Setting tokens on a visualization click
Use predefined tokens to turn a dashboard experience from viewing to interactive discovery. Tokens capture information when a user clicks different visualization elements. You can then use the token elsewhere in the dashboard to control the data for a different visualization. Setting tokens on a visualization click updates associated inputs using the same token, but multiple inputs cannot set the same token.
Dashboard Studio supports three predefined tokens:
- name
- value
- row.<fieldname>.value
The following table represents the predefined token availability and how captured values vary according to visualization type.
| Visualization | name | value | row.<fieldname>.value |
|---|---|---|---|
| splunk.area | Y-axis field name of the series/location clicked | Y-axis value of the series/location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.bar | Y-axis field name of the series/location clicked | Y-axis value of the series/location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.bubble | Y-axis field name of the series/location clicked | Y-axis value of the series/location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.choropleth.svg | Name of the area clicked | Value of the area clicked | n/a |
| splunk.column | Y-axis field name of the series/location clicked | Y-axis value of the series/location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.ellipse | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| splunk.map (Marker) | n/a | n/a | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.map (Bubble) | Name of the area clicked | Value of the area clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.map (Choropleth) | Name of the area clicked | Value of the area clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.pie | Field name of the value clicked | Value of the location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.rectangle | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| splunk.sankey | Field name of the value clicked | Value of the area clicked | n/a |
| splunk.scatter | Y-axis field name of the series/location clicked | Y-axis value of the series/location clicked | Value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked |
| splunk.singlevalue | Field name of the majorValue | Value of the majorValue | n/a |
| splunk.singlevalueicon | Field name of the majorValue | Value of the majorValue | n/a |
| splunk.table | Field name of the cell clicked | Value of the cell clicked | Value in the specified series in the same row as the cell clicked |
Setting tokens
- Navigate to the Interactions section of the Configuration panel.
- Click +Add Interaction
- In the On Click dropdown, select Set Tokens
- Click +Set Another Token
- In the Set Token dropdown select either Use predefined token or Enter static value.
- A predefined token captures information to display dynamically
- A static value is a string
- In the Create a name field, type a name for your token. Token names are used to reference the token elsewhere in the dashboard with the
$token_name$syntax - In the Choose an event field, select either name, value, or row.<fieldname>.value
- name is the field name of the value/location clicked
- value is the value of the location clicked
- row.<fieldname>.value is the value in the specified series corresponding to the location clicked
- (Optional) In the Default Value field, enter a default value. For more details about default token values, see Default token.
- Click Apply
- Add your token to a search or visualization within your dashboard.
Default token
A token's default value exists for the moments before a user has interacted with a dashboard component. A token's value will change and update when users interact with dashboard elements. For example, a token can update when a user clicks on a visualization. Without a default token, a visualization will remain blank until a user interacts with a dashboard element associated with a token. Use default tokens to display data and prevent empty visualizations.
You can set a default token in the UI by navigating to the Interactions section of the Configuration panel and following the steps for setting a token. After setting your default, the defaults section of your dashboard definition updates with a tokens section. In the Configuration panel, you cannot specify a default value in the Set token section if a default value is already specified on an associated input using the same token.
The following is an example of a defaults section after a token receives a default setting.
"defaults": {
"dataSources": {
"ds.search": {
"options": {
"queryParameters": {
"latest": "$global_time.latest$",
"earliest": "$global_time.earliest$"
}
}
}
},
"tokens": {
"default": {
"tokenName": {
"value": "1986"
}
}
}
},
To set default token values for inputs, see Adding and configuring inputs.
Token filters
Token filters ensure that you correctly capture the value of a token.
| Filter | Description |
|---|---|
Wrap value in quotes$token_name|s$
|
Ensures that quotation marks surround the value referenced by the token. Escapes all quotation characters, ", within the quoted value.
|
HTML format$token_name|h$
|
Ensures that the token value is valid for HTML formatting.
Token values for the <HTML> element use this filter by default. |
URL format$token_name|u$
|
Ensures that the token value is valid to use as a URL.
Token values for the <link> element use this filter by default. |
Specify no character escaping$token_name|n$
|
Prevents the default token filter from running. No characters in the token are escaped. |
The following code snippet uses the |s filter to place quotation marks around the value returned from a token:
<search>
<query>
index=_internal sourcetype=$sourcetype_tok|s$ | timechart count by sourcetype
</query>
</search>
If the value of sourcetype_tok is access_combined, it builds the following search string:
index=_internal sourcetype="access_combined" | timechart count by sourcetype
Example of setting a token
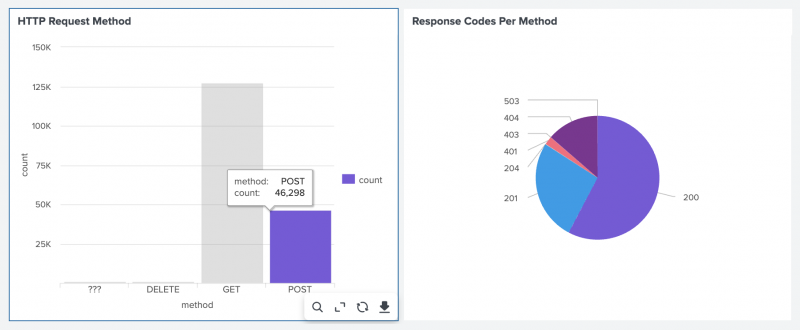
You can specify a token that passes along information between different visualizations. The following example shows two charts. One is a column chart that displays HTTP methods and their usage frequency, and the other is a pie chart that shows the analysis of HTTP response codes for a given HTTP method. When users click on a method in the column chart, the pie chart shows a breakdown of all response codes for the clicked method. The data connection between the two visualizations is achieved by setting up a token on the column chart $method$=row.method.value and passing the $method$ token to the search in the pie chart.
Source code
The following is a source code example of setting a token. Notice how the token is given the name method in the column chart's options and how that name is used in the token name syntax as $method$ in Search_2.
The example also sets the default value POST on the token method. Before any user clicks a visualization, a pie chart visualization will display the results for POST, preventing an empty visualization.
Notice the following stanzas:
eventHandlerscontains a token calledmethoddefaultscontains atokensstanza that sets the valuePOSTonmethodviz_pie_chartcontains a description that filters for$method$
{
"visualizations": {
"viz_column_chart": {
"type": "splunk.column",
"dataSources": {
"primary": "ds_qBGlESX2"
},
"eventHandlers": [
{
"type": "drilldown.setToken",
"options": {
"tokens": [
{
"token": "method",
"key": "row.method.value"
}
]
}
}
],
"showProgressBar": false,
"showLastUpdated": false,
"title": "HTTP Request Method"
},
"viz_pie_chart": {
"type": "splunk.pie",
"dataSources": {
"primary": "ds_c8AfQapt"
},
"title": "Response Codes for Method $method$"
}
},
"dataSources": {
"ds_qBGlESX2": {
"type": "ds.search",
"options": {
"query": "index=_internal \n| stats count by method"
},
"name": "Search_1"
},
"ds_c8AfQapt": {
"type": "ds.search",
"options": {
"query": "index=_internal method=$method$\n| stats count by status"
},
"name": "Search_2"
}
},
"defaults": {
"dataSources": {
"ds.search": {
"options": {
"queryParameters": {
"latest": "$global_time.latest$",
"earliest": "$global_time.earliest$"
}
}
}
},
"tokens": {
"default": {
"method": {
"value": "GET"
}
}
}
},
"inputs": {
"input_global_trp": {
"type": "input.timerange",
"options": {
"token": "global_time",
"defaultValue": "-24h@h,now"
},
"title": "Global Time Range"
}
},
"layout": {
"tabs": {
"items": [
{
"layoutId": "layout_1",
"label": "New tab"
}
]
},
"layoutDefinitions": {
"layout_1": {
"type": "grid",
"structure": [
{
"item": "viz_column_chart",
"type": "block",
"position": {
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"w": 600,
"h": 400
}
},
{
"item": "viz_pie_chart",
"type": "block",
"position": {
"x": 600,
"y": 0,
"w": 600,
"h": 400
}
}
]
}
},
"globalInputs": [
"input_global_trp"
]
},
"description": "",
"title": "Set Tokens on Click - Example"
}
| Adding and configuring inputs | Linking interactions |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!