Detect Categorical Outliers Experiment Assistant workflow
The Detect Categorical Outliers Experiment Assistant identifies data that indicate interesting or unusual events. This Assistant allows non-numeric and multi-dimensional data, such as string identifiers and IP addresses.
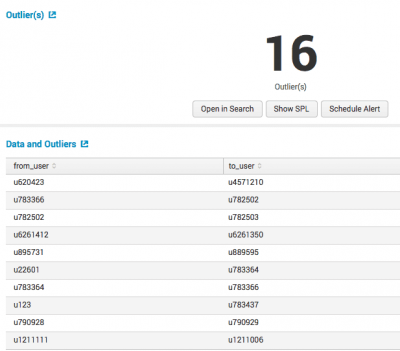
The following image illustrates results from the showcase example in the Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit with Bitcoin data.
Available algorithm
The Detect Categorical Outliers Assistant uses the following algorithm:
- Probabilistic measures
Create an Experiment to detect categorical outliers
The Detect Categorical Outliers Experiment Assistant identifies data that indicate interesting or unusual events. To detect categorical outliers, input data and select the fields for which to look for unusual combinations or a coincidence of rare values. When multiple fields have rare values, the result is an outlier.
Assistant workflow
Follow these steps to create a Detect Categorical Outliers Experiment.
- From the MLTK navigation bar, click Experiments.
- If this is the first Experiment in MLTK, you will land on a display screen of all six assistants. Select the Detect Categorical Outliers block.
- If you have at least one Experiment in MLTK, you will land on a list view of Experiments. Click the Create New Experiment button.
- Fill in an Experiment Title, and add a description. Both the name and description can be edited later if needed.
- Click Create.
- Run a search, and be sure to select a date range.
- Select the fields you want to analyze.
The list populates every time you run a search.
- (Optional) Add notes to this Experiment. Use this free form block of text to track the selections made in the Experiment parameter fields. Refer back to notes to review which parameter combinations yield the best results.
- Click Detect Outliers. The Experiment is now in a Draft state.
Draft versions allow you to alter settings without committing or overwriting a saved Experiment. This Experiment is not stored to Splunk until it is saved.
The following table explains the differences between a draft and a saved Experiment:Action Draft Experiment Saved Experiment Create new record in Experiment history Yes No Run Experiment search jobs Yes No (As applicable) Save and update Experiment model No Yes (As applicable) Update all Experiment alerts No Yes (As applicable) Update Experiment scheduled trainings No Yes
Interpret and validate results
After you detect outliers, review your results and the corresponding tables. Results often have a few outliers. You can use the following methods to better evaluate your Experiment results:
Result Definition Outliers This result shows the number of events flagged as outliers. Total Events This result shows the total number of events that were evaluated. Data and Outliers This table lists the events that marked as outliers, and the corresponding reason that the event is marked as an outlier.
Save the Experiment
Once you are getting valuable results from your Experiment, save it. Saving your Experiment results in the following actions:
- Assistant settings saved as an Experiment knowledge object.
- The Draft version saves to the Experiment Listings page.
- Any affiliated scheduled trainings and alerts update to synchronize with the search SPL and trigger conditions.
You can load a saved Experiment by clicking the Experiment name.
Deploy the Experiment
Saved detect categorical outlier Experiments include options to manage, but not to publish.
In Experiments built using the Detect Categorical Outlier Assistant a model is not persisted, meaning you will not see an option to publish. However, you can achieve the same results as publishing the Experiment through the steps below for Outside the Experiment framework.
Within the Experiment framework
To manage your Experiment, perform the following steps:
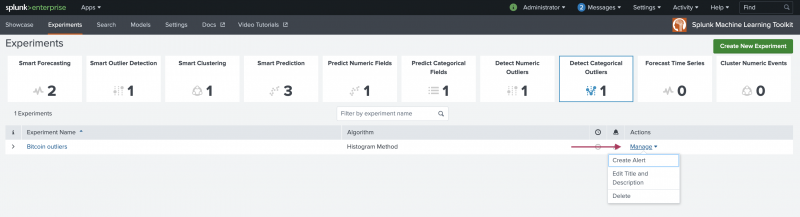
- From the MLTK navigation bar, choose Experiments. A list of your saved Experiments populates.
- Click the Manage button available under the Actions column.
The toolkit supports the following Experiment management options:
- Create and manage Experiment-level alerts. Choose from both Splunk platform standard trigger conditions, as well as from Machine Learning Conditions related to the Experiment.
- Edit the title and description of the Experiment.
- Delete an Experiment.
Updating a saved Experiment can affect affiliates alerts. Re-validate your alerts once you complete the changes. For more information about alerts, see Getting started with alerts in the Splunk Enterprise Alerting Manual.
Experiments are always stored under the user's namespace, meaning that changing sharing settings and permissions on Experiments is not supported.
Outside the Experiment framework
- Click Open in Search to generate a New Search tab for this same dataset. This new search opens in a new browser tab, away from the Assistant.
This search query uses all data, not just the training set. You can adjust the SPL directly and see the results immediately. You can also save the query as a Report, Dashboard Panel or Alert. - Click Show SPL to generate a modal window/ overlay showing the search query that you used to fit the model. Copy the SPL to use in other aspects of your Splunk instance.
Learn more
To learn about implementing analytics and data science projects using Splunk's statistics, machine learning, and built-in custom visualization capabilities, see the Splunk Education course Splunk 8.0 for Analytics and Data Science.
| Detect Numeric Outliers Experiment Assistant workflow | Forecast Time Series Experiment Assistant workflow |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Machine Learning Toolkit: 5.3.3, 5.4.0, 5.4.1, 5.4.2, 5.5.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!