Bubble chart
Use a bubble chart to visualize multiple series data in three dimensions. Bubble position represents two dimensions of the data series. Bubble size represents the third dimension.
Data formatting
To create a bubble chart, start with a search that generates multiple data series. Use this syntax to generate the series.
... | <stats_command> <y-axis_field> <x-axis_field> <bubble_size_field>
A single group-by field in the query generates a visualization with all bubbles in the same color. To get series colors with the stats command, use two group-by fields. This generates a bubble for each unique combination of those two fields. The value of the second field determines the series color.
Configuration options
Bubble chart configurations include the following options. Use the Format menu to adjust these settings.
- Minimum and maximum bubble marker size
- Axis titles
- X-axis label rotation and truncation
- Axis scale, interval, minimum and maximum values
- Abbreviate y-axis and x-axis numerical values
Create a bubble chart
Prerequisites
Review the following details about building column and bar charts.
Steps
- Write a search that generates three data series.
- Run the search.
- Select the Statistics tab below the search bar. The statistics table here should have four columns.
- Select the Visualization tab and use the Visualization Picker to select the bubble chart visualization.
- (Optional) Use the Format menu to configure the visualization.
Example
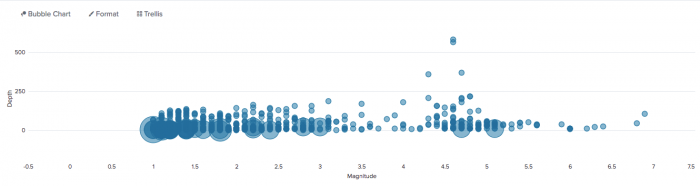
This search aggregates earthquake events by location. It generates data series representing the magnitude, depth, and count for each earthquake location.
source="earthquakes.csv" | stats count by place, mag, depth
The search generates a bubble chart where the x-axis and y-axis plot magnitude and depth. The bubble size indicates the relative count value for a particular location.
| Scatter chart | Event annotations for charts |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 7.1.0, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.1.5, 7.1.6, 7.1.7, 7.1.8, 7.1.9, 7.1.10, 7.2.0, 7.2.1, 7.2.2, 7.2.3, 7.2.4, 7.2.5, 7.2.6, 7.2.7, 7.2.8, 7.2.9, 7.2.10, 7.3.0, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.3.3, 7.3.4, 7.3.5, 7.3.6, 7.3.7, 7.3.8, 7.3.9, 8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, 8.0.6, 8.0.7, 8.0.8, 8.0.9, 8.0.10, 8.1.0, 8.1.1, 8.1.2, 8.1.3, 8.1.4, 8.1.5, 8.1.6, 8.1.7, 8.1.8, 8.1.9, 8.1.10, 8.1.11, 8.1.12, 8.1.13, 8.1.14, 8.2.0, 8.2.1, 8.2.2, 8.2.3, 8.2.4, 8.2.5, 8.2.6, 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9, 8.2.10, 8.2.11, 8.2.12, 9.0.0, 9.0.1, 9.0.2, 9.0.3, 9.0.4, 9.0.5, 9.0.6, 9.0.7, 9.0.8, 9.0.9, 9.0.10, 9.1.0, 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.1.5, 9.1.6, 9.1.7, 9.1.8, 9.1.9, 9.2.0, 9.2.1, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.2.5, 9.2.6, 9.3.0, 9.3.1, 9.3.2, 9.3.3, 9.3.4, 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!