Detect Numeric Outliers
The Detect Numeric Outliers assistant determines values that appear to be extraordinarily higher or lower than the rest of the data. When a situation violates the expectations for a parameter, it results in an outlier. Identified outliers are indicative of interesting, unusual, and possibly dangerous events.
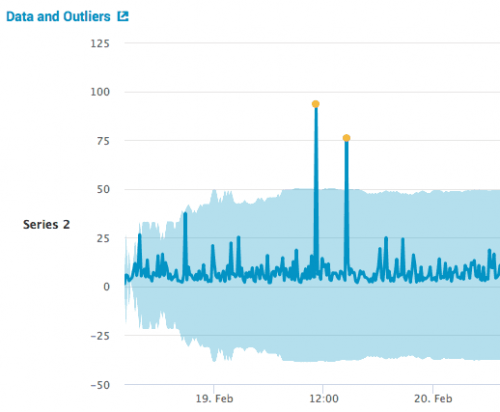
This assistant is restricted to one numeric data field. In the visualization below, the yellow dots indicate outliers.
Algorithm
The Detect Numeric Outliers assistant uses the following distribution statistics (threshold methods):
- Standard deviation
- Median absolute deviation
- Interquartile range
Workflow
- Create a Detect Numeric Outliers Experiment, including the provision of a name.
- On the resulting page, run a search.
- Select a Field to analyze and a Threshold method. When picking a method, consider both the distribution of the data as well as how the method impacts outlier detection
The list populates every time you run a search. - Specify a value for the Threshold multiplier.
Note that the larger the number, the larger the outlier envelope. And thus, the fewer the outliers. - (Optional) In the Sliding window field, specify the number of values to use to compute each slice of the outlier envelope.
A sliding window is useful if the distribution of your data changes frequently. If you do not specify a sliding window, the assistant uses the whole dataset which results in an outlier envelope of uniform size. - Select Include current point to include the current point in the calculations before assessing whether it is an outlier. Only available if you use the Sliding window option.
- (Optional) In Fields to split by, select up to 5 fields.
In the visualizations, the data points are grouped by field. If more than one split by field is specified, the visualizations are grouped by the combination of the values of the fields.
It is better to split by a categorical field than a numeric field. For example, if you detect outliers in grocery store purchases and analyze thequantityfield, you could split bystore_IDto group thequantitydata points by store. - Click Detect Outliers. View any changes to this model under the Experiment History tab.
| Method | Application |
|---|---|
| Standard Deviation | This method is appropriate If your data exhibits a normal distribution. Since the standard deviation method centers on the mean, it is more impacted by outliers. |
| Median Absolute Deviation | This method applies a stricter interpretation of outliers than standard deviation because the measurement centers on the median and uses Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) instead of standard deviation. |
| Interquartile Range | This method is appropriate when your data exhibits an asymmetric distribution. Instead of centering the measurement on a mean or median, it uses quartiles to determine whether a value is an outlier. |
'Important note: The model will now be saved as a Draft only. In order to update alerts or reports, click the Save button in the top right of the page.''
Interpret and validate
After you detect outliers, review your results in the tables and visualizations. Results commonly have a few outliers.
| Result | Application |
|---|---|
| Data and Outliers | Outliers, represented by yellow dots, are datapoint that fall outside of the light blue envelope. A chart to the right of the graph reports the total number of outliers. Hover over a yellow dot to see the value and quantity of an outlier. To learn more about the nature of the outlier, click it to drill down to the search query to see the base of the data point. |
| Split by fields | If you selected a field to split by, then the Data and Outliers chart displays up to 10 values that you can add or remove from the chart. The chart groups the data points based on split by field values. For example, if there are 3 split by field values, the chart will be broken out into 3 separate charts for each split value. The number of outliers for each split by field value is displayed to the right of the chart. |
| Outlier Count Over Time chart | This chart plots the outliers over time, and only appears if you use time series data. If you specify more than one split, the chart shows the outlier count for each field value. To see which values are too high or too low, check the box for Split outliers above and below threshold. If you split by field, each field contains a value for outliers above and below the threshold. |
| Data Distribution histogram | This histogram shows the distribution, and displays the number of data points within the threshold (the light blue area) and the number of data points outside the threshold. |
| Data and Outliers table | This table shows each outlier the corresponding value, as well as the the lists of values for any split by field. |
| Outlier Split Value Distribution | If you specified one or more split by fields, this table displays the number of outliers for each split value or combination of split values. |
Deploy
- Click the Save button in the top right corner of the page. You can edit the title and add or edit and associated description. Click Save when ready.
- Click Open in Search to open a new Search tab, or click Show SPL to see the search query that was used to fit the model.
- Under the Experiments tab, you can see experiments grouped by assistant analytic. Under the Manage menu, choose to:.
- Create Alert
- Edit Title and Description
- Click Create Alert to set up an alert that is triggered when the the number of outliers outside both thresholds, (above the upper threshold, or below the lower threshold) exceeds a specified value. Once at least one alert is present, the bell icon will be highlighted in blue.
For example, you could use this same query on a different data set.
If you make changes to the saved experiment you may impact affiliated alerts. Re-validate your alerts once experiment changes are complete.
For more information about alerts, see Getting started with alerts in the Splunk Enterprise Alerting Manual.
| Predict Categorical Fields | Detect Categorical Outliers |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Machine Learning Toolkit: 3.2.0, 3.3.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!