All DSP releases prior to DSP 1.4.0 use Gravity, a Kubernetes orchestrator, which has been announced end-of-life. We have replaced Gravity with an alternative component in DSP 1.4.0. Therefore, we will no longer provide support for versions of DSP prior to DSP 1.4.0 after July 1, 2023. We advise all of our customers to upgrade to DSP 1.4.0 in order to continue to receive full product support from Splunk.
Summarize records with the stats function
Use the Stats function to perform one or more aggregation calculations on your streaming data. For each aggregation calculation that you want to perform, specify the aggregation functions, the subset of data to perform the calculation on (fields to group by), the timestamp field for windowing, and the output fields for the results.
After the given window time has passed, the stats function outputs the records in your data stream with the user-defined output fields, the fields to group by, and the window length that the aggregations occurred in. The stats function drops all other fields from the record's schema.
The stats function has no concept of wall clock time, and the passage of time is based on the timestamps of incoming records. The Stats function tracks the latest timestamp it received in the stream as the "current" time, and it determines the start and end of windows using this timestamp. Once the difference between the current timestamp and the start timestamp of the current window is greater than the window length, that window is closed and a new window starts. However, since events may arrive out of order, the grace period argument allows the previous window W to remain "open" for a certain period G after its closing timestamp T. Until we receive a record with a timestamp C where C > T + G, any incoming events with timestamp less than T are counted towards the previous window W. See the Stats usage section for more information.
List of aggregation functions
You can use the following aggregation functions within the Stats streaming function:
- average: Calculates the average in a time window.
- count: Counts the number of non-null values in a time window.
- max: Returns the greatest value in a time window.
- min: Returns the lowest value in a time window.
- sum: Returns the sum of values in a time window.
Count the number of non-null sources per host in a 60 second time window
Suppose you wanted to count the number of times a source appeared in a given time window per host. This example does the following:
- Uses the count aggregation function to count the number of non-null sources and outputs the result to
num_events_with_source_field. - Groups the fields in the output by
host. - Executes the aggregations in a time window of 60 seconds based on the
timestampof your record.
Steps
- From the Canvas View of your pipeline, click on the + icon and add the Stats function to your pipeline.
- In the Stats function, add a new Group By.
- In Field/Expression, type
host. - Click OK.
- In Field/Expression, type
- In the Timestamp field, type
timestamp. - In the Window length field, type
60and select seconds from the drop-down list. - Configure the Stats function to count the number of non-null
sourcevalues.- Click the New Aggregations drop-down list, and select count.
- Type
sourcein Field/Expression, andnum_events_with_source_fieldin Output Field.
- Click Validate.
- Click the Start Preview
 button and the Stats function to verify that your data is being aggregated. In this example, we are using a time window of 60 seconds, so your preview data for Stats shows up after 60 seconds have passed between the timestamps of your records.
button and the Stats function to verify that your data is being aggregated. In this example, we are using a time window of 60 seconds, so your preview data for Stats shows up after 60 seconds have passed between the timestamps of your records.
If your data stream contained the following data:
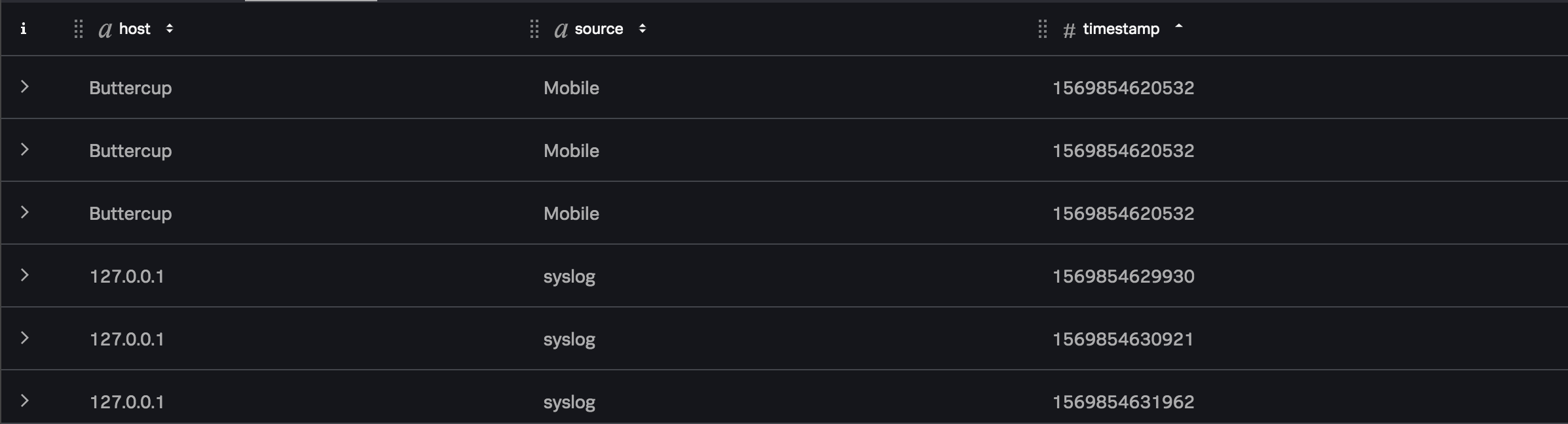
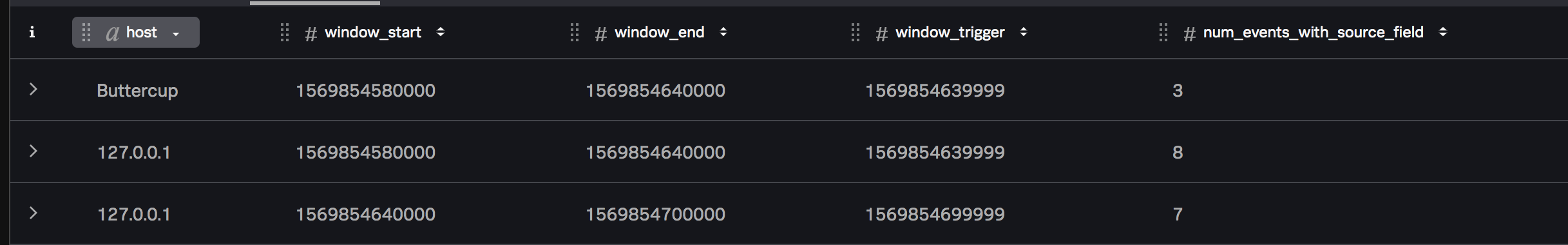
Following this example, the Stats function would contain the following output:
See also
| Working with nested data | About lookups |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Data Stream Processor: 1.3.0, 1.3.1, 1.4.0, 1.4.1, 1.4.2, 1.4.3, 1.4.4, 1.4.5, 1.4.6
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!