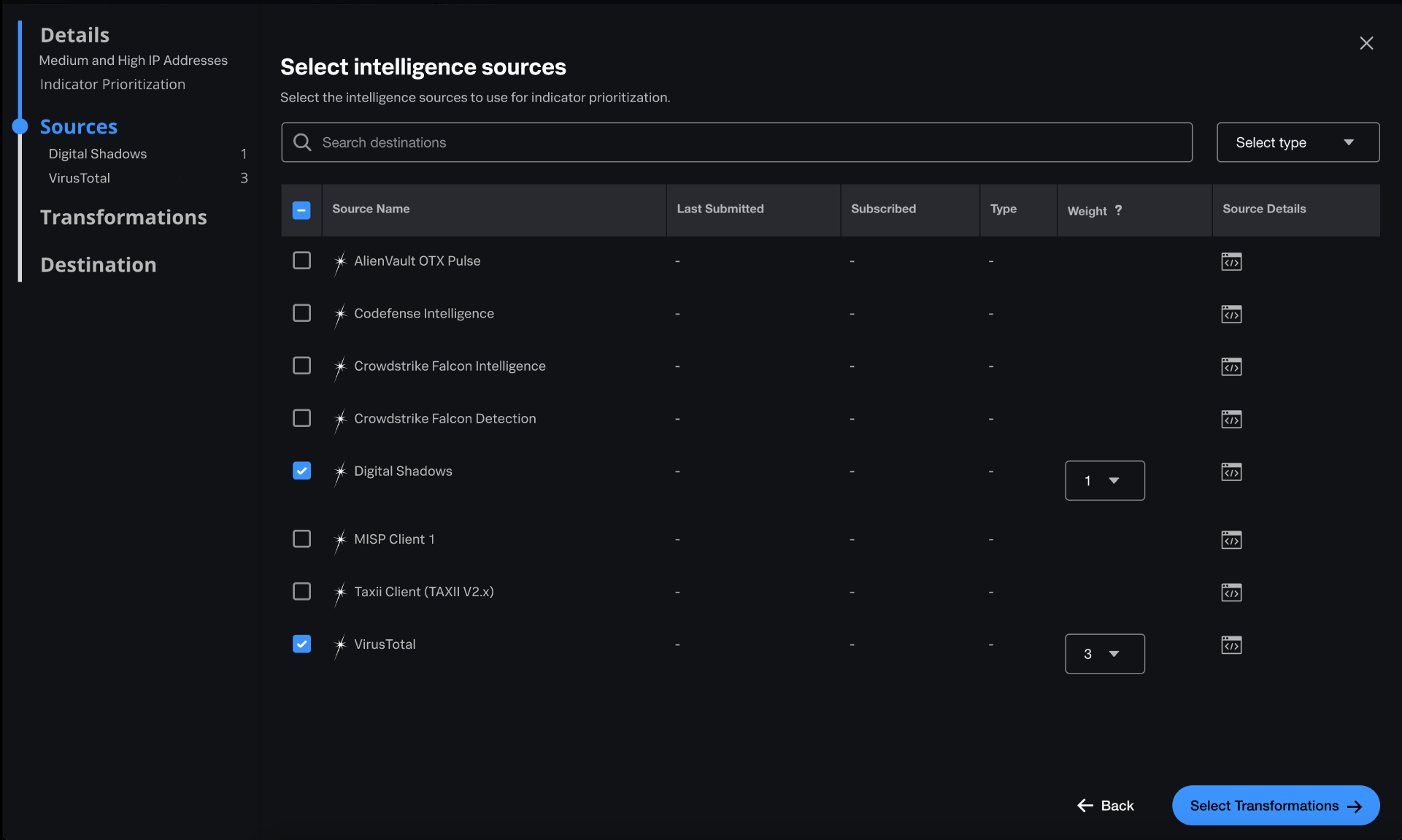
Wei selects intelligence sources for indicator prioritization
In Splunk Mission Control, intelligence sources are feeds that enrich your internal event data with threat intelligence. Intelligence sources can be internal or external.
Wei uses Threat Intelligence Management to normalize, score, and prioritize data from their desired intelligence sources by following these steps:
- Wei sends Buttercup Games' internal event data to Threat Intelligence Management.
- To normalize the data, Wei selects two external sources: Digital Shadows and VirusTotal.
- The weight of an intelligence source represents the source's influence in the final indicator scoring. Because Wei wants to prioritize VirusTotal over Digital Shadows in the scoring, they set the weight of Digital Shadows to 1 and the weight of VirusTotal to 3. This means 25% of the score comes from Digital Shadows and 75% from VirusTotal.
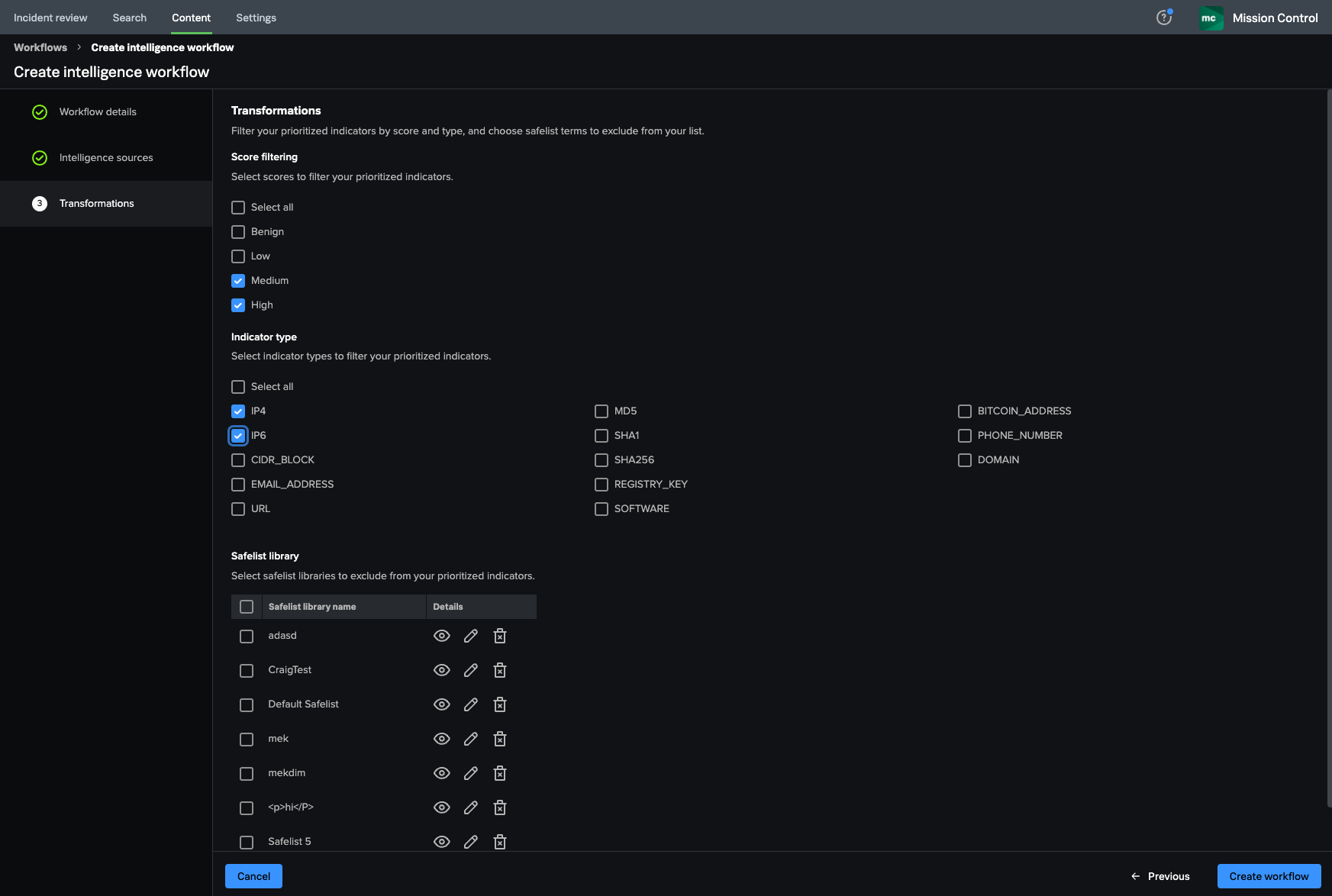
Wei filters the prioritized indicators
To identify only malicious IP addresses, Wei filters the prioritized indicators from Digital Shadows and VirusTotal for IP4 and IP6 indicators with Medium and High scores.
Now that Wei has created a list of prioritized indicators for IP addresses, they select Create workflow to save it. The workflow now appears in Wei's list of intelligence workflows.
Every few minutes, Threat Intelligence Management runs a data processing pipeline that applies the preferences specified in the workflow to Wei's entire intelligence library and sends the resulting records to Splunk Mission Control.
Wei activates the intelligence workflow for data processing
After navigating to Content and then Workflows in Splunk Mission Control, Wei activates the intelligence workflow they created and begins to investigate incidents involving malicious IP addresses.
Summary
In this scenario, Wei used Splunk Mission Control to reduce false positives for IP addresses by creating a workflow that periodically normalizes data against intelligence sources, passes the data through filters specified in the workflow, and transforms the results into a destination data repository.
Learn more
To learn more about Threat Intelligence Management in Splunk Mission Control, see:
| Scenario: Alex automates a security workflow in Splunk Mission Control | Scenario: Wei creates an intelligence workflow in Splunk Mission Control to enrich data |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Mission Control: Current
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!