Custom visualizations in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit
The Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit includes several reusable custom visualizations that you can use in your own dashboards. Each visualization expects data in a certain format with certain fields, that you can see in the syntax portion of the visualization descriptions.
Custom visualization workflow
Follow these steps to apply a custom visualization to your data. You can use these custom visualizations on any Splunk platform instance on which the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit is installed:
- Run a search from the Search page in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit or the default Search & Reporting app on the Splunk platform.
- Click the Visualization tab, then click the menu at the top left to display available visualizations.
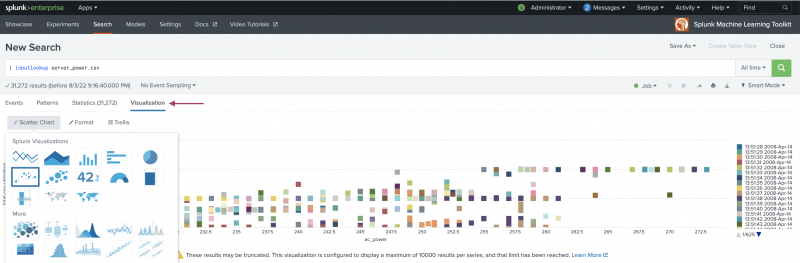
- Select a visualization.
Many of these visualizations also display within the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit Assistants. For more information on step-by-step Assistant options, see MLTK guided workflows.
3D Scatter Plot
Use the 3D Scatter Plot to see patterns in your data. Look for clusters of similar data points, or drill down to identify singular data points.
Syntax
| table clusterId x y z [clusterColor]
| eval clusterColor = case(clusterId=0, "teal", clusterId=2, "#09B1DF") | table clusterId x y z clusterColor
The clusterColor parameter is optional. The clusterColor parameter supports written color names or any hex color code. To review the list of supported color names, see the GitHub bahamas10 css color names. If no clusterColor parameter is provided the scatter plot uses default css colors supported in all modern web browsers.
The | table clusterId x y z line must be provided for the visualization to render properly.
Example
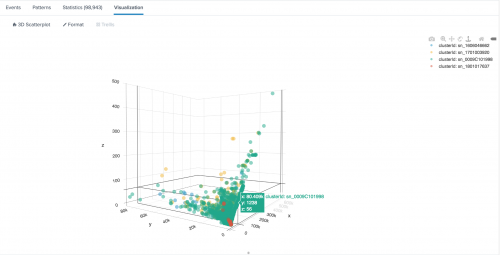
The following example uses 3D Scatter Plot on sample data.
| inputlookup firewall_traffic.csv | eval clusterId=serial_number, x=bytes_received, y=bytes_sent, z=packets_received, clusterColor = case(clusterId="sn_0009C101998", "#56BD93") | table clusterId x y z clusterColor
Example output
The following example shows 3D Scatter Plot on sample data.
Boxplot Chart
Use the Boxplot Chart to show the minimum, lower quartile, median, upper quartile, and maximum of each field.
Boxplot requires the input of the macro | `boxplot` in order to render. Failing to include the macro renders an error.
Syntax
| `boxplot`
The box plot chart visualization expects five rows corresponding to min, max, median, lower quartile and upper quartile, in any order.
exactperc25is the lower quartileexactperc75is the upper quartile
Example
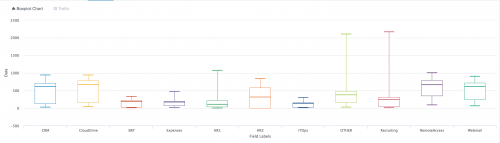
The following example uses Boxplot Chart on sample data.
| inputlookup app_usage.csv | `boxplot`
Example output
The following image shows Boxplot Chart on sample data.
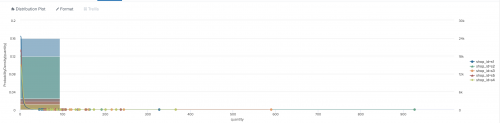
Distribution Plot
Use the Distribution Plot to show the output of the DensityFunction algorithm. This visualization can be called with either the fit or apply commands.
This visualization requires the use of fit DensityFunction or apply in combination with show_density=True show_options="feature_variables, split_by, params".
Syntax
| fit DensityFunction <field> [by "<fields>"] show_density=True show_options="feature_variables, split_by, params"
Example
The following example uses Distribution Plot on sample data.
| fit DensityFunction "quantity" by "shop_id" dist=auto threshold=0.01 show_density=True show_options="feature_variables,split_by,params"
Example output
The following example shows Distribution Plot on sample data.
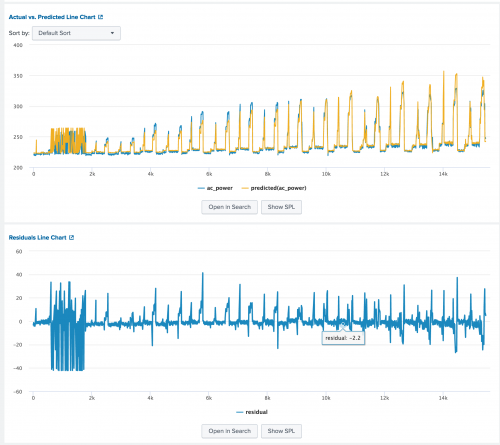
Downsampled Line Chart
Use the Downsampled Line Chart to show values and trends over time implementing downsampling to show large numbers of points.
Syntax
| table <x_axis> <y_axis_1> <y_axis_2>
Example
The following example uses Downsampled Line Chart on sample data.
| table _time, "median_house_value", "predicted(median_house_value)"
Example output
The following image shows the Actual vs. Predicted Line Chart and the Residuals Line Chart that are also available when using the Predict Numeric Fields Assistant.
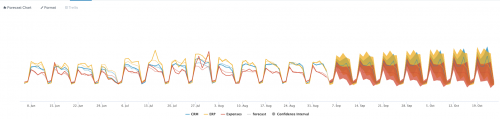
Forecast Chart
Use the Forecast Chart to show the forecasted value for data This visualization is available in the Forecast Time Series Assistant and Smart Forecasting Assistant, which use different macros to produce the output:
- The Forecast Time Series Assistant uses the
fitorpredictcommands with the ARIMA algorithm. - The Smart Forecasting Assistant uses the
fitcommand with the StateSpaceForecast algorithm.
Syntax
| timechart count [by comparison_category] | modvizpredict (<field>, <algorithm>, <future_timespan>, <holdback>, <confidence_interval>)
| fit ARIMA [_time] <field_to_forecast> order=<int>-<int>-<int> [forecast_k=<int>] [conf_interval=<int>] [holdback=<int>] | `forecastviz(<forecast_k>, <holdback>, <field_to_forecast>, <conf_interval>)`
| fit StateSpaceForecast variable_name1 [variable_name2] [variable_name3] [variable_name4] [variable_name5] output_metadata=true [conf_interval=<int>] | `smartforecastviz(<variable_name1> [,<variable_name2>] [, <variable_name3] [, <variable_name4] [, <variable_name5>])`
Examples
The following examples use Forecast Chart on sample data.
| inputlookup exchange.csv | fit ARIMA _time rate holdback=5 conf_interval=95 order=1-0-1 forecast_k=10 as prediction | `forecastviz(10, 5, "rate", 95)`
| inputlookup app_usage.csv | fields CRM ERP Expenses | fit StateSpaceForecast CRM ERP output_metadata=true holdback=0 forecast_k=50 conf_interval=50 into app_usage_model | `smartforecastviz(CRM, ERP)`
Example output
The following image shows the Forecast Chart on sample data.
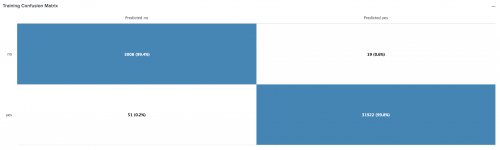
Heatmap Plot
Use the Heatmap Plot to show data values as colors in a table matrix.
Syntax
| `confusionmatrix(<x_axis>, <y_axis>)`
Example
The following example uses Heatmap Plot on sample data.
| inputlookup firewall_traffic.csv | head 50000 | fit AutoPrediction "has_known_vulnerability" from "bytes_received" "packets_received" "packets_sent" "bytes_sent" "used_by_malware" test_split_ratio=0.3 into "default_model_name" | eval "_split"=case('_split'="Test", "Testing", '_split'="Training", "Training") | where '_split'="Testing" | `confusionmatrix("has_known_vulnerability", "predicted(has_known_vulnerability)")`
Example output
The following example shows Heatmap Plot on sample data.
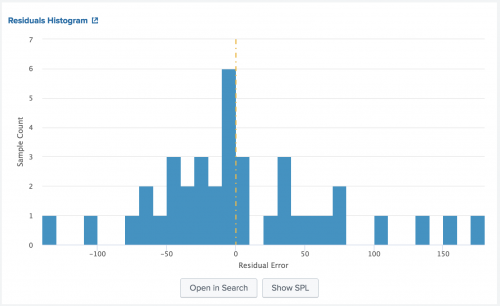
Histogram Chart
Use the Histogram Chart to show continuous data as bucketed by the bin command.
Syntax
| `histogram(<field, bins>)`
Example
The following example uses Histogram Chart on sample data.
| bin residual bins=100
Example output
The following image shows the Residuals Histogram on sample data.
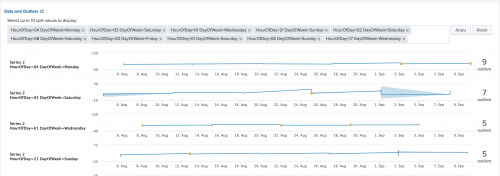
Outliers Chart
Use the Outliers Chart to show the acceptable range for a value and to highlight the points that are outside of this range.
Syntax
| table _time, <outlier_variable>, <lower_bound>, <upper_bound>
Example
The following example uses Outliers Chart on sample data.
| table _time, quantity, lowerBound, upperBound, isOutlier
Example output
The following image shows the Outliers Chart on sample data.
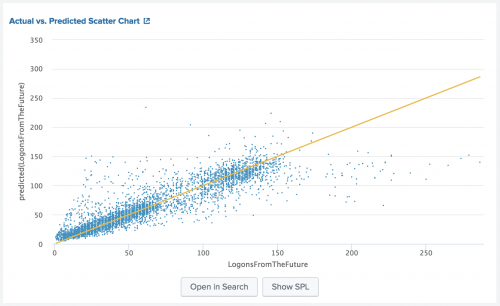
Scatter Line Chart
Use the Scatter Line Chart to show the relationships between discrete values in two dimensions, as well as an additional identity (x=y) line.
Syntax
| table <x_axis> <y_axis>
Example
The following example uses Scatter Line Chart on sample data.
| table "median_house_value" "predicted(median_house_value)"
Example output
The following image shows Scatter Chart on sample data.
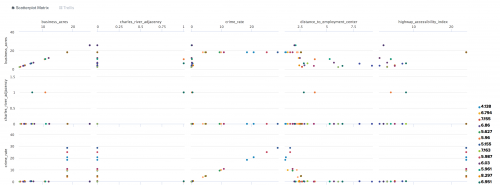
Scatterplot Matrix
Use the Scatterplot Matrix to show the relationships between discrete values in multiple dimensions.
All field values must be numeric in order to render the Scatterplot Matrix.
Syntax
| table <name_category>, <dimension_1>, <dimension_2>, <dimension_3>
Example
The following example uses Scatterplot Matrix on sample data.
| table cluster, "avg_rooms_per_dwelling", "business_acres", "median_house_value"
Example output
The following example shows the Scatterplot Matrix on sample data.
| Search macros in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit | Algorithms in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Machine Learning Toolkit: 5.4.0, 5.4.1, 5.4.2, 5.5.0






 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!