Configure workload rules
Workload rules provide an automated way to assign searches to workload pools and monitor running searches. Workload management evaluates workload rules in the order in which they are listed. If a search meets the predicate condition defined in a rule, a specified action is taken. Workload rules are evaluated for every new search and reevaluated every 10 seconds.
There are two types of workload rules:
- Search placement rules
- Search monitoring rules
Search placement rules determine the pool in which a search is placed when you start a search. Predicates that you can define to control search placement include app, role, user, index, search_type, search_mode, and search_time_range. You can use search placement rules to ensure that high-priority searches are assigned to pools that provide adequate resources, while low-priority searches are restricted.
Search monitoring rules automatically trigger actions on running searches based on the defined rule predicate and the status of the search. When you create a monitoring rule, you must specify a runtime value in the predicate. If a search exceeds the runtime value, workload management performs the specified action. Supported actions are Abort search, Display in Messages, and Move search to alternate Pool. You can use monitoring rules to manage heavy search loads and prevent rogue processes from monopolizing pool resources.
Workload rules apply to base searches only. Workload rules do not apply to subsearches.
Create a workload rule in Splunk Web
To create a workload rule in Splunk Web:
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management.
- Click Add Workload Rule.
- Define the following fields to configure a new workload rule:
Field Action Name Specify the name of the workload rule. Predicate (Condition) Specify a predicate (condition) that must match to trigger this rule. The predicate syntax is <type>=<value> with optional AND, OR, NOT, (). For example, app=search AND role=powertriggers all searches belonging to both the Search app and the power role.
Valid predicate types are
app,role,index,user,search_type,search_mode,search_time_range, andruntime.
For supported predicate values, see Specify predicate values in the next section on this page.
In complex predicates,AND,OR, andNOToperators must be upper case. Lower case is not supported.Schedule (Optional) Set a schedule for the workload rule. The schedule determines the time period during which the rule is valid.
If set toAlways On(the default), the rule remains valid indefinitely and does not expire.
If set toTime Range, the rule is valid during the specified time range only and expires when the time range ends.
If set toEvery Day,Every Week, orEvery Month, the rule becomes valid on a recurring basis during the specified time range every day, on the specified days of the week, or on the specified days of the month.
The schedule time for a workload rule is based on the system timezone, regardless of the timezone set for an individual user in the UI.Action Specify the action to perform when a search meets the predicate condition.
Place search in a Pool(the default) assigns searches that meet the predicate condition to the specified workload pool.
Abort searchkills the search process.
Display a Messageshows a message in the job inspector to users that have all of the following required capabilities:list_workload_pools,edit_workload_pools,list_workload_rules, andselect_workload_rules.
Move search to alternate Poolmoves the running search to a different specified pool.
Abort search,Display a Message, andMove search to alternate Poolactions apply to in-progress searches only. You must specify aruntimecondition to enable these actions. For example, the predicateindex=_internal AND runtime>1mtriggers the specified action on all searches that containindex=_internaland run for more than one minute.
ThePlace search in a poolaction is not valid with rules containing aruntimecondition.Abort search,Display in Messages, andMove search to alternate Poolactions are valid only when aruntimecondition exists.Workload Pool Select the workload pool to which this rule applies. User Message Enter a custom message that notifies the end user when a search triggers the workload rule action. For example, "Search runtime exceeded 30 seconds. The search was moved to the high_perf pool."
A user message is required with theDisplay a Messageaction, and is optional for other actions. Messages are limited to a maximum of 140 characters.
When a search triggers the rule action, the user message appears in the Jobs manager in Splunk Web: Click Activity > Jobs > Job. It also appears under the Job menu in the Search app. - Click Submit.
Specify predicate values
The table describes valid predicate values for each type of workload rule predicate:
| Predicate type | Valid values |
|---|---|
app |
Name of the app. For example, app=searchThe correct name to specify for an app is the name of the app directory located in |
role |
Name of the role. For example, role=admin.The For information on how role inheritance impacts |
user |
Name of any valid user. For example, user=bob. The reserved internal user "nobody" is invalid. The reserved internal user "splunk-system-user" is valid.The |
index |
Name of the index. For example, index=_internal. Value can refer to internal or public index.The
|
search_type |
Supports adhoc, scheduled, datamodel_acceleration, report_acceleration, and summary_index search types.
|
search_mode |
Supports realtime and historical search modes.
|
search_time_range |
search_time_range predicate values match against the time range of a search. For example, if you specify search_time_range>4h, any search whose time range exceeds 4 hours is subject to the specified action.Supports
Searches that run over the "all time" time range only match against rules that specify the
|
runtime |
The amount of time that a search must run in a workload pool to trigger a specified action, such as Abort search, Display in Messages, or Move search to alternate Pool. For example, if you specify runtime>1m, any search in the pool that runs for more than 1 minute is subject to the specified action. By default, Valid time units for Note: |
For workload rule use case examples, see Workload Management examples.
Enable workload rules
You can enable or disable individual workload rules. This lets you create and save multiple different workload rules and apply them as needed. Individual workload rules are enabled by default when you create them. Disabled workload rules are not evaluated and have no effect on running searches.
To enable or disable an individual workload rule:
- In Splunk Web, click Settings > Workload Management > Workload Rules.
- In the Status column, toggle the switch to enable or disable the individual workload rule.
The workload management feature must be enabled for workload rules to apply to searches. In Splunk Cloud Platform, the workload management feature is enabled for the sc_admin role by default and cannot be disabled.
Monitor triggered workload rule actions
When a running search triggers a workload rule action, information about the action appears in the Search job inspector. This includes the action that was taken on the search and the timestamp. If a search triggers multiple rules, the information appears in reverse chronological order.
To view details of a workload rule action:
- In Splunk Web, click Activity > Jobs.
- Find the specific search job and click Job > Inspect Job > Search job properties.
- View details of the workload rule action under the
workload_action_informationproperty.
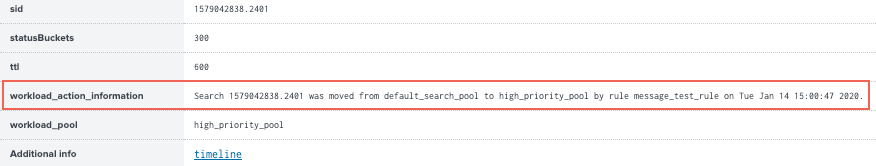
To view the workload_action_information property, you must have list_workload_pools and select_workload_pools capabilities.
| Workload Management overview | Configure admission rules to prefilter searches |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk Cloud Platform™: 9.1.2312, 9.2.2403, 9.2.2406, 9.3.2408 (latest FedRAMP release), 9.3.2411
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!