All DSP releases prior to DSP 1.4.0 use Gravity, a Kubernetes orchestrator, which has been announced end-of-life. We have replaced Gravity with an alternative component in DSP 1.4.0. Therefore, we will no longer provide support for versions of DSP prior to DSP 1.4.0 after July 1, 2023. We advise all of our customers to upgrade to DSP 1.4.0 in order to continue to receive full product support from Splunk.
Connecting a Splunk forwarder to your DSP pipeline
When creating a data pipeline in the , you can connect to a Splunk heavy forwarder or universal forwarder and use it as a data source. You can get data from a forwarder into a pipeline, transform the data as needed, and then send the transformed data out from the pipeline to a destination of your choosing.
To connect to a forwarder as a data source, you must complete the following tasks:
- Create a self-signed SSL certificate, and upload it to the Forwarders service. Then, configure your heavy forwarder or universal forwarder to trust the client certificate. See Create a connection between a Splunk forwarder and the Forwarders service.
- If your DSP account has the user role instead of the admin role, you'll need your DSP administrator to grant you permissions to use the Forwarders service. See Allow DSP users to use the Forwarders service.
- Create a pipeline that starts with the Forwarders Service source function.
- See the Building a pipeline chapter in the Use the Data Stream Processor manual for instructions on how to build a data pipeline.
- See Get data from Forwarders Service in the Function Reference manual for more information about the source function.
- If you are using a universal forwarder as a data source, process the data to make sure that events are not being truncated or grouped unexpectedly. See Process data from a universal forwarder in DSP.
When you activate the pipeline, the source function starts collecting the data that is being forwarded by the Splunk forwarder.
How forwarded data is collected
A forwarder is a Splunk Enterprise instance that sends data to another Splunk Enterprise instance, such as an indexer or another forwarder, or to a third-party system. In this case, the forwarder sends data to the Forwarders service that runs within DSP, and your data pipeline ingests that data from the Forwarders service. The Forwarders service identifies incoming connections from forwarders by the client certificate on the forwarder.
The following diagram shows how data is streamed from a Splunk forwarder into DSP and then sent out to a destination.
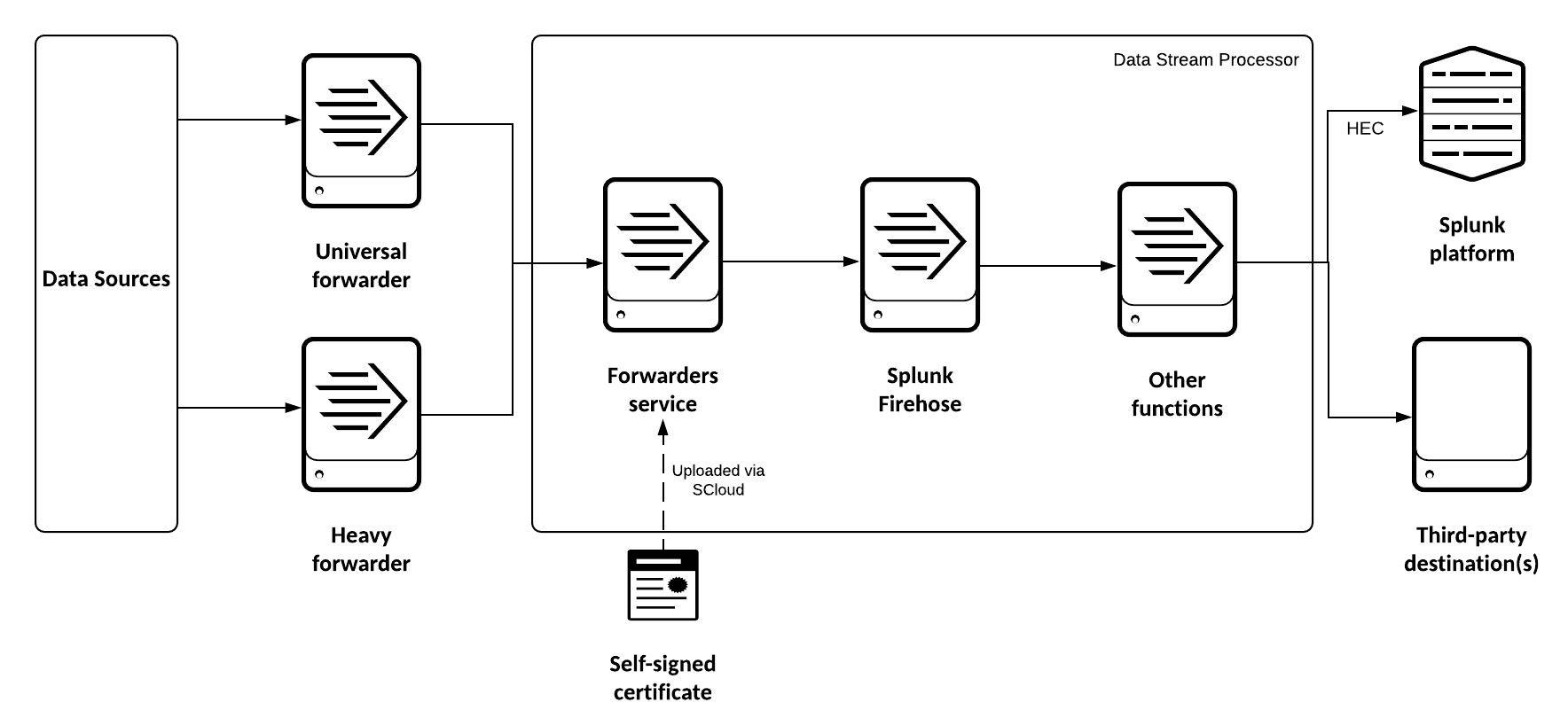
The data from the Forwarders service has the following schema:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| body | Contains the payload of the event. The default data type of the body field is a union of all possible types. To pass body as an argument to a downstream function that requires a specific type, you must first cast body to that specific type.
|
| attributes | Contains metadata fields about your forwarder. |
| host | Contains information about the host for your forwarder. |
| source | Contains information about the source for your forwarder. |
| source_type | Contains information about the source_type for your forwarder. |
| timestamp | Contains the timestamp of your event. When receiving data from a heavy forwarder, DSP uses the timestamp determined and extracted by the heavy forwarder. When receiving data from a universal forwarder, which does not do any processing of your events, DSP sets the timestamp to the time when the event was ingested. |
| nanos | Contains nanoseconds beyond the timestamp. |
| id | Contains a unique ID of the event. If it is not specified, the system generates an ID. |
| Managing connections in the | Create a connection between a Splunk forwarder and the Forwarders service |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Data Stream Processor: 1.2.0, 1.2.1-patch02, 1.2.1, 1.2.2-patch02, 1.2.4, 1.2.5, 1.3.0, 1.3.1, 1.4.0, 1.4.1, 1.4.2, 1.4.3, 1.4.4, 1.4.5, 1.4.6
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!