Filters
Apply filters to sort Journeys by Attribute, time, step, or step sequence.
Top Clusters
Select a Cluster to filter by the frequency of a Journey occurrence. For example, If you select a Cluster labeled 40%, all Journeys shown occurred 40% of the time.
Attributes
Attributes are characteristics of an event, such as price, geographic location, or color. Select an Attribute field value or range to filter your Journeys. You can select multiple Attributes. The numeric count associated with each attribute reflects the number of Journeys that contain each attribute. The numeric value does not reflect the total number of times the attribute appears in the data.
Step
A Step is the status of an action or process you want to track. For an order system Flow Model, the steps in a Journey might consist of the order placed, the order shipped, the order in transit, and the order delivered. To view journeys that certain steps select + on each step. To view journeys that do not contain certain steps select - on each step.
Journey Duration
A Journey contains all the Steps that a user or object executes during a process. For example, suppose you create a Flow Model to analyze order system data for an online clothes retailer. A sample Journey in this Flow Model might track an order from time of placement to delivery.
Start Time
Select a duration to view all Journeys that started within the selected time period.
Start and End
Select a step to view Journeys that start or end with said step. You can select multiple steps.
Followed By
Select a combination of two steps to look for particular step sequences in Journeys. There are four followed by filters in SBF. Let's walk through a few examples using the following diagram to illustrate the differences among the followed by filters. This diagram shows three Journeys, where each Journey contains a different combination of steps.
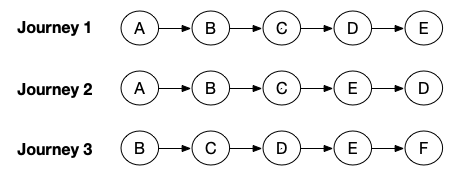
Eventually followed by
Suppose you select step A eventually followed by step D. In relation to the example, this filter combination returns Journeys 1 and 2.
Immediately followed by
Suppose you select step C immediately followed by step D. In relation to the example, this filter combination returns Journeys 1 and 3.
Not eventually followed by
Suppose you select step A not eventually followed by step D. In relation to the example, this filter combination returns Journey 3. By this logic, SBF returns journeys that do not include step A or Step D, such as Journey 3.
Not immediately followed by
Suppose you select step A not immediately followed by step D. In relation to the example, this filter combination returns Journey 1, 2 and 3. SBF looks for Journeys with step sequences where step A does not immediately followed by step D. By this logic, SBF returns journeys that might not include step A or Step B.
Path Duration
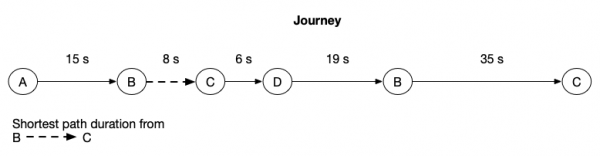
In SBF, a path is the span between two steps in a Journey. Path duration is the time elapsed between two steps in a Journey. Select a start step, end step and specify up to two ranges to filter by path duration. If your Journey contains steps that repeat several times, the path duration refers to the shortest duration between the two steps. For example, if you select the path from step B to step C, SBF selects the step B that is shortest distance from the step C in your Journey. So, If you select steps B to C and a path duration of 0-10 seconds SBF returns this Journey because the shortest path between steps B to C is within the 0-10 seconds range.
In the following example, the shortest path duration from step B to step C is the 8 second duration denoted by the dotted arrow.
Occurrence
You can filter by step occurrence or path occurrence.
Step occurrence
A step occurrence is the number of times a step appears in a Journey. To filter by step occurrence, select the step from the drop down and the occurrence count in the histogram.
Path occurrence
A path occurrence is the number of times two consecutive steps appear in a Journey. To filter by path occurrence, select a first step and second step from the drop down and the occurrence count in the histogram. You can select a maximum of two occurrences.
| Flowchart | A/B comparison |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Business Flow (EOL): -Latest-
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!